Abstract
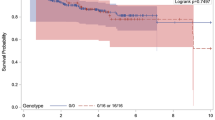
The p53 tumor suppressor gene has a central role in the defense against cancer, including breast cancer, and contains a polymorphic variant (Arg/Pro) at codon 72 that has been shown to have different biological properties regarding apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Earlier studies have shown allele specific loss of heterozygosity (LOH) at this particular site and we aimed to investigate its biological relevance in codon 72 heterozygous breast cancer patients (i.e., survival and age of disease onset). 199 postmenopausal cases were analyzed for LOH using MegaBACE1000 and statistics was performed using Statistical Package for Social Sciences. LOH was found in totally 124 (62.3%) patients and the Pro allele (n = 103) was significantly more often deleted compared to the Arg allele (n = 21) (P = 0.001). Patients with LOH of the Arg allele were diagnosed at an earlier age (mean age 62.5 years) than those with loss of the Pro allele (mean age 69.2 years) (P = 0.011). LOH of the Arg allele was also associated with worse survival (P = 0.05). LOH in comparison to ROH correlated significantly with increased S-phase fraction. Tumor size, stage or number of positive lymph nodes was not related to LOH. Our results and earlier findings suggest a selective loss of the Pro allele during carcinogenesis that might confer a growth advantage for cancer cells. On the other hand, it appears to be more harmful for patients to loose the Arg allele since we found that loss of this allele was associated with earlier onset and worse prognosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hollstein M, Sidrowsky D, Vogelstein B, Harris C (1991) p53 Mutations in human cancers. Science 253:46–53
Giaccia AJ, Kastan MB (1998) The complexity of p53 modulation: emerging patterns from divergent signals. Genes Dev 12:2973–2983
Thomas M, Kalita A, Labrecque S, Pim D, Banks L, Matlashewski G (1999) Two polymorphic variants of wild-type p53 differ biochemical and biologically. Mol Cell Biol 19:1092–1100
Dumont P, Leu JI, Della AC, Pietra DL, Murphy G (2003) The codon72 polymorphic variants of p53 have markedly different apoptotic potential. Nat Genet 33:357–365
Sullivan A, Syed N, Gasco M, Bergmaschi D, Trigiante G, Attard M, Hiller I, Farrel PJ, Smith P, Lu X, Crook T (2004) Polymorphism in wild-type p53 modulates response to chemotherapy in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 23:3328–3337
Pim D, Banks L (2004) p53 Polymorphic variants at codon72 exerts different effects on cell cycle progression. Int J Cancer 108:196–199
Bergamaschi D, Samuels Y, Sullivan A, Zvelebil M, Breyssens H, Bisso A, Del Sar G, Syed N, Smith P, Gasco M, Crook T, Lu X (2006) iASPP preferentially binds proline-rich region and modulate apoptotic function of codon 72-polymorphic p53. Nat Genet 38:1133–1141
Tommiska J, Eerola H, Heinonen M, Salonen L, Kaare M, Tallila J, Ristimaki A, Smitten KV, Aittomaki K, Heikkila P, Blomqvist C, Nevanlinna H (2005) Breast cancer patients with p53 Pro 72 homozygous genotype have a poorer survival. Clin Cancer Res 11:5098–5103
Papadakis EN, Dokianakis DN, Spandidos DA (2000) p53 Codon72 polymorphism as a risk factor in the development of breast cancer. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun 3:389–392
Byuru N, Tigli H, Dalay N (2003) p53 Codon72 polymorphism in breast cancer. Oncol Rep 10:711–714
Huang XE, Hamajima N, Katsuda N, Matsuo K, Hirose K, Mizutani M, Iwata H, Miura S, Tokudome S, Tajima K (2003) Association of p53 codon Arg72Pro and p73 G4C14-to-A4T14 at exon 2 genetic polymorphism with the risk of Japanese breast cancer. Breast cancer 10:307–311
Noma C, Miyoshi Y, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y, Noguchi S (2004) Association of p53 codon72 polymorphism (Arg72Pro) with estrogen receptor positive breast cancer risk in Japanese women. Cancer Lett 210:197–203
Mabrouk I, Baccouche S, Abed R, Mokdad-Gargouri R, Mosbah A, Said S, Daoud J, Frikha M, Jlidi R, Gargouri A (2003) No evidence of correlation between p53 codon72 polymorphism and risk of bladder or breast carcinoma in Tunisian patients. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1010:764–770
Bonafe M, Ceccarelli C, Farabegoli F, Santini D, Taffurelli M, Barbi C, Marzi E, Trapassi C, Storci G, Oliveri F, Franceschi C (2003) Retention of the codon72 Arginine allele is associated with a reduction of disease-free and overall survival in Arginine/Proline heterozygous breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 9:4860–4864
Schneider-Stock R, Boltz C, Peters B, Szibor R, Landt O, Meyer F, Roessner A (2004) Selective loss of codon72 Proline p53 and frequent mutational inactivation of retained Arginine allel in colorectal cancer. Neoplasia 6:529–535
Mitra S, Banerjee S, Misra C, Singh RK, Roy A, Sengupta A, Panda CK, Roychoudhury S (2007) Interplay between human papilloma virus infection and p53 gene alterations in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma of an Indian population. J Clin Pathol 60:1040–1047
Toyama T, Zhang Z, Nishio M, Hamaguchi M, Kondo N, Iwase H, Iwata H, Takahashi S, Yamashita H, Fujii Y (2007) Association of TP53 codon 72 polymorphism and the outcome of adjuvant therapy in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res 9:R34
Kyndi M, Alsner J, Hansen LL, Sorensen F, Overgaard J (2006) LOH rather than genotypes of TP53 codon 72 is associated with disease-free survival in primary breast cancer. Acta Oncol 45:602–609
Wegman P, Elingarami S, Carstensen J, Stål O, Nordenskjöld B, Wingren S (2007) Genetic variants of CYP3A5, CYP2D6, SULT1A1, UGT2B15 and tamoxifen response in postmenopausal patients with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 9(1):R7
Brooks LA, Tidy JA, Gusterson B, Hiller L, O′Nions J, Gasco M, Marin MC, Farrel PJ, Kaelin W, Crook T (2000) Preferential retention of codon72 Arginine p53 in squamous cell carcinoma of the vulva occurs in cancers positive and negative for human papillomavirus. Cancer Res 60:6875–6877
Buller RE, Sood A, Fullenkamp C, Sorosky J, Powills K, Anderson B (1997) The influence of the p53 codon72 polymorphism on ovarian carcinogenesis and prognosis. Cancer Gene Ther 4:239–245
Papadakis ED, Soulitiz N, Spandidos DA (2002) Association of p53 codon72 Polymorphism with advanced lung cancer: the Arg allele is preferentially retained in tumours arising in Arg/Pro germline heterozygotes. Br J Cancer 87:1013–1018
Kawaguchi H, Ohno S, Araki K, Miyazaki M, Saeki H, Watanabe M, Tanaka S, Sugimachi K (2000) p53 Polymorphism in human papillomavirus- associated esophageal cancer. Cancer Res 60:2753–2755
Furihata M, Takeuchi T, Matsumoto M, Kurabayashi A, Ohtsuki Y, Terao N, Kuwahara M, Shuin T (2002) p53 Mutation arising in Arg 72 allele in the tumorigenesis and development of carcinoma of the urinary tract. Clin Cancer Res 8:1192–1198
Marin M, Jost C, Brooks L, Irwin M, Nions J, Tidy J, James N, McGregor J, Harwood C, Yulug I, Vousdrn K, Allday M, Gusterson B, Ikawa S, Hinds P, Crook T, Kaelin W (2000) A common polymorphism acts as an intragenic modifier of mutant p53 behaviour. Nat Genet 25:47–54
Tada M, Furuuchi K, Kaneda M, Matsumoto J, Takahashi M, Hirai A, Mitsumoto Y, Iggo R, Moriuchi T (2001) Inactivating of the remaining p53 allele or the alternate p73? Preferential selection of the Arg polymorphism in cancer with recessive p53 mutant but not transdominant mutants. Carcinogenesis 22:515–517
Bergamaschi D, Gasco M, Hiller L, Sullivan A, Syed N, Trigiante G, Yulug I, Merlano M, Numico G, Comino A, Attard M, Reelfs O, Gusterson B, Bell AK, Heath V, Tavassoli M, Farell PJ, Smith P, Lu X, Crook T (2003) p53 Polymorphism influences response in cancer chemotherapy via modulation of p73-dependent apoptosis. Cancer Cell 3:387–402
Szymanowska A, Jassem E, Dziadziuszko R, Borg A, Limon J, Gulida G, Rzyman W, Jassem J (2005) Increased risk of non-small cell lung cancer and frequency of somatic TP53 mutations in pro72 carrier of the arg72pro polymorphism. Lung cancer 52:9–14
Hu Y, McDermott M, Ahrendt S (2005) The codon 72 proline allele is associated with p53 gene mutations in non-small cell ung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:2502–2509
Xu Y, Yao L, Zhao A, Ouyang T, Li J, Wang T, Fan Z, Fan T, Lin B, Lu Y, Xie Y (2008) Effect of codon 72 genotype on breast cancer survival depends on p53 status. Int J Cancer 122:2761–2766
Vannini I, Zoli W, Tesei A, Rosetti M, Sansone P, Storci G, Passardi A, Massa I, Ricci M, Gusolfini D, Fabbri F, Ulivi P, Brigliadori G, Amodori D, Bonafe M (2008) Role of p53 codon 72 arginine allele in cell survival in vitro and in the clinical outcome of patients with advanced breast cancer. Tumor Biol 29:145–151
Xu Y, Yao L, Ouyang T, Li J, Wang T, Fan Z, Lin B, Lu Y, Xie Y (2005) p53 Codon 72 polymorphism predicts the pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:7328–7333
Nordgard S, Alnas G, Hihn B, Lingjarde OC, Liestol K, Tsalenko A, Sorli T, Lonning PE, Borresen AL, Kristensen V (2008) Pathway based analysis of SNPs with relevance to 5-FU therapy: relation to intratumoral mRNA expression and survival. Int J Cancer 123:577–585
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the Swedish Cancer and Allergy Society, the Swedish Cancer Society, Gunnar Nilsson Cancer Foundation and Percy Falks Cancer Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wegman, P.P., Marcus, N.J., Malakkaran, B.P. et al. Biological significance of allele specific loss of the p53 gene in breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Treat 118, 15–20 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-008-0212-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-008-0212-1