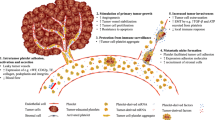
Abstract
Platelets sequester angiogenesis regulatory proteins which suggests an avenue for developing biomarkers to monitor disease. We describe a comparison of angiogenesis regulatory proteins found in platelets of colorectal cancer patients and normal controls. Platelet and plasma content of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), platelet derived growth factor (PDGF), platelet factor 4 (PF4), thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) and endostatin in 35 patients with colon cancer were compared with 84 age-matched healthy controls using ELISAs. We standardized the platelet preparation procedure, introduced process controls and normalized the respective protein levels to platelet numbers using an actin ELISA. Statistically significant differences were found in the median levels of VEGF, PF4 and PDGF in platelets of patients with cancer compared to healthy individuals. Platelet concentrations in cancer patients versus controls were: VEGF 1.3 versus 0.6 pg/106, PF4 18.5 versus 9.4 ng/106, and PDGF 34.1 versus 21.0 pg/106. Multivariable logistic regression analysis indicated that PDGF, PF4 and VEGF were independent predictors of colorectal carcinoma and as a set provided statistically significant discrimination (area under the curve = 0.893, P < .0001). No significant differences were detected for bFGF, endostatin, or TSP-1. Reference Change Value analysis determined that the differences seen were not clinically significant. Plasma levels yielded no correlations.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- bFGF:
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor
- PDGF:
-
Platelet derived growth factor
- PF4:
-
Platelet factor 4
- TSP-1:
-
Thrombospondin-1
- PRP:
-
Platelet rich plasma
- PPP:
-
Platelet poor plasma
- CBC:
-
Complete blood count
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme linked immune sorbent assay
References
Carmeliet P (2005) Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature 438:932–936
Folkman J (2007) Angiogenesis: an organizing principle for drug discovery? Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:273–287
Fuhrmann-Benzakein E, Ma MN, Rubbia-Brandt L et al (2000) Elevated levels of angiogenic cytokines in the plasma of cancer patients. Int J Cancer 85:40–45
Nguyen M (1997) Angiogenic factors as tumor markers. Invest New Drugs 15:29–37
Peterson JE, Zurakowski D, Italiano JE Jr et al (2010) Normal ranges of angiogenesis regulatory proteins in human platelets. Amer. J. Hematology 85:487–493
Klement GL, Kikuchi L, Kieran M (2004) Early tumor detection using platelet uptake of angiogenesis regulators. Blood 104 (abstr 839)
Klement GL, Yip T–T, Cassiola F et al (2009) Platelets actively sequester angiogenesis regulators. Blood 113:2835–2842
Saldago R, Benoy I, Bogers J et al (2001) Platelets and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF): a morphological and functional study. Angiogenesis 4:37–43
Gonzalez FJ, Rueda A, Sevilla I et al (2004) Shift in the balance between circulating thrombospondin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor in cancer patients: Relationship to platelet a-granule content and primary activation. Int J Biol Markers 19:221–228
Hartwig JC (2008) The platelet cytoskeleton. In: Gresele P, Fuster V, López JA, Page CP, Vermylen J (eds) Platelets in hematologic and cardiovascular disorders. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 75–97
Cervi D, Yip TT, Bhattacharya N et al (2008) Platelet-associated PF4 as a biomarker of early tumor growth. Blood 111:1201–1207
Fraser CG (2001) Changes in serial results. In: Biological variation: from principals to practice. AACC Press, Washington, DC, pp 67–90
Grubbs F (1969) Procedures for detecting outlying observations in samples. Technometrics 11:1–21
Altman DG (1991) Practical statistics for medical research. Chapman & Hall, Boca Raton, FL, pp 29–47
Pepe MS (2003) The statistical evaluation of medical tests for classification and prediction. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 66–95
Katz MH (2006) Multivariable analysis: a practical guide for clinicians, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 96–136
Zaslavsky A, Baek K-H, Lynch RC et al (2010) Platelet-derived thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) is a critical negative regulator and potential biomarker of angiogenesis. Blood 115:4605–4613
Folkman J, Browder T, Palmblad J (2001) Angiogenesis research: guidelines for translation to clinical application. Thromb Haemost 86:23–33
George ML, Eccles SA, Tutton MG, Abulafi M, Swift RI (2000) Correlation of plasma and serum vascular endothelial growth factor levels with platelet count in colorectal cancer: Clinical Evidence of Platelet Scavenging? Clin Cancer Res 6:3147–3152
Åkerblom B, Lindahl TL, Larsson A (2002) ADP activation induces bFGF binding to platelets in vitro. Upsala J Med Sci 107:165–171
Salgado R, Vermeulen PB, Benoy I et al (1999) Platelet number and interleukin-6 correlate with VEGF but not with bFGF serum levels of advanced cancer patients, Brit. J of Cancer 80:892–897
Gasic GJ, Gasic TB, Stewart CC (1968) Antimetastatic effects associated with platelet reduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 61:46–52
Pedersen LM, Milman N (1996) Prognostic significance of thrombocytosis in patients with primary lung cancer. Eur Respir J 9:1826–1830
Ikeda M, Furukawa H, Imamura H et al (2002) Poor prognosis associated with thrombocytosis in patients with gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 9:287–291
Verheul HM, Hoekman K, Luykx-de Bakker S et al (1997) Platelet: transporter of vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin Cancer Res 3:2187–2190
Italiano JE Jr, Richardson JL, Patel-Hett S (2008) Angiogenesis is regulated by a novel mechanism: pro- and antiangiogenic proteins are organized into separate alpha granules and differentially released. Blood 111:1227–1233
Ma L, Perini R, McKnight W et al (2005) Proteinase activated receptors 1 and 4 counter-regulate endostatin and VEGF release from human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:216–220
Ellis LM, Takahashi Y, Liu W, Shaheen R (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor in human colon cancer: Biology and therapeutic implications. Oncologist 5(suppl 1):11–15
Zetter BR (1998) Angiogenesis and tumor metastasis. Annu Rev Med 49:407–424
Lindmark G, Sundberg C, Glimelius B (1993) Stromal expression of platelet-derived growth factor beta-receptor and platelet-derived growth factor B-chain in colorectal cancer. Lab Invest 69(6):682–689
Acknowledgments
This paper is dedicated to Judah Folkman, MD. We thank Dr. Marsha Moses of Children’s Hospital Boston for a helpful review of this manuscript. We thank Betsy Valles of Massachusetts General Hospital and Sean Downing of Children’s Hospital Boston and for their work in collecting and archiving cancer patient samples. We thank Dennis Robords of Ortho Clinical Diagnostics, Abdo Abou-Slaybi and Marlieke de Bruin of Children’s Hospital Boston for technical assistance. We thank Sean Downing of Children’s Hospital Boston and Lucius (Tad) Fox and John Backus of Ortho Clinical Diagnostics for discussions. We also thank John Backus for providing colonoscopy samples from Mayo Clinic. Ortho Clinical Diagnostics provided the funding for this work.
Conflict of interest
Jon Peterson was—and Marsha Oenick is—employed by and compensated by Ortho Clinical Diagnostics. Joseph Italiano and David Zurakowski were compensated as consultants to Ortho Clinical Diagnostics. No others have anything to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peterson, J.E., Zurakowski, D., Italiano, J.E. et al. VEGF, PF4 and PDGF are elevated in platelets of colorectal cancer patients. Angiogenesis 15, 265–273 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-012-9259-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-012-9259-z