Abstract
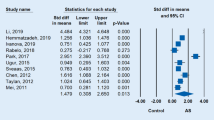
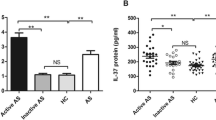
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic, inflammatory, rheumatological disease affecting primarily the sacroiliac joint and vertebral column, with an etiology that remains obscure. Cytokines are soluble proteins that have specific roles in inflammatory response, arranging the interaction between cells of the immune system both in natural and specific immune reactions. This study was planned to evaluate the relation between the level of cytokines and the clinical and laboratory findings of patients with AS compared to healthy subjects. In this study, we demonstrated increased serum levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R), Interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in patients with AS compared with healthy subjects. Only IL-1β levels were not increased in AS patients. We found a correlation between C-reactive protein and IL-6 levels and between erythrocyte sedimentation rate and sIL-2R, IL-6 and TNF-α levels. Only the sIL-2R level was correlated with Bath AS Metrology Index and Bath AS Functional Index. We suggest that sIL-2R, IL-6, and TNF-α may have a role in the pathogenesis of AS and that their serum levels can be used as disease activity parameters and tools for diagnosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banks RE, Whicher T, Thompson D, Bird HA (1998) Investigation of the rheumatic diseases. In: Maddison PJ, Isenberg DA, Woo P, Glass DN (eds) Oxford textbook of rheumatology. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 623–631
Dinarello CA, Moldawer LL (1999) Proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Amgen, Thousand Oaks, CA
Toussirot E, Lafforgue P, Boucraut J et al (1994) Serum levels of IL-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α, soluble interleukin 2 receptor and soluble CD8 in seronegative spondyloarthropathies. Rheumatol Int 13:175–180
Keystone EC, Jaglal S, Shore A (1986) Interleukin 1 and interleukin 2 generation by peripheral blood cells from patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol 13(5):944–947
Dinarello CA (1989) Interleukin-1 and other growth factors. In: Kelly WN et al (eds) Textbook of rheumatology, 3rd edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, PA, pp 285–299
Lipsky PE, Van der Heijde DM, St Clair EW et al (2003) Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-tumor necrosis factor trial in rheumatoid arthritis with Concomitant Therapy Study Group. N Engl J Med 343:1594–1602
Moreland LW, Schiff MH, Baumgartner SW et al (1999) Etanercept theraphy in rheumatoid arthritis. A randomized controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 130:478–486
Rudwaleit M, Listing J, Brandt J et al (2004) Prediction of a major clinical response (BASDAI 50) to tumor necrosis factor alpha blockers in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 63(6):665–670
Keller C, Webb A, Davis J (2003) Cytokines in the seronegative spondyloarthropathies and their modification by TNF blockade: a brief report and literature review. Ann Rheum Dis 62(12):1128–1132
Goei A, Steven MM, Sjef M et al (1985) Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A comparison of the Rome, New York and modified New York criteria in patients with a positive clinical history screening test for ankylosing spondylitis. Br J Rheumatol 24:242–249
Garret S, Jenkinson T et al (1994) A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index. J Rheumatol 21:2286–2291
Cain A, Garret S et al (1994) A new approach to defining functional ability in ankylosing spondylitis. The development of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index. J Rheumatol 21:2281–2285
Kennedy LG et al (1993) Ankylosing spondylitis: the correlation between a new metrology score and radiology. Br J Rheumatol 34:767–770
Vazquez-Del Mercado M et al (2002) Interleukin 1β (IL-1β), IL-10, tumor necrosis factor-α and cellular proliferation index in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patient with ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol 29(3):522–526
Mc Cormack PL, Wellington K (2004) Etanercept: in ankylosing spondylitis. BioDrugs 18(3):199–205 (discussion 206)
Haibel H, Rudwaleit M, Listing J et al (2005) Open label trial of anakinra in active ankylosing spondylitis over 24 weeks. Ann Rheum Dis 64(2):296–298
Gratacos J et al (1994) Serum cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β and IFN-δ) in ankylosing spondylitis: a close correlation between serum IL-6 and disease activity and severity. Br J Rheumatol 33:927–931
Sonel B, Tutkak H, Duzgun N (2002) Serum levels of IL-1beta, TNF-alfa, IL-8 and acute phase proteins in seronegative spondyloarthropathies. Joint Bone Spine 69:463–467
Liu HC, Hsieh KH (1987) Elevated serum interleukin-2 receptor; increased in vitro immunoglobulin synthesis and lack of response to testosterone-enhanced in vitro interleukin-2 production in ankylosing spondylitis. Zhonghua Min Guo Wei Sheng Wu Ji Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 20(1):1–8
Tutuncu ZN et al (1994) Interleukin-6 acute phases reactance and clinical status in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 53:425–428
Claudepierre P, Rymer J-C, Authier F-J et al (1997) A relationship between TGF-β1 or IL-6 plasma levels and clinical features of spondyloarthropathies. Br J Rheumatol 37:400–406
Falkenbach A, Herold M (1998) In ankylosing spondylitis serum interleukin-6 correlates with the degree of mobility restriction, but not with short-term changes in the variables for mobility. Rheumatol Int 18:103–106
Taylor PC, Williams RO, Feldman M (2004) Tumour necrosis factor α as a therapeutic target for immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Curr Opin Biotechnol 15:557–563
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bal, A., Unlu, E., Bahar, G. et al. Comparison of serum IL-1β, sIL-2R, IL-6, and TNF-α levels with disease activity parameters in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol 26, 211–215 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-006-0283-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-006-0283-5