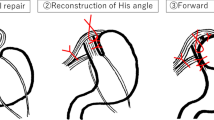
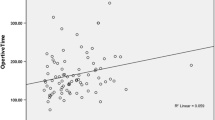
Abstract
From January 1994 to December 2004, 118 patients with recurrent gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) after fundoplication underwent laparoscopic redo Nissen fundoplication. The patients ranged in age from 6 months to 19 years (mean, 7 years), and weighed from 6.4 to 85 kg. Of the 118 patients, 64 had previous open fundoplications, 53 had previous laparoscopic fundoplications, and 19 had more than one previous fundoplication. All the procedures had been successfully completed laparoscopically. The average operative time was 100 min. The intraoperative complication rate was 1.1%. The average time to full feeding was 1.8 days, and the average hospital stay was 2.2 days. The postoperative complication rate was 3.6%. The wrap failure rate during an average follow-up period of 48 months was 6%. Laparoscopic redo Nissen fundoplication for a failed antireflux procedure is a safe and effective procedure. It has the same benefits as a primary laparoscopic Nissen for GERD, with low morbidity and a quicker recovery. Early follow-up evaluation suggests that the long-term outcome is superior to that associated with open redo fundoplication.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collins JB, Georgeson KE, Vicente Y, Hardin WD (1995) Comparison of open and laparoscopic gastrostomy and fundoplication in 120 patients. J Pediatr Surg 30: 1065–1071
Espisito C, Becmur F, Centon A (2003) Laparoscopic reoperation following unsuccessful antireflux surgery in childhood. Semin Laparosc Surg 9: 177–179
Floch NR, Hinder RA, Klinger PJ, Branton SA, Seelig MH, Banner T, Filipi CJ (1999) Is laparoscopic surgery for failed antireflux surgery feasible? Arch Surg 134: 733–737
Fonkalsrud EW, Ashcraft KW, Coran AG, Ellis DG, Grosfeld JL, Tunnell WP, Weber TR (1998) Surgical treatment of gastroesophageal reflux in children: a combined hospital study of 7,467 patients. Pediatrics 101: 419–422
Fonkalsrud EW, Berquist W, Vargas J, et al. (1987) Surgical treatment of gastroesophageal reflux syndrome in infants and children. Am J Surg 154: 11–18
Hinder RA, Filipi CJ, Wetscher G, Neary P, DeMeester TR, Perdikis G (1994) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication is an effective treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Surg 220: 472–481
Jolley SG, Ide Smith E, Tunnel WP (1987) Protective antireflux operation with feeding gastrostomy: experience in children. Ann Surg 201: 736–739
Longis B, Grousseau D, Alain JL, Terrier G (1996) Laparoscopic fundoplication in children: our first 30 cases. J Laparoendosc Surg 6(Suppl 1): s21–s29
Papasavas PK, Yeaney WW, Landreneau RJ (2004) Reoperative laparoscopic fundoplication for the treatment of failed fundoplication. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 128: 509–516
Rosemurgy AS, Arnaoutakis DJ, Thometz DP, Biaitic O, Giarelli NB, Bloomston M, Goldin SG, Albrink MH (2004) Reoperation fundoplications are effective treatment for dysphagia and recurrent gastroesophageal reflux. Am Surg 70: 1061–1087
Rothenberg SS (1997) Experience with laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication in infants and children less than 10 kg. Presented at the Society of American Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Surgeons, San Diego, CA, March 1997
Rothenberg SS (2004) First decades experience with laparoscopic fundoplication in infants and children. J Pediatr Surg 40: 142–147
Tan S, Wulkan ML (2002) Minimally invasive surgical techniques in reoperative surgery for gastroesophageal reflux disease in infants and children. Am Surg 68: 989–992
Turnage RH, Oldham KT, Coran AG, Blane LE (1989) Late results of fundoplication for gastroesphageal reflux in infants and children. Surgery 105: 457–463
Weerts JM, Dallemagne B, Hamoir E, Demarche M, Markiwicz S, Jehaes C, Lombard R, Demoulu JL, Etienne M, Ferron PE (1993) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: detailed analysis of 132 patients. Surg Laparosc Endosc 3: 359–364
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rothenberg, S.S. Laparoscopic redo Nissen fundoplication in infants and children. Surg Endosc 20, 1518–1520 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-005-0123-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-005-0123-8