Abstract
Background
Laparoscopically assisted sigmoid resection has become an accepted method for treating uncomplicated diverticulitis. This prospective study aimed to compare the results of laparoscopic sigmoid resection for uncomplicated and complicated sigmoid diverticular disease used to check the indication for the complicated stages of diverticulitis.
Methods
All patients who underwent laparoscopic resection for sigmoid diverticulitis at the authors’ hospital between 1999 and 2005 were divided into two groups: group 1 (uncomplicated diverticular disease) and group 2 (complicated diverticular disease). The exclusion criteria specified generalized peritonitis, signs of sepsis, and extensive previous abdominal surgery.
Results
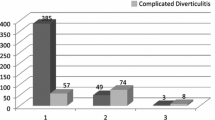
Of the 203 patients (108 men and 95 women) who underwent laparoscopically assisted resection during the examination period, 112 were assigned to group 1 and 91 to group 2. Differences in favor of group 1 were found for the duration of surgery (154 vs 166 min), the conversion rate (1.8% vs 9.9%), the postoperative wound infections (2.7% vs 13.2%), and the postoperative hospitalization period (12.3 ± 3.9 vs 15.0 ± 5.6 days). No significant differences were seen in any other areas such as completion of nutritional buildup (4.6 vs 5.0 days) or time until the first postoperative bowel movement (2.8 vs 3.3 days). Total postoperative morbidity (16.1% vs 26.4%; p = 0.10) tended to be increased in group 2, but this difference was not statistically significant.
Conclusions
Laparoscopic sigmoid resection can be performed for patients who have complicated diverticulitis without significantly increasing their overall morbidity. This group of patients could benefit from the advantages of the minimally invasive procedure despite a longer operating time and a higher conversion rate.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouillot JL, Aouad K, Badawy A, Alamowitch B, Alexandre HJ (1998) Elective laparoscopic-assisted colectomy for diverticular disease: a prospective study in 50 patients. Surg Endosc 12: 1393–1396
Chautems RC, Ambrosetti P, Ludwig A, Mermillod B, Morel P, Soravia C (2002) Long-term follow-up after first acute episode of sigmoid diverticulitis: is surgery mandatory? A prospective study of 118 patients. Dis Colon Rectum 45: 962–966
Farmakis N, Tudor RG, Keighley RG (1994) The 5-year natural history of complicated diverticular disease. Br J Surg 81: 733–735
Franklin Jr ME, Dorman JP, Jacobs M, Plasencia G (1997) Is laparoscopic surgery applicable to complicated colonic diverticular disease? Surg Endosc 11: 1021–1025
Germer CT, Buhr HJ (2002) Sigmoid diverticulitis: surgical indications and timing. Chirurg 73: 681–689
Gonzales R, Smith CD, Mattar SG, Venkatesh KR, Mason E, Duncan T, Wilson R, Miller J, Ramshaw BJ (2004) Laparoscopic vs open resection for the treatment of diverticular disease. Surg Endosc 18: 276–280
Hansen O, Stock W (1999) Prophylaktische Operation bei der Divertikelkrankheit des Kolons: Stufenkonzept durch exakte Stadieneinteilung. Langenbecks Arch Chir Suppl II: 1257
Hinchey EJ, Schaal PG, Richards GK (1978) Treatment of perforated diverticular disease of the colon. Adv Surg 12: 85–109
Jacobs M, Verdeja JC, Goldstein HS (1991) Minimally invasive colon resection (laparoscopic colectomy). Surg Laparosc Endosc 1: 144–150
Jun S, Stollmann N (2002) Epidemiology of diverticular disease. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 16: 529–542
Kehlet H, Wilmore DW (2002) Multimodal strategies to improve surgical outcome. Am J Surg 183: 630–641
Köckerling F, Schneider C, Reymond MA, Scheidbach H, Scheuerlein H, Konradt J, Bruch HP, Zornig C, Köhler L, Bärlehner L, Kuthe A, Szinicz G, Richter HA, Hohenberger W (1999) Laparoscopic resection of sigmoid diverticulitis: results of a multicenter study. Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery Study Group. Surg Endosc 13: 567–571
Köhler L (1999) Endoscopic surgery: what has passed the test? World J Surg 23: 816–824
Köhler L, Sauerland S, Neugebauer E (1999) Diagnosis and treatment of diverticular disease: results of a consensus development conference. The Scientific Committee os European Association for Endoscopic Surgery. Surg Endosc 13: 430–436
Le Moine MC, Fabre JM, Vacher C, Navarro F, Picot MC, Domergue J (2003) Factors and consequences of conversion in laparoscopic sigmoidectomy for diverticular disease. Br J Surg 90: 232–236
Marusch F, Gastinger I, Schneider C, Scheidbach H, Konradt J, Bruch HP, Köhler L, Bärlehner E, Köckerling F, Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery Study Group (LCSSG) (2001) Importance of conversion for results obtained with laparoscopic colorectal surgery. Dis Colon Rectum 44: 207–214
Parks TG (1975) Natural history of diverticular disease of the colon. Clin Gastroenterol 4: 53–69
Rose J, Schneider C, Yildirim C, Geers P, Scheidbach H, Köckerling F (2004) Complications in laparoscopic colorectal surgery: results of a multicentre trial. Tech Coloproctol 8: s25–s28
Scheidbach H, Schneider C, Rose J, Konradt J, Gross E, Bärlehner E, Pross M, Schmidt U, Köckerling F, Lippert H (2004) Laparoscopic approach to treatment of sigmoid diverticulitis: changes in the spectrum of indications and results of a prospective, multicenter study on 1,545 patients. Dis Colon Rectum 47: 1883–1888
Schiedeck TH, Schwandner O, Bruch HP (1998) Laparoscopic sigmoid resection in diverticulitis. Chirurg 69: 846–853
Schwandner O, Farke S, Bruch HP (2005) Laparoscopic colectomy for diverticulitis is not associated with increased morbidity when compared with nondiverticular disease. Int J Colorectal Dis 20: 165–172
Schwandner O, Farke S, Fischer F, Eckmann C, Schiedeck TH, Bruch HP (2004) Laparoscopic colectomy for recurrent and complicated diverticulitis: a prospective study of 396 patients. Langenbecks Arch Surg 389: 97–103
Schwandner O, Schiedeck TH, Bruch HP (1999) The role of conversion in laparoscopic colorectal surgery: do predictive factors exist? Surg Endosc 13: 151–156
Siriser F (2004) Laparoscopic-assisted colectomy for diverticularsigmoiditis: a single-surgeon prospective study of 65 patients. Surg Endosc 13: 811–813
Trebuchet G, Lechaux D, Lecalve JL (2002) Laparoscopic left colon resection for diverticular disease. Surg Endosc 16: 18–21
Vargas HD, Ramirez RY, Hoffman GC, Hubbard GW, Gould RJ, Wohlgemuth SD, Ruffin WK, Hatter JE, Kolm P (2000) Defining the role of laparoscopic-assisted sigmoid colectomy for diverticulitis. Dis Colon Rectum 43: 1726–1731
Wilmore DW, Kehlet H (2001) Management of patients in fast track surgery. BMJ 322: 473–476
Wong WD, Wexner SD, Lowry A, Vernava A, Burnstein M, Denstman F, Fazio V, Kerner B, Moore R, Oliver G, Peters W, Ross T, Senatore P, Simmang C (2000) Practice parameters for the treatment of sigmoid diverticulitis: supporting documentation. Dis Colon Rectum 43: 290–297
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reissfelder, C., Buhr, H.J. & Ritz, JP. Can laparoscopically assisted sigmoid resection provide uncomplicated management even in cases of complicated diverticulitis?. Surg Endosc 20, 1055–1059 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-005-0529-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-005-0529-3