Abstract
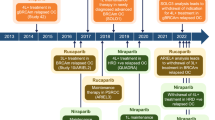
Few types of cancer have had their treatment evolve as rapidly as metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). Since 2005, six new targeted therapies with proven efficacy have been approved for the treatment of mRCC. The downside is that our knowledge about the mechanisms of action of these therapies and the intrinsic and extrinsic mechanism of resistance has not evolved equally fast, and many questions remain unanswered. The only approved agent to date in the European Union for patients who progress on sunitinib or sorafenib is everolimus. The results of the phase III trial comparing axitinib vs. sorafenib after failure on sunitinib, bevacizumab, temsirolimus, or cytokines have recently been published, and axitinib has recently been licensed by the Food and Drugs Administration. Other phase III trials that are being conducted include a comparison between everolimus plus bevacizumab and everolimus after failure on tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and between temsirolimus and sorafenib after failure on sunitinib. In this article, we will review the available evidence from clinical studies on sequential therapy for mRCC, including those that are still in progress. In addition, information on the mechanism of resistance or tolerance to first-line therapy, recommendations of the main practice guidelines for second-line treatment, potential therapies for third or successive treatment lines, and the major reasons why patients who progress may benefit from a change of mechanism of action will also be discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schrader, A. J., Varga, Z., Hegele, A., Pfoertner, S., Olbert, P., & Hofmann, R. (2006). Second-line strategies for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Classics and novel approaches. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 132(3), 137–149.
Escudier, B., Chevreau, C., Lasset, C., Douillard, J. Y., Ravaud, A., Fabbro, M., et al. (1999). Cytokines in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: is it useful to switch to interleukin-2 or interferon after failure of a first treatment? Groupe Francais d’Immunotherape. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 17(7), 2039–2043.
Motzer, R. J., Escudier, B., Oudard, S., Hutson, T. E., Porta, C., Bracarda, S., et al. (2010). Phase 3 trial of everolimus for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: final results and analysis of prognostic factors. Cancer, 116(18), 4256–4265.
FDA. Everolimus (Afinitor®)—Full prescribing information: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/022334lbl.pdf. Accessed on October 2011).
Shojaei, F., Wu, X., Malik, A. K., Zhong, C., Baldwin, M. E., Schanz, S., et al. (2007). Tumor refractoriness to anti-VEGF treatment is mediated by CD11b+Gr1+ myeloid cells. Nature Biotechnology, 25(8), 911–920.
Welti, J. C., Gourlaouen, M., Powles, T., Kudahetti, S. C., Wilson, P., Berney, D. M., et al. (2011). Fibroblast growth factor 2 regulates endothelial cell sensitivity to sunitinib. Oncogene, 30(10), 1183–1193.
Ferrara, N. (2010). Role of myeloid cells in vascular endothelial growth factor-independent tumor angiogenesis. Current Opinion in Hematology, 17(3), 219–224.
Carew, J. S., Kelly, K. R., & Nawrocki, S. T. (2011). Mechanisms of mTOR inhibitor resistance in cancer therapy. Targeted Oncology, 6(1), 17–27.
Bergers, G., & Hanahan, D. (2008). Modes of resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nature Reviews Cancer, 8(8), 592–603.
Hudes, G. R. (2009). Targeting mTOR in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer, 115(10 Suppl), 2313–2320.
Ellis, L. M., & Hicklin, D. J. (2009). Resistance to targeted therapies: Refining anticancer therapy in the era of molecular oncology. Clinical Cancer Research, 15(24), 7471–7478.
Escudier, B., Eisen, T., Stadler, W. M., Szczylik, C., Oudard, S., Siebels, M., et al. (2007). Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. The New England Journal of Medicine, 356(2), 125–134.
Escudier, B., Eisen, T., Stadler, W. M., Szczylik, C., Oudard, S., Staehler, M., et al. (2009). Sorafenib for treatment of renal cell carcinoma: Final efficacy and safety results of the phase III treatment approaches in renal cancer global evaluation trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 27(20), 3312–3318.
Sternberg, C. N., Szczylik, C., Lee, E., Salman, P. V., Mardiak, J., Davis, I. D., et al. (2009). A randomized, double-blind phase III study of pazopanib in treatment-naive and cytokine-pretreated patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). ASCO Meeting Abstracts, 27(15S), 5021.
Dudek, A. Z., Zolnierek, J., Dham, A., Lindgren, B. R., & Szczylik, C. (2009). Sequential therapy with sorafenib and sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer, 115(1), 61–67.
Eichelberg, C., Heuer, R., Chun, F. K., Hinrichs, K., Zacharias, M., Huland, H., et al. (2008). Sequential use of the tyrosine kinase inhibitors sorafenib and sunitinib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A retrospective outcome analysis. European Urology, 54(6), 1373–1378.
Sablin, M. P., Negrier, S., Ravaud, A., Oudard, S., Balleyguier, C., Gautier, J., et al. (2009). Sequential sorafenib and sunitinib for renal cell carcinoma. Journal of Urology, 182(1), 29–34. discussion.
Porta, C., Procopio, G., Carteni, G., Sabbatini, R., Bearz, A., Chiappino, I., et al. (2011). Sequential use of sorafenib and sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma (RCC): An Italian multicentre retrospective analysis of 189 patient cases. BJU International, 108(8b), E250–E257.
Buchler, T., Klapka, R., Melichar, B., Brabec, P., Dušek, L., Vyzula, R., et al. (2011). Sunitinib followed by sorafenib or vice versa for metastatic renal cell carcinoma—Data from the Czech registry. Annals of Oncology, 2, 2011.
Zimmermann, K., Schmittel, A., Steiner, U., Asemissen, A. M., Knoedler, M., Thiel, E., et al. (2009). Sunitinib treatment for patients with advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma after progression on sorafenib. Oncology, 76(5), 350–354.
Di Lorenzo, G., Carteni, G., Autorino, R., Bruni, G., Tudini, M., Rizzo, M., et al. (2009). Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with sunitinib-refractory metastatic renal cell cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 27(27), 4469–4474.
Shepard, D. R., Rini, B. I., Garcia, J. A., Hutson, T. E., Elson, P., Gilligan, T., et al. (2008). A multicenter prospective trial of sorafenib in patients (pts) with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (mccRCC) refractory to prior sunitinib or bevacizumab. ASCO Meeting Abstracts, 26(15_suppl), 5123.
Rini, B.I., Escudier, B., Tomczak, P., Kaprin, A., Szczylik, C., & Hutson, T.E. et al. (2011). Comparative effectiveness of axitinib versus sorafenib in advanced renal cell carcinoma (AXIS): a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet, 378, 1931–1939.
Garcia, J. A., Hutson, T. E., Elson, P., Cowey, C. L., Gilligan, T., Nemec, C., et al. (2010). Sorafenib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma refractory to either sunitinib or bevacizumab. Cancer, 116(23), 5383–5390.
Rini, B. I., Michaelson, M. D., Rosenberg, J. E., Bukowski, R. M., Sosman, J. A., Stadler, W. M., et al. (2008). Antitumor activity and biomarker analysis of sunitinib in patients with bevacizumab-refractory metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 26(22), 3743–3748.
Motzer, R. J., Escudier, B., Oudard, S., Hutson, T. E., Porta, C., Bracarda, S., et al. (2008). Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Lancet, 372(9637), 449–456.
Knox, J. J., Kay, A. C., Schiff, E., Hollaender, N., Rouyrre, N., Ravaud, A., et al. (2010). First-line everolimus followed by second-line sunitinib versus the opposite treatment sequence in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). ASCO Meeting Abstracts, 28(15_suppl), TPS232.
Grundbichler, M., Mlineritsch, B., Ressler, S., Moik, M., Kappacher, A., Rosenlechner, S., et al. (2011). Efficacy of temsirolimus after previous treatment with sunitinib, sorafenib or everolimus in advanced renal cell cancer. Oncology, 80(1–2), 34–41.
Gerullis, H., Bergmann, L., Maute, L., Ecke, T. H., Eimer, C., Bagner, J. W., et al. (2010). Feasibility of sequential use of sunitinib and temsirolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Medical Oncology, 27(2), 373–378.
Weikert, S., Kempkensteffen, C., Busch, J., Johannsen, M., Grünwald, V., Zimmermann, K., et al. (2012). Sequential mTOR inhibitor treatment with temsirolimus in metastatic renal cell carcinoma following failure of VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. World Journal of Urology. doi:10.1007/s00345-011-0676-1.
Vitali, G., Duca, M., Fugazza, C., Longoni, S., Trinca, S., Ceraulo, D., et al. (2010). Temsirolimus in second or subsequent line in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC): Better activity in good-intermediate prognosis patients. ASCO Meeting Abstracts, 28(15_suppl), e15081.
Ferrari, V. D., Fogazzi, G., Valcamonico, F., Amoroso, V., Procopio, G., Nonnis, D., et al. (2010). III–IV line of target therapy in advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). ASCO Meeting Abstracts, 28(15_suppl), e15148.
Agostino, N.M., Gingrich, R., & Drabick, J.J. (2010). Bevacizumab demonstrates prolonged disease stabilization in patients with heavily pretreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a case series and review of the literature. Advanced Urology, 2010, 687043.
Di Lorenzo, G., Buonerba, C., Federico, P., Rescigno, P., Milella, M., Ortega, C., et al. (2010). Third-line sorafenib after sequential therapy with sunitinib and mTOR inhibitors in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. European Urology, 58(6), 906–911.
Blesius, A., Beuzelink, B., Chevreau, C., Ravaud, A., Rolland, F., Oudard, S., et al. (2010). Are TKIs still active in patients treated with TKI and everolimus? Experience from 36 patients treated in France in the RECORD 1 trial. Annals of Oncology, 21(8_suppl), 908P.
Grunwald, V., Seidel, C., Fenner, M., Ganser, A., Busch, J., & Weikert, S. (2011). Treatment of everolimus-resistant metastatic renal cell carcinoma with VEGF-targeted therapies. British Journal of Cancer, 105(11), 1635–1639.
Angevin, E., Lin, C., Pande, A. U., Lopez, J. A., Gschwend, J., Harzstark, A. L., et al. (2010). A phase I/II study of dovitinib (TKI258), a FGFR and VEGFR inhibitor, in patients (pts) with advanced or metastatic renal cell cancer: Phase I results. ASCO Meeting Abstracts, 28(15_suppl), 3057.
Tannir, N. M., Wong, Y., Kollmannsberger, C. K., Ernstoff, M. S., Perry, D. J., Appleman, L. J., et al. (2010). Phase II trial of linifanib in patients with advanced renal cell cancer (RCC) after sunitinib failure. ASCO Meeting Abstracts, 28(15_suppl), 4527.
Harshman, L. C., McMillan, A., & Srinivas, S. (2010). Treatment of refractory metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with bevacizumab and RAD001. ASCO Meeting Abstracts, 28(15_suppl), TPS236.
Larkin, J., Swanton, C., & Pickering, L. (2011). Optimizing treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma by changing mechanism of action. Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy, 11(4), 639–649.
Fernando, N. T., Koch, M., Rothrock, C., Gollogly, L. K., D’Amore, P. A., Ryeom, S., et al. (2008). Tumor escape from endogenous, extracellular matrix-associated angiogenesis inhibitors by up-regulation of multiple proangiogenic factors. Clinical Cancer Research, 14(5), 1529–1539.
Oudard, S., Ravaud, A., & Escudier, B. (2010). Sequencing of therapeutic agents in the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma: Focus on mechanism of action. Annals of Urology, 1(1), 11–19.
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Kidney Cancer—Version 2.2011. http://www.nccn.org/clinical.asp. Accessed on October, 2011).
Escudier, B., & Kataja, V. (2010). Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Annals of Oncology, 21(Suppl 5), v137–v139.
Jean-Jacques, P., Geraldine, P., Bernard, E., Tim, E., Axel, B., Cora, S., et al. (2011). ICUD-EAU International Consultation on Kidney Cancer 2010: Treatment of Metastatic Disease. European Urology, 60(4), 684–690.
de Reijke, T. M., Bellmunt, J., van Poppel, H., Marreaud, S., & Aapro, M. (2009). EORTC-GU group expert opinion on metastatic renal cell cancer. European Journal of Cancer, 45(5), 765–773.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of Novartis Oncology Spain, which has facilitated the necessary meetings to evaluate and discuss all the data presented in this review, and Dr. Ximena Alvira from HealthCo SL (Madrid, Spain) for assistance in the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest that may inappropriately influence this work. J. Bellmunt has received honoraria and lectures fees from Novartis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larriba, J.L.G., Espinosa, E., Carbonero, I.G. et al. Sequential therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: pre-clinical and clinical rationale for selecting a second- or subsequent-line therapy with a different mechanism of action. Cancer Metastasis Rev 31 (Suppl 1), 11–17 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-012-9354-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-012-9354-z