Abstract
Background
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can be overlooked as the cause of chronic cough (CC) when typical gastrointestinal symptoms are absent or minimal. We analyzed the outcomes of Nissen fundoplication (NF) for patients who failed medical therapy for CC attributable only to GERD (G-CC). We performed a prospective outcome evaluation of 21 consecutive patients with G-CC undergoing NF from 1997 to 2000 at a tertiary care university hospital.
Materials and Methods
Twenty-one patients without prior antireflux surgeries had G-CC diagnosed by a clinical profile and 24-h pH monitoring showing a cough-reflux correlation. Respiratory symptoms alone were present in 53% of patients. NF was performed when G-CC persisted despite intensive medical therapy, including an antireflux diet. Preoperatively, all patients underwent 24-h pH monitoring, esophageal manometry, barium swallow, gastric emptying study, bronchoscopy, and upper endoscopy. NF was utilized in all cases, laparoscopically in 18. Before and after surgery, patients graded their cough severity using the Adverse Cough Outcome Survey (ACOS). Quality of life was measured using the Sickness Impact Profile (SIP).
Results
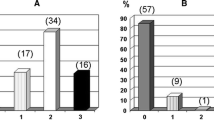
Postoperatively, 18 patients (86%) reported an improvement of their cough. G-CC considerably improved in 16/21 patients (76%), with complete resolution in 13 patients (62%). Mild to moderate improvement was found in 2 patients (10%). Patient-reported cough severity (ACOS) and quality of life (SIP) both significantly improved early (6–12 weeks) postoperatively and persisted during the long-term (1 year) follow-up. The average hospital length of stay was 1.78±0.2 (1–4) days for the laparoscopic (n=18) and 6.3±1.2 (4–8) days for the open surgery (n=3) groups.
Conclusion
Twenty-four-hour esophageal pH monitoring is a valuable tool for preoperative cough—reflux correlation. Antireflux surgery is effective in carefully selected patients whose refractory CC is attributable only to GERD. NF controls the severity of cough while improving the quality of life. Outcomes are further enhanced using laparoscopic procedures with shorter hospital stays.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Allen CJ, Anvari M (1998) Gastro-oesophageal reflux related cough and its response to laparoscopic fundoplication. Thorax 53: 963–968
DeMeester TR, Bonavina L, Iascone C, Courtney JV, Skinner DB (1990) Chronic respiratory symptoms and occult gastroesophageal reflux: a prospective clinical study and results of surgical therapy. Ann Surg 211: 337–345
French CL, Irwin RS, Curley FJ, Krikorian CJ (1998) The impact of chronic cough on quality of life. Arch Intern Med 158: 1657–1661
Hunter JG, Trus TL, Branum GD, Waring JP, Wood WC (1996) A physiologic approach to laparoscopic fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Surg 223: 673–687
Ing AJ (1997) Cough and gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Med 103: 91S-96S
Irwin RS, Boulet LP, Cloutier MM, Fuller R, Gold PM, Hoffstein V, Ing AJ, McCool FD, O’Byrne P, Poe RH, Prakash UB, Pratter MR, Rubin BK (1998) Managing cough as a defence mechanism and as a symptom. A consensus panel report of the American College of Chest Physicians. Chest 114: 133S-181S
Irwin RS, Curley FJ, French CL (1990) Chronic cough. The spectrum and frequency of causes, key components of the diagnostic evaluation, and outcome of specific therapy. Am Rev Respir Dis 141: 640–647
Irwin RS, French CL, Curley FJ, Zawacki JK, Bennett FM (1993) Chronic cough due to gastroesophageal reflux. Clinical, diagnostic, and pathogenetic aspects. Chest 104: 1511–1517
Irwin RS, Madison JM (2000) Anatomical diagnostic protocol in evaluating chronic cough with specific reference to gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Med 108: 126S-130S
Irwin RS, Madison JM (2000) The diagnosis and treatment of cough. N Engl J Med 343: 1715–1721
Irwin RS, Richter JE (2000) Gastroesophageal reflux and chronic cough. Am J Gastroenterol 95: S9-S14
Irwin RS, Zawacki JK (1999) Accurately diagnosing and successfully treating chronic cough due to gastroesophageal reflux disease can be difficult. Am J Gastroenterol 94: 3095–3098
Irwin RS, Zawacki JK, Curley FJ, French CL, Hoffman PJ (1989) Chronic cough as the sole presenting manifestation of gastroesophageal reflux. Am Rev Respir Dis 40: 1294–1300
Johnson WE, Hagen JA, DeMeester TR, Kauer WKH, Ritter MP, Peters JH, Brenner CG (1996) Outcome of respiratory symptoms after antireflux surgery on patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Arch Surg 131: 489–492
Patti MG, Arcerito M, Tamburini A, Diener U, Feo CV, Safadi B, Fisichella P, Way LW (2000) Effects of laparoscopic fundoplication on gastroesophageal reflux disease-induced respiratory symptoms. J Gastrointest Surg 4: 143–149
So JBY, Zeitel SM, Rattner DW (1998) Outcome of atypical symptoms attributed to gastroesophageal reflux treated by laparoscopic fundoplication. Surgery 124: 28–32
Tobin RW, Pope CE II, Pellegrini CA, Emond MJ, Sillery J, Raghu G (1998) Increased prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 158: 1804–1808
Wetscher GJ, Glaser K, Hinder RA, Perdikis G, Klingler A, Pointner R (1997) Respiratory symptoms in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease following medical therapy and following antireflux surgery. Am J Surg 174: 639–643
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Novitsky, Y.W., Zawacki, J.K., Irwin, R.S. et al. Chronic cough due to gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Endosc 16, 567–571 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-001-8328-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-001-8328-y