Abstract
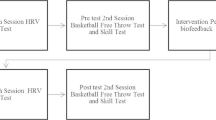
Coping with pressure and anxiety is an ineluctable demand of sports performance. Heart rate variability (HRV) Biofeedback (BFB) shall be used as a tool for self regulating physiological responses resulting in improved psycho physiological interactions. For further analysis, the present study has been designed to examine the relationship between anxiety and performance and also effectiveness of biofeedback protocol to create stress-eliciting situation in basketball players. Thirty basketball players of university level and above (both male and female) aged 18–28 years, who scored a minimum of 20 in state trait anxiety inventory, were randomly divided into three equal groups- Experimental (Biofeedback) group, Placebo group and Control (No Treatment) group. The BFB group received HRV BFB training for 10 consecutive days for 20 min that included breathing at individual’s resonant frequency through a pacing stimulus; Placebo group was shown motivational video clips for 10 consecutive days for 10 min, whereas No Treatment Control group was not given any intervention. Two way repeated measure ANOVA was applied to analyze the differences within and between the groups. Anxiety, coping self-efficacy, heart rate variability, respiration rate, and performance (dribbling, passing and shooting) at session 1, 10 and 1 month follow up were statistically significant in each group along with interaction of group and time (p < 0.001). Also, all the measures showed statistically significant inter group difference (p < 0.05). The findings are harmonious with existing data on HRV BFB as a strategy for dealing with anxiety. The Placebo group showed improvement in self efficacy and performance post training. The Control group showed no change in any variable except performance. The results of the study support the idea that HRV BFB lowers the anxiety and thus there seems to be a potential association between HRV BFB and performance optimization.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anyadubalu, C. C. (2010). Self-efficacy, anxiety, and performance in the English language among middle-school students in English language program in Satri Si Suriyothai School, Bangkok. International Journal of Human and Social Sciences, 5(3), 193–198.
Babiloni, C., Percio, C. D., Iacoboni, M., Infarinato, F., Lizio, R., Marzano, N., et al. (2008). Golf putt outcomes are predicted by sensorimotor cerebral EEG rhythms. Journal of Physiology, 58(1), 131–139.
Barrow, H., & McGee, R. (1979). A practical approach to measurement in physical education. Philadelphia, PA: Lea & Febiger.
Chesney, M. A., Neilands, T. B., Chambers, D. B., Taylor, J. M., & Folkman, S. (2006). A validity and reliability study of the coping self-efficacy scale. British Journal of Health Psychology, 11, 421–437.
Dahlbeck, D. T., & Lightsey, O. R., Jr. (2008). Generalized self-efficacy, coping, and self-esteem as predictors of psychological adjustment among children with disabilities or chronic illnesses. Children’s Health Care, 37(4), 293–315.
Dehdari, T., Heidarnia, A., Ramezankhani, A., Sadeghian, S., & Ghofranipour, F. (2008). Anxiety, self efficacy expectation and social support in patients after coronary angioplasty and coronary bypass. Iranian journal of public health, 3(4), 119–125.
Hammond, D. C. (2007). Neurofeedback for the enhancement of athletic performance and physical balance. The Journal of the American Board of Sport Psychology, 1, 1–9.
Hassett, A. L., Radvanski, D. C., Vaschillo, E. G., Vaschillo, B., Sigal, L. H., Karavidas, M. K., et al. (2007). A pilot study of the efficacy of heart rate variability (HRV) biofeedback in patients with fibromyalgia. Applied Psychophysiology Biofeedback, 32, 1–10.
Humara, M. (1999). The relationship between anxiety and performance: A cognitive-behavioral perspective. Athletic insight, the online journal of sport psychology, 1(2), 1–14.
Jordanova, N. P., & Demerdzieva, A. (2010). Biofeedback training for peak performance in sport: Case study. Macedonian journal of medical sciences, 3(2), 113–118.
Lagos, L., Vaschillo, E., Vaschillo, B., Lehrer, P., Bates, M., & Pandina, R. (2008). Heart rate variability biofeedback for dealing with competitive anxiety: A case study. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 36(3), 109–115.
Lehrer, P. M., Vaschillo, E. G., & Vaschillo, B. (2000). Resonant frequency biofeedback training to increase cardiac variability: Rationale and manual for training. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 25, 177–191.
Lehrer, P., Vaschillo, E., Vaschillo, B., Lu, S. E., Eckberg, D. L., Edelberg, R., et al. (2003). Heart rate variability biofeedback increases baroreflex gain and peak expiratory flow. Psychosomatic Medicine, 65, 796–805.
Lehrer, P., Vaschillo, E., Lu, S. E., Eckberg, D., Vaschillo, B., Scardella, A., et al. (2006). Heart rate variability biofeedback: Effects of age on heart rate variability, baroreflex gain, and Asthma. Chest, 129, 278–284.
Nicholls, A. R., Polman, R., & Levy, A. R. (2010). Coping self-efficacy, pre-competitive anxiety, and subjective performance among athletes. European journal of sport science, 10(2), 97–102.
Raymond, J., Sajid, I., Parkinson, L. A., & Gruzelier, J. H. (2005). Biofeedback and dance performance: A preliminary investigation. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 30, 65–73.
Spielberger, C. D. (1966). Theory and research on anxiety. In C. S. Spielberger (Ed.), Anxiety and behaviour (pp. 3–20). New York: Academic Press.
Spielberger, C. D., Gorsuch, R. L., & Lushene, R. E. (1970). Manual for the state-trait anxiety inventory (STAI). Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press.
Sutarto, A. P., Wahab, M. N. A., & Zin, N. M. (2010). Heart rate variability (HRV) biofeedback: A new training approach for operator’s performance enhancement. Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management, 3(1), 176–198.
Strack, B. W. (2003). Effect of heart rate variability (HRV) biofeedback on batting performance in baseball. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B, the Sciences and Engineering, 64(3), 1540B.
Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. (1996). Heart rate variability: Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. European Heart Journal, 17, 354–381.
Weinberg, R. S., Fowler, C., Jackson, A., Bagnall, J., & Bruya, L. (1991). Effect of goal difficulty on motor performance: A replication across tasks and subjects. Journal of Sport & Exercise Psychology, 13, 160–173.
Wheat, A. L., & Larkin, K. T. (2010). Biofeedback of heart rate variability and related physiology: A critical review. Applied Psychophysiology Biofeedback, 35, 229–242.
Wilmore, J., & Costill, D. (2004). Physiology of sport and exercise (5th ed.). USA: Human Kinetics Publishers.
Wilson, G., & Pritchard, M. (2005). Comparing sources of stress in college student athletes and non-athletes. Athletic Insight: The Online Journal of Sport Psychology, 7(1), 1–8.
Zupan, M. F., Arata, A. W., Wile, A., & Parker, R. (2006). Visual adaptations to sports vision enhancement training: A study of collegiate athletes at the US air force academy. In Optometry today/Optics today (Vol. 46, pp. 43–48).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, M., Garg, K. The Effect of Heart Rate Variability Biofeedback on Performance Psychology of Basketball Players. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 37, 131–144 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-012-9185-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-012-9185-2