Abstract
Purpose
Apixaban, a direct factor Xa inhibitor recently approved for thromboembolic prophylaxis in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AF), is increasingly used in patients undergoing catheter ablation of AF. However, large randomized studies supporting its use in the ablation context are still lacking. We undertook the present meta-analysis to assess the impact of apixaban in terms of thromboembolic and bleeding events in patients undergoing AF ablation as compared to warfarin.
Methods
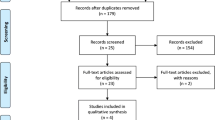
MEDLINE/PubMed, Cochrane Library, and references reporting AF ablation and apixaban were screened and studies included if matching inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Results
One randomized and five nonrandomized studies were included in the analysis. Patients enrolled were 1691 patients (668 on apixaban and 1023 on warfarin). There was no heterogeneity in all the outcome comparisons. No deaths were reported. We did not observe any difference between apixaban and warfarin with respect to thromboembolic events (OR = 1.10, 95 % CI 0.24–5.16), major bleedings (OR = 1.56, 95 % CI 0.59–4.13), cardiac tamponade (OR 1.69, 95 % CI 0.52–5.54), minor bleedings (OR 0.96, 95 % CI 0.58–1.59), and the composite endpoint of death, thromboembolic events, and bleedings (OR 1.03, 95 % CI 0.65–1.64).
Conclusions
The rates of death, thromboembolic events, major bleedings including cardiac tamponade, and minor bleedings in patients on apixaban undergoing AF ablation are very low and similar to that seen in patients treated with uninterrupted warfarin. Although primary driven by nonrandomized studies, these results support apixaban as periprocedural anticoagulation during AF ablation procedures.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AF:
-
Atrial fibrillation
- PV:
-
Pulmonary vein
- PVI:
-
Pulmonary vein isolation
- CA:
-
Catheter ablation
- LA:
-
Left atrium
- LVEF:
-
Left ventricular ejection fraction
- NOACs:
-
Novel oral anticoagulants
- VKA:
-
Vitamin K antagonist
- TIA:
-
Transient ischemic attack
- ACT:
-
Activated clotting time
- INR:
-
International normalized ratio
- ICE:
-
Intracardiac echocardiography
- AADs:
-
Antiarrhythmic drugs
- LMWH:
-
Low-molecular-weight heparin
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- CT:
-
Computerized tomography
- SCE:
-
Silent cerebrovascular event
- ES:
-
Effect size
References
Lloyd-Jones DM, Wang TJ, Leip EP, Larson MG, Levy D, Vasan RS, et al. Lifetime risk for development of atrial fibrillation: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2004;110(9):1042–6.
Chen LY, Shen WK. Epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: a current perspective. Heart Rhythm. 2007;4(3 Suppl):S1–6.
Calkins H, Kuck KH, Cappato R, Brugada J, Camm AJ, Chen SA, et al. 2012 HRS/EHRA/ECAS Expert Consensus Statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: recommendations for patient selection, procedural techniques, patient management and follow-up, definitions, endpoints, and research trial design. Europace. 2012;14(4):528–606.
Cappato R, Calkins H, Chen SA, Davies W, Iesaka Y, Kalman J, et al. Updated worldwide survey on the methods, efficacy, and safety of catheter ablation for human atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2010;3(1):32–8.
Spragg DD, Dalal D, Cheema A, Scherr D, Chilukuri K, Cheng A, et al. Complications of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: incidence and predictors. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2008;19(6):627–31.
Dorbala S, Cohen AJ, Hutchinson LA, Menchavez-Tan E, Steinberg JS. Does radiofrequency ablation induce a prethrombotic state? Analysis of coagulation system activation and comparison to electrophysiologic study. J CardiovascElectrophysiol. 1998;9(11):1152–60.
Ren JF, Marchlinski FE, Callans DJ. Left atrial thrombus associated with ablation for atrial fibrillation: identification with intracardiac echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43(10):1861–7.
Santangeli P, Di Biase L, Horton R, Burkhardt JD, Sanchez J, Al-Ahmad A, et al. Ablation of atrial fibrillation under therapeutic warfarin reduces periprocedural complications: evidence from a meta-analysis. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2012;5(2):302–11.
Ruff CT, Giugliano RP, Braunwald E, Hoffman EB, Deenadayalu N, Ezekowitz MD, et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Lancet. 2014;383(9921):955–62.
Spinler SA, Shafir V. New oral anticoagulants for atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2012;126(1):133–7.
Connolly SJ, Ezekowitz MD, Yusuf S, Eikelboom J, Oldgren J, Parekh A, et al. Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(12):1139–51.
Patel MR, Mahaffey KW, Garg J, Pan G, Singer DE, Hacke W, et al. Rivaroxaban versus warfarin in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(10):883–91.
Granger CB, Alexander JH, McMurray JJ, Lopes RD, Hylek EM, Hanna M, et al. Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(11):981–92.
Keating GM. Apixaban: a review of its use for reducing the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Drugs. 2013;73(8):825–43.
Lu D, Liu Q, Wang K, Zhang QI, Shan QJ. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of apixaban in patients undergoing catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2016;39(1):54–9.
Kuwahara T, Abe M, Yamaki M, Fujieda H, Abe Y, Hashimoto K, et al. (2016). Apixaban versus Warfarin for the prevention of periprocedural cerebral Thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation ablation: multicenter prospective randomized study. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. 2009;339:b2535.
Altman DG, Schulz KF, Moher D, Egger M, Davidoff F, Elbourne D, et al. The revised CONSORT statement for reporting randomized trials: explanation and elaboration. Ann Intern Med. 2001;134(8):663–94.
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA. 2000;283(15):2008–12.
Menzies D. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2011;15(5):582–93.
Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. (2011). The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses [webpage on the Internet]. Ottawa, ON: Ottawa Hospital Research Institute; 2011. Available from: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.as.
Higgins JPT, Green S. (editors). (2011). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org
Bin Abdulhak AA, Kennedy KF, Gupta S, Giocondo M, Ramza B, Wimmer AP. Effect of pre procedural interrupted apixaban on heparin anticoagulation during catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: a prospective observational study. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2015;44(2):91–6.
Di Biase L, Lakkireddy D, Trivedi C, Deneke T, Martinek M, Mohanty S, et al. Feasibility and safety of uninterrupted periprocedural apixaban administration in patients undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation: results from a multicenter study. Heart Rhythm. 2015;12(6):1162–8.
Kaess BM, Ammar S, Reents T, Dillier R, Lennerz C, Semmler V, et al. Comparison of safety of left atrial catheter ablation procedures for atrial arrhythmias under continuous anticoagulation with apixaban versus phenprocoumon. Am J Cardiol. 2015;115(1):47–51.
Nagao T, Inden Y, Yanagisawa S, Kato H, Ishikawa S, Okumura S, et al. Differences in activated clotting time among uninterrupted anticoagulants during the periprocedural period of atrial fibrillation ablation. Heart Rhythm. 2015;12(9):1972–8.
Rillig A, Lin T, Plesman J, Heeger CH, Lemes C, Metzner A, et al. Apixaban, rivaroxaban and dabigatran in patients undergoing atrial fibrillation ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2016;27(2):147–53.
Kok LC, Mangrum JM, Haines DE, Mounsey JP. Cerebrovascular complication associated with pulmonary vein ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2002;13(8):764–7.
Natale A, Raviele A, Arentz T, Calkins H, Chen SA, Haissaguerre M, et al. Venice Chart international consensus document on atrial fibrillation ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2007;18(5):560–80.
Connolly SJ, Eikelboom J, O’Donnell M, Pogue J, Yusuf S. Challenges of establishing new antithrombotic therapies in atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2007;116(4):449–55.
Mavrakanas T, Bounameaux H. The potential role of new oral anticoagulants in the prevention and treatment of thromboembolism. Pharmacol Ther. 2011;130(1):46–58.
Hohnloser SH, Camm AJ. Safety and efficacy of dabigatran etexilate during catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis of the literature. Europace. 2013;15(10):1407–11.
Garg J, Chaudhary R, Krishnamoorthy P, Shah N, Natale A, Bozorgnia B. Safety and efficacy of uninterrupted periprocedural rivaroxaban in patients undergoing atrial fibrillation catheter ablation: A metaanalysis of 1,362 patients. Int J Cardiol. 2016;203(15):906–8.
Ellis ER, Culler SD, Simon AW, Reynolds MR. Trends in utilization and complications of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation in Medicare beneficiaries. Heart Rhythm. 2009;6(9):1267–73.
Shah RU, Freeman JV, Shilane D, Wang PJ, Go AS, Hlatky MA. Procedural complications, rehospitalizations, and repeat procedures after catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;59(2):143–9.
Deshmukh A, Patel NJ, Pant S, Shah N, Chothani A, Mehta K, et al. In-hospital complications associated with catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in the United States between 2000 and 2010: analysis of 93 801 procedures. Circulation. 2013;128(19):2104–12.
Siegal DM, Curnutte JT, Connolly SJ, Lu G, Conley PB, Wiens BL, et al. Andexanet alfa for the reversal of factor Xa inhibitor activity. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(25):2413–24.
Konduru SV, Cheema AA, Jones P, Li Y, Ramza B, Wimmer AP. Differences in intraprocedural ACTs with standardized heparin dosing during catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation in patients treated with dabigatran vs. patients on uninterrupted warfarin. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2012;35(3):277–84.
Winkle RA, Mead RH, Engel G, Kong MH, Patrawala RA. Atrial fibrillation ablation using open-irrigated tip radiofrequency: experience with intraprocedural activated clotting times ≤210 seconds. Heart Rhythm. 2014;11(6):963–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blandino, A., Bianchi, F., Biondi-Zoccai, G. et al. Apixaban for periprocedural anticoagulation during catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 1691 patients. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 46, 225–236 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-016-0141-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-016-0141-6