Abstract
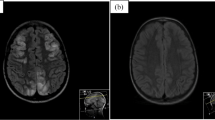
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) is a reversible, predominantly posterior, leukoencephalopathy associated with renal insufficiency, hypertension, or immunosuppressant drugs. We describe two children with PRES whose primary diagnoses were idiopathic nephrotic syndrome and lupus nephritis. Cranial magnetic resonance (MR) imaging at the onset of PRES showed strong hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted imaging with restricted apparent diffusion coefficient values predominantly in the posterior region. Such findings have been rarely reported in children with PRES and initially suggested irreversible brain damage; however, both children fully recovered clinically as well as radiologically. Our findings suggest the limitations of cranial MR imaging for diagnosing PRES. Further experience with cranial MR imaging, including diffusion-weighted imaging with apparent diffusion coefficient mapping, is required to improve diagnostic accuracy and the ability to predict outcomes in patients with early-stage PRES. At present, initial imaging studies do not necessarily provide sufficient evidence for a firm diagnosis of PRES or the prediction of outcomes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, Breen J, Pao L, Wang A, et al. A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:494–500.
Ikeda M, Ito S, Hataya H, Honda M, Anbo K. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy in a patient with minimal-change nephrotic syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001;37:E30.
Ishikura K, Ikeda M, Hamasaki Y, Hataya H, Shishido S, Asanuma H, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in children: its high prevalence and more extensive imaging findings. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;48:231–8.
Ishikura K, Ikeda M, Hamasaki Y, Hataya H, Nishimura G, Hiramoto R, et al. Nephrotic state as a risk factor for developing posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in paediatric patients with nephrotic syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:2531–6.
Punaro M, Abou-Jaoude P, Cimaz R, Ranchin B. Unusual neurologic manifestations (II): posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) in the context of juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2007;16:576–9.
Parvex P, Pinsk M, Bell LE, O’Gorman AM, Patenaude YG, Gupta IR. Reversible encephalopathy associated with tacrolimus in pediatric renal transplants. Pediatr Nephrol. 2001;16:537–42.
Kanekiyo T, Hara J, Matsuda-Hashii Y, Fujisaki H, Tokimasa S, Sawada A, et al. Tacrolimus-related encephalopathy following allogeneic stem cell transplantation in children. Int J Hematol. 2005;81:264–8.
Vaughan CJ, Delanty N. Hypertensive emergencies. Lancet. 2000;356:411–7.
Lamy C, Oppenheim C, Meder JF, Mas JL. Neuroimaging in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. J Neuroimaging. 2004;14:89–96.
Doelken M, Lanz S, Rennert J, Alibek S, Richter G, Doerfler A. Differentiation of cytotoxic and vasogenic edema in a patient with reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome using diffusion-weighted MRI. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2007;13:125–8.
Covarrubias DJ, Luetmer PH, Campeau NG. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: prognostic utility of quantitative diffusion-weighted MR images. Am J Neuroradiol. 2002;23:1038–48.
Weening JJ, D’Agati VD, Schwartz MM, Seshan SV, Alpers CE, Appel GB, et al. The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. Kidney Int. 2004;65:521–30.
Schwartz RB. Hyperperfusion encephalopathies: hypertensive encephalopathy and related conditions. Neurologist. 2002;8:22–34.
Casey SO, Sampaio RC, Michel E, Truwit CL. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: utility of fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MR imaging in the detection of cortical and subcortical lesions. Am J Neuroradiol. 2000;21:1199–206.
Schwartz RB, Mulkern RV, Gudbjartsson H, Jolesz F. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in hypertensive encephalopathy: clues to pathogenesis. Am J Neuroradiol. 1998;19:859–62.
Schaefer PW, Buonanno FS, Gonzalez RG, Schwamm LH. Diffusion-weighted imaging discriminates between cytotoxic and vasogenic edema in a patient with eclampsia. Stroke. 1997;28:1082–5.
Kinoshita T, Moritani T, Shrier DA, Hiwatashi A, Wang HZ, Numaguchi Y, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of posterior reversible leukoencephalopathy syndrome: a pictorial essay. Clin Imaging. 2003;27:307–15.
Benziada-Boudour A, Schmitt E, Kremer S, Foscolo S, Riviere AS, Tisserand M, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a case of unusual diffusion-weighted MR images. J Neuroradiol. 2009;36:102–5.
Pearson ER, D’Souza RJ, Hamilton-Wood C, Nicholls AJ, Beaman M. Hypertensive encephalopathy and nephrotic syndrome: a possible link? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999;14:1750–2.
Leroux G, Sellam J, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Le Thi Huong D, Combes A, Tieulie N, et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome during systemic lupus erythematosus: four new cases and review of the literature. Lupus. 2008;17:139–47.
Williams FM, Chinn S, Hughes GR, Leach RM. Critical illness in systemic lupus erythematosus and the antiphospholipid syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002;61:414–21.
Zhang YX, Liu JR, Ding MP, Huang J, Zhang M, Jansen O, et al. Reversible posterior encephalopathy syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Intern Med. 2008;47:867–75.
Conflict of interest
All the authors have declared no competing interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Ishikura, K., Hamasaki, Y., Sakai, T. et al. Children with posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome associated with atypical diffusion-weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient. Clin Exp Nephrol 15, 275–280 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-010-0380-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-010-0380-2