Abstract
Background
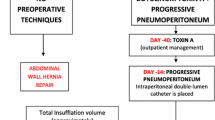
A rarely used technique for enabling closure of large ventral hernias with loss of domain is preoperative progressive pneumoperitoneum (PPP), which uses intermittent insufflation to gradually stretch the contracted abdominal wall muscles, increasing the capacity of the abdominal cavity. This allows the re-introduction of herniated viscera into the abdominal cavity and assists in closure of giant hernias which may otherwise be considered inoperable.
Methods
This was a prospective study assessing 16 patients between 2013 and 2015 with multi-recurrent ventral hernia. All patients were treated preoperatively with both Botulinum Toxin A (BTA) injections to the lateral abdominal wall muscles to confer flaccid paralysis, and short-term PPP to passively expand the abdominal cavity. All patients underwent serial abdominal CT imaging, with pre- and post-treatment circumference measurements of the peritoneal cavity and hernia sac, prior to undergoing operative mesh repair of their hernia.
Results
The mean hernia defect size was 236 cm2, with mean 28 % loss of domain. The mean overall duration of PPP was 6.2 days. The mean gain in abdominal circumference was 4.9 cm (5.6 %) (p 0.002) after BTA and PPP. Fascial closure and mesh hernia repair were performed in all 16 patients, with no patients suffering from postoperative abdominal hypertension, ventilatory impairment, or wound dehiscence. There are no hernia recurrences to date. Eight patients (50 %) experienced PPP-related complications, consisting of subcutaneous emphysema, pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, pneumocardium, and metabolic acidosis. No complication required intervention.
Conclusions
PPP is a useful adjunct in the repair of complex ventral hernia. It passively expands the abdominal cavity, allowing viscera to re-establish right of domain. At the same time, it helps to minimize the risks of postoperative abdominal compartment syndrome and the sequelae of fascial closure under tension. However, its benefits must be carefully weighed with the risk of serious complications, such as infection, perforation, pneumothorax, and pneumomediastinum.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moreno IG (1947) Chronic eventrations and large hernias. Surgery 22:945–953
Farooque F, Jacombs A, Roussos R, Read JW, Dardano AN, Edye M, Ibrahim N (2016) Preoperative abdominal muscle elongation with botulinum toxin A for complex incisional ventral hernia repair. ANZ J Surg 86:79–83
Elstner KE, Jacombs ASW, Read JW, Rodriguez O, Edye M, Cosman PH, Dardano AN, Zea A, Boesel T, Mikami DJ, Craft C, Ibrahim N (2016) Laparoscopic repair of complex ventral hernia facilitated by pre-operative chemical component relaxation using botulinum toxin A. Hernia 20:209–219. doi:10.1007/s10029-016-1478-6
Elstner KE, Read JW, Rodriguez-Acevedo O, Cosman PH, Dardano AN, Jacombs ASW, Edye M, Zea A, Boesel T, Mikami DJ, Ibrahim N (2016) Pre-operative chemical component relaxation using botulinum toxin A: enabling laparoscopic repair of complex ventral hernia. Surg Endosc. doi:10.1007/s00464-016-5030-7 (Epub June 2016)
Mayagoitia JC, Suarez D, Arenas JC, Diaz de Leon V (2006) Preoperative progressive pneumoperitoneum in patients with abdominal-wall hernias. Hernia 10:213–217
Sabbagh C, Dumont F, Robert B, Badaoui R, Verhaeghe P, Regimbeau JM (2011) Peritoneal volume is predictive of tension-free fascia closure of large incisional hernias with loss of domain: a prospective study. Hernia 15:559–565
Raynor RW, Guercio LRM (1989) The place for pneumoperitoneum in the repair of massive hernia. World J Surg 13:581–585
Oprea V, Matei O, Gheorghescu D, Leuca D, Buia F, Rosianu M, Dinca M (2014) Progressive preoperative pneumoperitoneum (PPP) as an adjunct for surgery of hernias with loss of domain. Chirugia 109:664–669
Sabbagh C, Dumont F, Fuks D, Yzet T, Verhaeghe P, Regimbeau JM (2012) Progressive preoperative pneumoperitoneum preparation (the Goni Moreno protocol) prior to large incisional hernia surgery: volumetric, respiratory and clinical impacts. A prospective study. Hernia 16:33–40
Sanders DL, Kingsnorth AN (2012) The modern management of incisional hernias. BMJ 344:37–42
Kingsnorth AN, Sivarajasingham N, Wong S, Butler M (2004) Open mesh repair of incisional hernias with significant loss of domain. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 86:363–366
McAdory RS, Cobb WS, Carbonell AM (2009) Progressive preoperative pneumoperitoneum for hernias with loss of domain. Am Surg 75:504–509
Lopez Sanclemente MC, Robres J, Lopez Cano M, Barri J, Lozoya R, Lopez S, Vasco MA, Buqueras MC, Subirana H, Jorba R (2013) Progressive preoperative pneumoperitoneum in patients with giant hernias of the abdominal wall. Cir Esp 91:444–449
Caldironi MW, Romano M, Bozza F, Pluchinotta AM, Pelizzo MR, Toniato A, Ranzato R (1990) Progressive pneumoperitoneum in the management of giant incisional hernias: a study of 41 patients. BJS 77:306–308
Quraishi AHM, Borkar MM, Mastud MM, Jannawar GG (2013) Pre-operative progressive pneumoperitoneum for repair of a large incisional hernia. Updates Surg 65:165–168
Murr MM, Mason EE, Scott DH (1994) The use of pneumoperitoneum in the repair of giant hernias. Obes Surg 4:323–327
Willis S, Schumpelick V (2000) Use of progressive pneumoperitoneum in the repair of giant hernias. Hernia 4:105–111
Raynor RW, Del Guercio LRM (1985) Update on the use of preoperative pneumoperitoneum prior to the repair of large hernias of the abdominal wall. Surg Gynecol Obstet 161:367–371
Piskin T, Aydin C, Barut B, Dirican A, Kayaalp C (2010) Preoperative progressive pneumoperitoneum for giant inguinal hernias. Ann Saudi Med 30:317–320
Van Geffen HJ, Simmermacher RK (2005) Incisional hernia repair: abdominoplasty, tissue expansion, and methods of augmentation. World J Surg 29:1080–1085
Connolly DP, Perri FR (1969) Giant hernias managed by pneumoperitoneum. JAMA 209:71–74
Koontz AR (1958) Hernias that have forfeited the right of domicile. South Med J 51:165–168
Hamer DB, Duthie HL (1972) Pneumoperitoneum in the management of abdominal incisional hernia. BJS 59:372–375
Wadhera S, Khetan M, Bhatia P, John S, Bindal V, Mayyja A, Solecki R, Szura M, Pasternak A, Matyja M, Kalhan S, Huntington C, Augenstein V, Blair L, Cox T, Prasad T, Matthews B, Kercher K, Heniford BT, Elgamal A, Yampolski I, Greif F, Bustos-Jimenez M, Tamayo-Lopez MJ, Martin-Cartes JA, Patiti M, Mariani E, Stella P, Garcia-Pastor P, Carbonell-Tatay F, Cortes V, Pamies-Guilabert J, Renard Y, Lardiere-Deguelte S, Appere F, Kianmanesh R, Palot JP (2015) Incisional hernia: difficult cases 1. Hernia 19(Suppl 1):S97. doi:10.1007/BF03355333
Dumont F, Fuks D, Verhaeghe P, Brehant O, Sabbagh C, Riboulot M, Yzet T, Regimbeau JM (2009) Progressive pneumoperitoneum increases the length of abdominal muscles. Hernia 13:183–187
Astudillo R, Merrell R, Sanchez J, Olmedo S (1986) Ventral herniorrhaphy aided by pneumoperitoneum. Arch Surg 121:935–936
Coehlo JCU, Brenner AS, Freitas AT, Campos ACL, Wiederkehr JC (1993) Progressive preoperative pneumoperitoneum in the repair of large abdominal hernias. Eur J Surg 159:339–341
Johnson WC (1972) Preoperative progressive pneumoperitoneum in preparation for repair of large hernias of the abdominal wall. Am J Surg 124:63–68
Dasher WA, Black JPM, Weiss W, Bogen E (1954) Air embolism complicating pneumoperitoneum: a review. Am Rev Tuberc 69:396–405
Jernstrom P (1951) Air embolism during peritoneoscopy. Am J Clin Path 21:573
Taura P, Lopez A, Lacy AM, Anglada T, Beltran J, Fernandez-Cruz L, Targarona E, Garcia-Valdecasas JC, Marin JL (1998) Prolonged pneumoperitoneum at 15 mmHg causes lactic acidosis. Surg Endosc 12:198–201
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
John Read declares conflict of interest related to the submitted work as he receives financial remuneration from Medicare as a radiologist. Kristen Elstner, Omar Rodriguez-Acevedo, Kevin Ho-Shon, John Magnussen, and Nabeel Ibrahim declare no conflict of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elstner, K.E., Read, J.W., Rodriguez-Acevedo, O. et al. Preoperative progressive pneumoperitoneum complementing chemical component relaxation in complex ventral hernia repair. Surg Endosc 31, 1914–1922 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-5194-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-5194-1