Abstract
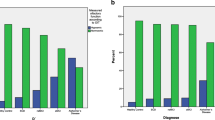
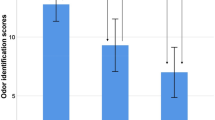
Olfactory impairment might be an important clinical marker and predictor of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In the present study, we aimed to compare the degree of olfactory identification impairment in each mild cognitive impairment (MCI) subtype, subjective memory impairment, and early AD dementia and assessed the relationship between olfactory identification and cognitive performance. We consecutively included 50 patients with amnestic MCI, 28 patients with non-amnestic MCI, 20 patients with mild AD, and 17 patients with subjective memory impairment (SMI). All patients underwent clinical and neuropsychological assessments. A multiple choice olfactory identification cross-cultural smell identification test was also utilized. Controlling for age and gender, olfactory impairment was significantly more severe in patients with AD and amnestic MCI compared with the results from the non-amnestic MCI and SMI groups. Higher scores on MMSE, verbal and non-verbal memory, and frontal executive function tests were significantly related to olfactory identification ability. In conclusion, olfactory identification is impaired in amnestic MCI and AD. These findings are consistent with previous studies. In amnestic MCI patients, this dysfunction is considered to be caused by underlying AD pathology.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attems J, Walker L, Jellinger KA (2014) Olfactory bulb involvement in neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Neuropathol 127:459–475
Velayudhan L (2015) Smell identification function and Alzheimer's disease: a selective review. Curr Opin Psychiatry 28(2):173–179. https://doi.org/10.1097/YCO.0000000000000146
Doty RL, Reyes PF, Gregor T (1987) Presence of both odor identification and detection deficits in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res Bull 18(5):597–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/0361-9230(87)90129-8
Morgan CD, Nordin S, Murphy C (1995) Odor identification as an early marker for Alzheimer's disease: impact of lexical functioning and detection sensitivity. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 17:793–803
Mesholam RI, Moberg PJ, Mahr RN, Doty RL (1998) Olfaction in neurodegenerative disease: a meta-analysis of olfactory functioning in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Arch Neurol 55(1):84–90. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.55.1.84
Chan A, Tam J, Murphy C, Chiu H, Lam L (2002) Utility of olfactory identification test for diagnosing Chinese patients with Alzheimer's disease. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 24:251–259
Murphy C, Jernigan TL, Fennema-Notestine C (2003) Left hippocampal volume loss in Alzheimer's disease is reflected in performance on odor identification: a structural MRI study. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 9(3):459–471. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1355617703930116
Devanand DP, Tabert MH, Cuasay K, Manly JJ, Schupf N, Brickman AM, Andrews H, Brown TR, DeCarli C, Mayeux R (2010) Olfactory identification deficits and MCI in a multi-ethnic elderly community sample. Neurobiol Aging 31(9):1593–1600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.09.008
Vasavada MM, Wang J, Eslinger PJ, Gill DJ, Sun X, Karunanayaka P, Yang QX (2015) Olfactory cortex degeneration in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis 45(3):947–958. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-141947
Vassilaki M, Christianson TJ, Mielke MM, Geda YE, Kremers WK, Machulda MM, Knopman DS, Petersen RC, Lowe VJ, Jack CR Jr, Roberts RO (2017) Neuroimaging biomarkers and impaired olfaction in cognitively normal individuals. Ann Neurol 81: 871–882, 6, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24960
Attems J, Lintner F, Jellinger K (2005) Olfactory involvement in aging and Alzheimer's disease: an autopsy study. J Alzheimers Dis 7:149–157
Wilson RS, Arnold SE, Schneider JA, Tang Y, Bennett DA (2007) The relationship between cerebral Alzheimer's disease pathology and odour identification in old age. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78(1):30–35. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2006.099721
Serby M, Larson P, Kalkstein D (1991) The nature and course of olfactory deficits in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Psychiatry 148:357–360
Albert MS, DeKosky ST, Dickson D, Dubois B, Feldman HH, Fox NC, Gamst A, Holtzman DM, Jagust WJ, Petersen RC, Snyder PJ, Carrillo MC, Thies B, Phelps CH (2011) The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement 7(3):270–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.008
Petersen RC (2011) Mild cognitive impairment. N Engl J Med 364(23):2227–2234. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMcp0910237
Devanand DP, Michaels-Marston KS, Liu X, Pelton GH, Padilla M, Marder K, Bell K, Stern Y, Mayeux R (2000) Olfactory deficits in patients with mild cognitive impairment predict Alzheimer's disease at follow-up. Am J Psychiatry 157(9):1399–1405. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.157.9.1399
Swan GE, Carmelli D (2002) Impaired olfaction predicts cognitive decline in nondemented older adults. Neuroepidemiology 21(2):58–67. https://doi.org/10.1159/000048618
Conti MZ, Vicini-Chilovi B, Riva M, Zanetti M, Liberini P, Padovani A, Rozzini L (2013) Odor identification deficit predicts clinical conversion from mild cognitive impairment to dementia due to Alzheimer's disease. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 28:391–399
Stanciu I, Larsson M, Nordin S, Adolfsson R, Nilsson LG, Olofsson JK (2014) Olfactory impairment and subjective olfactory complaints independently predict conversion to dementia: a longitudinal, population-based study. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 20(02):209–217. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1355617713001409
Devanand D, Lee S, Manly J, Andrews H, Schupf N, Doty RL, Stern Y, Zahodne LB, Louis ED, Mayeux R (2015) Olfactory deficits predict cognitive decline and Alzheimer dementia in an urban community. Neurology 84(2):182–189. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000001132
Westervelt HJ, Bruce JM, Coon WG, Tremont G (2008) Odor identification in mild cognitive impairment subtypes. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 30(2):151–156. https://doi.org/10.1080/13803390701287408
Vyhnalek M, Magerova H, Andel R, Nikolai T, Kadlecova A, Laczo J, Hort J (2015) Olfactory identification in amnestic and non-amnestic mild cognitive impairment and its neuropsychological correlates. J Neurol Sci 349:179–184
Busse A, Hensel A, Gühne U, Angermeyer M, Riedel-Heller S (2006) Mild cognitive impairment long-term course of four clinical subtypes. Neurology 67:2176–2185
Rabin LA, Smart CM, Crane PK, Amariglio RE, Berman LM, Boada M, Buckley RF, Chételat G, Dubois B, Ellis KA, Gifford KA, Jefferson AL, Jessen F, Katz MJ, Lipton RB, Luck T, Maruff P, Mielke MM, Molinuevo JL, Naeem F, Perrotin A, Petersen RC, Rami L, Reisberg B, Rentz DM, Riedel-Heller SG, Risacher SL, Rodriguez O, Sachdev PS, Saykin AJ, Slavin MJ, Snitz BE, Sperling RA, Tandetnik C, van der Flier WM, Wagner M, Wolfsgruber S, Sikkes SA (2015) Subjective cognitive decline in older adults: an overview of self-report measures used across 19 international research studies. J Alzheimers Dis 48(s1):S63–S86. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-150154
Fernandez-Blazquez MA, Avila-Villanueva M, Maestu F, Medina M (2016) Specific features of subjective cognitive decline predict faster conversion to mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis 52(1):271–281. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-150956
Park HD, Park KU, Kim KW, Song J, Chang HE, Heo SR, Lee HJ, Kim JQ (2007) Real-time multiplex PCR assay for genotyping of three apolipoprotein E alleles and two choline acetyltransferase alleles with three hybridization probes. Clin Chem Lab Med 45(3):346–350. https://doi.org/10.1515/CCLM.2007.075
Kang Y, Na D, Hahn S (2003) Seoul neuropsychological screening battery. Human brain research & consulting co., Incheon
McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, Hyman BT, Jack CR Jr, Kawas CH, Klunk WE, Koroshetz WJ, Manly JJ, Mayeux R, Mohs RC, Morris JC, Rossor MN, Scheltens P, Carrillo MC, Thies B, Weintraub S, Phelps CH (2011) The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer Dement 7: 263–269, 3, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005
Petersen RC (2004) Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J Intern Med 256(3):183–194. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2796.2004.01388.x
Stewart R (2012) Subjective cognitive impairment. Curr Opin Psychiatry 25(6):445–450. https://doi.org/10.1097/YCO.0b013e3283586fd8
Doty RL, Marcus A, William Lee W (1996) Development of the 12-item Cross-Cultural Smell Identification Test (CC-SIT). Laryngoscope 106:353–356
Talamo BR, Rudel R, Kosik KS, Lee VM-Y, Neff S, Adelman L, Kauer JS (1989) Pathological changes in olfactory neurons in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Nature 337(6209):736–739. https://doi.org/10.1038/337736a0
Braak H, Braak E (1994) Morphological criteria for the recognition of Alzheimer's disease and the distribution pattern of cortical changes related to this disorder. Neurobiol Aging 15(3):355–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/0197-4580(94)90032-9
Thompson MD, Knee K, Golden CJ (1998) Olfaction in persons with Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychol Rev 8:11–23
Djordjevic J, Jones-Gotman M, De Sousa K, Chertkow H (2008) Olfaction in patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 29(5):693–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.11.014
Lehrner J, Pusswald G, Gleiss A, Auff E, Dal-Bianco P (2009) Odor identification and self-reported olfactory functioning in patients with subtypes of mild cognitive impairment. Clin Neuropsychol 23:818–830
Wilson RS, Arnold SE, Schneider JA, Boyle PA, Buchman AS, Bennett DA (2009) Olfactory impairment in presymptomatic Alzheimer's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1170(1):730–735. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04013.x
Roberts RO, Christianson TJ, Kremers WK, Mielke MM, Machulda MM, Vassilaki M, Alhurani RE, Geda YE, Knopman DS, Petersen RC (2016) Association between olfactory dysfunction and amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease dementia. JAMA Neurol 73(1):93–101. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.2952
Luzzi S, Snowden JS, Neary D, Coccia M, Provinciali L, Lambon Ralph MA (2007) Distinct patterns of olfactory impairment in Alzheimer's disease, semantic dementia, frontotemporal dementia, and corticobasal degeneration. Neuropsychologia 45(8):1823–1831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2006.12.008
Kovacs T, Cairns N, Lantos P (1999) Beta-amyloid deposition and neurofibrillary tangle formation in the olfactory bulb in ageing and Alzheimer's disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 25:481–491
Kovács T, Cairns NJ, Lantos PL (2001) Olfactory centres in Alzheimer's disease: olfactory bulb is involved in early Braak's stages. Neuroreport 12(2):285–288. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001756-200102120-00021
Arnold SE, Lee EB, Moberg PJ, Stutzbach L, Kazi H, Han LY, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2010) Olfactory epithelium amyloid-β and paired helical filament-tau pathology in Alzheimer disease. Ann Neurol 67(4):462–469. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.21910
Growdon ME, Schultz AP, Dagley AS, Amariglio RE, Hedden T, Rentz DM, Johnson KA, Sperling RA, Albers MW, Marshall GA (2015) Odor identification and Alzheimer disease biomarkers in clinically normal elderly. Neurology 84(21):2153–2160. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000001614
Rahayel S, Frasnelli J, Joubert S (2012) The effect of Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease on olfaction: a meta-analysis. Behav Brain Res 231:60–74
Servello A, Fioretti A, Gualdi G, Di Biasi C, Pittalis A, Sollaku S, Pavaci S, Tortorella F, Fusetti M, Valenti M, Masedu F, Cacciafesta M, Marigliano V, Ettorre E, Pagliarella M (2015) Olfactory dysfunction, olfactory bulb volume and Alzheimer's disease: is there a correlation? A pilot study1. J Alzheimers Dis 48:395–402
Gómez-Isla T, Price JL, McKeel DW Jr, Morris JC, Growdon JH, Hyman BT (1996) Profound loss of layer II entorhinal cortex neurons occurs in very mild Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 16(14):4491–4500
Daulatzai MA (2015) Olfactory dysfunction: its early temporal relationship and neural correlates in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. J Neural Transm 122(10):1475–1497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-015-1404-6
Zola-Morgan S, Squire LR, Amaral DG, Suzuki WA (1989) Lesions of perirhinal and parahippocampal cortex that spare the amygdala and hippocampal formation produce severe memory impairment. J Neurosci 9(12):4355–4370
Zola-Morgan S, Squire LR, Ramus SJ (1994) Severity of memory impairment in monkeys as a function of locus and extent of damage within the medial temporal lobe memory system. Hippocampus 4(4):483–495. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.450040410
Insausti R, Marcos P, Arroyo-Jimenez M, Blaizot X, Martınez-Marcos A (2002) Comparative aspects of the olfactory portion of the entorhinal cortex and its projection to the hippocampus in rodents, nonhuman primates, and the human brain. Brain Res Bull 57:557–560
Braak H, Braak E (1997) Frequency of stages of Alzheimer-related lesions in different age categories. Neurobiol Aging 18(4):351–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0197-4580(97)00056-0
Jessen F, Feyen L, Freymann K, Tepest R, Maier W, Heun R, Schild HH, Scheef L (2006) Volume reduction of the entorhinal cortex in subjective memory impairment. Neurobiol Aging 27(12):1751–1756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.10.010
Striepens N, Scheef L, Wind A, Popp J, Spottke A, Cooper-Mahkorn D, Suliman H, Wagner M, Schild HH, Jessen F (2010) Volume loss of the medial temporal lobe structures in subjective memory impairment. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 29(1):75–81. https://doi.org/10.1159/000264630
Perrotin A, Mormino EC, Madison CM, Hayenga AO, Jagust WJ (2012) Subjective cognition and amyloid deposition imaging: a Pittsburgh compound B positron emission tomography study in normal elderly individuals. Arch Neurol 69(2):223–229. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2011.666
van Harten AC, Visser PJ, Pijnenburg YA, Teunissen CE, Blankenstein MA, Scheltens P, van der Flier WM (2013) Cerebrospinal fluid Aβ42 is the best predictor of clinical progression in patients with subjective complaints. Alzheimers Dement 9(5):481–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2012.08.004
Sohrabi HR, Bates KA, Rodrigues M, Taddei K, Laws SM, Lautenschlager NT, Dhaliwal SS, Johnston AN, Mackay-Sim A, Gandy S, Foster JK, Martins RN (2009) Olfactory dysfunction is associated with subjective memory complaints in community-dwelling elderly individuals. J Alzheimers Dis 17(1):135–142. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2009-1020
Jessen F, Amariglio RE, van Boxtel M, Breteler M, Ceccaldi M, Chetelat G, Dubois B, Dufouil C, Ellis KA, van der Flier WM, Glodzik L, van Harten AC, de Leon MJ, McHugh P, Mielke MM, Molinuevo JL, Mosconi L, Osorio RS, Perrotin A, Petersen RC, Rabin LA, Rami L, Reisberg B, Rentz DM, Sachdev PS, de la Sayette V, Saykin AJ, Scheltens P, Shulman MB, Slavin MJ, Sperling RA, Stewart R, Uspenskaya O, Vellas B, Visser PJ, Wagner M; Subjective Cognitive Decline Initiative (SCD-I) Working Group (2014) A conceptual framework for research on subjective cognitive decline in preclinical Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement 10: 844–852, 6, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2014.01.001
Jessen F, Wolfsgruber S, Wiese B, Bickel H, Mosch E, Kaduszkiewicz H, Pentzek M, Riedel-Heller SG, Luck T, Fuchs A, Weyerer S, Werle J, van den Bussche H, Scherer M, Maier W, Wagner M German Study on Aging, Cognition and Dementia in Primary Care Patients (2014) AD dementia risk in late MCI, in early MCI, and in subjective memory impairment. Alzheimers Dement 10: 76–83
Westervelt HJ, Stern RA, Tremont G (2003) Odor identification deficits in diffuse Lewy body disease. Cogn Behav Neurol 16(2):93–99. https://doi.org/10.1097/00146965-200306000-00002
Rami L, Loy CT, Hailstone J, Warren JD (2007) Odour identification in frontotemporal lobar degeneration. J Neurol 254(4):431–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-006-0379-5
Bacon AW, Bondi MW, Salmon DP, Murphy C (1998) Very early changes in olfactory functioning due to Alzheimer's disease and the role of apolipoprotein E in olfaction. Ann N Y Acad Sci 855(1 OLFACTION AND):723–731. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb10651.x
Graves AB, Bowen J, Rajaram L, McCormick W, McCurry S, Schellenberg G, Larson EB (1999) Impaired olfaction as a marker for cognitive decline interaction with apolipoprotein E ε4 status. Neurology 53: 1480–1487
Wang QS, Tian L, Huang YL, Qin S, He LQ, Zhou JN (2002) Olfactory identification and apolipoprotein E ε4 allele in mild cognitive impairment. Brain Res 951(1):77–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(02)03137-2
Hastings L, Miller M (2003) Influence of environmental toxicants on olfactory function. Neurol Dis Ther 57:575–592
Murphy C, Doty R, Duncan H (2003) Clinical disorders of olfaction. Neurol Dis Ther 57:461–478
Rupp CI, Kurz M, Kemmler G, Mair D, Hausmann A, Hinterhuber H, Fleischhacker WW (2003) Reduced olfactory sensitivity, discrimination, and identification in patients with alcohol dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27:432–439
Schubert CR, Cruickshanks KJ, Klein BE, Klein R, Nondahl DM (2011) Olfactory impairment in older adults: five-year incidence and risk factors. Laryngoscope 121(4):873–878. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.21416
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM
(DOCX 19 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, SJ., Lee, JE., Lee, KS. et al. Comparison of odor identification among amnestic and non-amnestic mild cognitive impairment, subjective cognitive decline, and early Alzheimer’s dementia. Neurol Sci 39, 557–564 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-018-3261-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-018-3261-1