Abstract
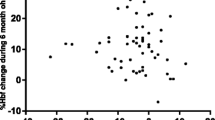
Red blood cell (RBC) deformability is a major determinant of the ability of the RBC to pass repeatedly through the microcirculation. A decrease in RBC deformability leads to tissue perfusion and organ dysfunction. The purpose of this study was to measure the rigidity of RBCs from human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) seropositive individuals and investigate its relation to immune status and viral load. A filtration method based on the initial flow rate principle was used to determine the index of rigidity (IR) of 53 samples from HIV patients and 53 healthy individuals. The mean IR was significantly increased in patients with HIV compared to healthy individuals (P < 0.01). IR was inversely correlated with current CD4+ T-lymphocyte counts (P < 0.0001). High CD4 cell counts (>200cells/μl) are related to low IR values, independently of the viral load (VL). No differences in rigidity were noted between the VL groups, although there was a trend towards an increased IR in patients with high VL within the group of CD4<200. RBC deformability is decreased in HIV disease, in a degree mainly related to CD4 depletion. Further studies are needed to elucidate the underlying mechanisms and the role of VL in highly immunocompromised HIV patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mittler JE, Sulzer B, Neumann AU, Perelson AS (1998) Influence of delayed production on viral dynamics in HIV-1 infected patients. Math Biosci 152:143–163
Ho DD, Neumann AU, Perelson AS, Chen W, Leonard JM, Markowits M (1995) Rapid turnover of plasma varions and CD-4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection. Nature 373:123
Calenda V, Chermann JC (1992) The effects of HIV on hematopoiesis. Eur J Haemotol 48(4):181–186
Monsuez JJ, Dufaux J, Vittecoq D, Flaud P (2000) Hemorheology in asymptomatic HIV-infected patients. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 23:59–66
Yunis NA, Stone VE (1998) Cardiac manifestations of HIV/AIDS: a review of disease spectrum and clinical management. Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol 18(2):145–154
Xiou RJ, Jun C, Berglund O (1991) Microcirculatory disturbances in AIDS patients. Microvasc Res 42(2):151–159
Kim A, Dadgostar H, Holland GN et al (2006) Hemorheologic abnormalities associated with HIV infection: altered erythrocyte aggregation and deformability. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47(9):3927–3932
Engstrom RE Jr, Hollant GN, Hardy WD, Meiselman HJ (1990) Hemorheologic abnormalities in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection and ophthalmic microvasculopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 109:153–161
Rampling MW, Boca Raton FL (1988) Red cell aggregation and yield stress. Clinical Blood Rheology, CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 11–44
Hanss M (1983) Erythrocyte filterability measurement by the initial flow rate method. Biorheology 20:199–211
Hanss M, Koutsouris D (1985) The role of membrane lipids in erythrocyte rheology. Colloids Surf 14:261–268
Yung CW, Harris A, Massicotte S et al (1996) Retinal flow indices in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Br J Ophthalmol 80:723–727
Lim MC, Cumberland WG, Minassian SL et al (2001) Decreased macular leukocyte velocity in human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals. Am J Ophthalmol 132:711–719
Tufail A, Holland GN, Fisher TC et al (2000) Increased polymorphonuclear leukocyte rigidity in HIV infected individuals. Br J Ophthalmol 84:727–731
Goldenberg DT, Holland GN, Cumberland WG et al (2002) An assessment of polymorphonuclear leukocyte rigidity in HIV infected individuals after immune recovery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43:1857–1861
Dadgostar H, Holland GN, Huang X et al (2006) Hemorheologic abnormalities associated with HIV infection: in vivo assessment of retinal microvascular blood flow. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47(9):3933–3938
Doukas MA (1992) Human immunodeficiency virus associated anaemia. Med Clin North Am 76:699–709
Baskurt OK (1996) Activated granulocyte induced alterations in red blood cells and protection by antioxidant enzymes. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 16:49–56
Baskurt OK, Meiselman HJ (1998) Activated polymorphonuclear leukocytes affect red blood cell aggregability. J Leukoc Biol 63:89–93
Claster S, Chiu DTY, Quintanilla A et al (1984) Neutrophils mediated lipid peroxidation in human red cells. Blood 64:1079–1084
Ali H, Haribabu B, Richardson RM, Snyderman R (1997) Mechanisms of inflammation and leukocyte activation. Med Clin North Am 81:1–28
Elbim C, Prevot MH, Bouscarat F et al (1994) Popymorphonuclear neutrophils from HIV-infected patients show enhanced activation, diminished fMLP-induced L-selectin shedding, and impaired oxidative burst after cytocine priming. Blood 84:2759–2766
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Athanassiou, G.A., Moutzouri, A.G., Gogos, C.A. et al. Red blood cell deformability in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 29, 845–849 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-010-0936-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-010-0936-9