Abstract
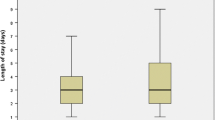
The Rapid Recovery Program (RRP) is an accelerated discharge programme aimed at reducing the length of stay (LOS) and improving patient satisfaction. Its principles are discussed, and our early experience of 847 hip and knee arthroplasty patients described. Three groups were identified: Pre-RRP implementation (Pre-RRP), Post-RRP implementation who did not attend our pre-operative educational Joint Replacement School (JRS) (RRP-JRS) and Post-RRP who did attend JRS (RRP + JRS). Mean LOS (days) for hip arthroplasty was 11 (Pre-RRP), 6.4 (RRP + JRS) and 8.7 (RRP-JRS) (P < 0.05). Mean LOS (days) for knee arthroplasty was 8.5 (Pre-RRP) (P < 0.05), 5.9 (RRP + JRS) and 5.8 (RRP-JRS). RRP reduced LOS and pre-operative education further reduced LOS in hip arthroplasty. We believe these effects are produced by streamlining perioperative processes, education and improving patient experience.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berend KR, Lombardi AV Jr, Mallory TH (2004) Rapid recovery protocol for peri-operative care of total hip and total knee arthroplasty patients. Surg Technol Int 13:239–247
Isaac D, Falode T, Liu P, I’Anson H, Dillow K, Gill P (2005) Accelerated rehabilitation after total knee replacement. Knee 12:346–350
Husted H, Holm G (2006) Fast track in total hip and knee arthroplasty—experiences from Hvidovre University Hospital, Denmark. Injury 37 Suppl 5:S31–S35
Pilot P, Bogie R, Draijer WF, Verburg AD, van Os JJ, Kuipers H (2006) Experience in the first four years of rapid recovery; is it safe? Injury 37(Suppl 5):S37–S40
Husted H, Holm G, Jacobsen S (2008) Predictors of length of stay and patient satisfaction after hip and knee replacement surgery: fast-track experience in 712 patients. Acta Orthop 79:168–173
Lombardi AV Jr, Viacava AJ, Berend KR (2006) Rapid recovery protocols and minimally invasive surgery help achieve high knee flexion. Clin Orthop Relat Res 452:117–122
Steele MK III, McLean MB, Gaunt R, Browning WA (2000) The joint ventures program: improving outcomes and satisfaction in joint surgery patients. J Clin Outcomes Manage 7:28–30
Brunenberg DE, van Steyn MJ, Sluimer JC, Bekebrede LL, Bulstra SK, Joore MA (2005) Joint recovery programme versus usual care: an economic evaluation of a clinical pathway for joint replacement surgery. Med Care 43:1018–1026
Pearson S, Moraw I, Maddern GJ (2000) Clinical pathway management of total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective comparative study. Aust N Z J Surg 70:351–354
Dowsey MM, Kilgour ML, Santamaria NM, Choong PF (1999) Clinical pathways in hip and knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomised controlled study. Med J Aust 170:59–62
Kim S, Losina E, Solomon DH, Wright J, Katz JN (2003) Effectiveness of clinical pathways for total knee and total hip arthroplasty: literature review. J Arthroplasty 18:69–74
Vanhaecht K, Sermeus W, Tuerlinckx G, Witters I, Vandenneucker H, Bellemans J (2005) Development of a clinical pathway for total knee arthroplasty and the effect on length of stay and in-hospital functional outcome. Acta Orthop Belg 71:439–444
Healy WL, Iorio R, Ko J, Appleby D, Lemos DW (2002) Impact of cost reduction programs on short-term patient outcome and hospital cost of total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84-A:348–353
Scranton PE Jr (1999) The cost effectiveness of streamlined care pathways and product standardization in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 14:182–186
Reilly KA, Beard DJ, Barker KL, Dodd CA, Price AJ, Murray DW (2005) Efficacy of an accelerated recovery protocol for Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty—a randomised controlled trial. Knee 12:351–357
McDonald S, Hetrick S, Green S (2004) Pre-operative education for hip or knee replacement. Cochrane Database Syst RevCD003526
Butler GS, Hurley CA, Buchanan KL, Smith-VanHorne J (1996) Prehospital education: effectiveness with total hip replacement surgery patients. Patient Educ Couns 29:189–197
Daltroy LH, Morlino CI, Eaton HM, Poss R, Liang MH (1998) Preoperative education for total hip and knee replacement patients. Arthritis Care Res 11:469–478
Cooil J, Bithell C (1997) Pre-operative education for patients undergoing total hip replacement: a comparison of two methods. Physiother Theory Pract 13:163
Wijgman AJ, Dekkers GH, Waltje E, Krekels T, Arens HJ (1994) No positive effect of preoperative exercise therapy and teaching in patients to be subjected to hip arthroplasty. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 138:949–952
Liang MH, Katz JN, Phillips C, Sledge C, Cats-Baril W (1991) The total hip arthroplasty outcome evaluation form of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Results of a nominal group process. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Task Force on Outcome Studies. J Bone Joint Surg Am 73:639–646
Mitchell M (2003) Patient anxiety and modern elective surgery: a literature review. J Clin Nurs 12:806–815
Crowe J, Henderson J (2003) Pre-arthroplasty rehabilitation is effective in reducing hospital stay. Can J Occup Ther 70:88–96
Coudeyre E, Jardin C, Givron P, Ribinik P, Revel M, Rannou F (2007) Could preoperative rehabilitation modify postoperative outcomes after total hip and knee arthroplasty? Elaboration of French clinical practice guidelines. Ann Readapt Med Phys 50:189–197
Vukomanovic A, Popovic Z, Durovic A, Krstic L (2008) The effects of short-term preoperative physical therapy and education on early functional recovery of patients younger than 70 undergoing total hip arthroplasty. Vojnosanit Pregl 65:291–297
McGregor AH, Rylands H, Owen A, Dore CJ, Hughes SP (2004) Does preoperative hip rehabilitation advice improve recovery and patient satisfaction? J Arthroplasty 19:464–468
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Rapid Recovery Team for their work in the implementation of the project and specifically Sheridan Hanson, Teresa Box and Sheridan Methuen.
Conflict of interest
No funds were received in support of this study. No benefits in any form have been or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gordon, D., Malhas, A., Goubran, A. et al. Implementing the Rapid Recovery Program in primary hip and knee arthroplasty in a UK state run hospital. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 21, 151–158 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-010-0690-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-010-0690-9