Abstract
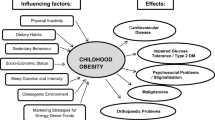
We investigated the prevalence of overweight and obesity in German schoolchildren and analyzed determinants of overweight. In the context of a randomized intervention study, a baseline cross-sectional assessment was carried out in 2006. During a physical examination, height, weight, skin fold thickness, and upper arm and waist circumferences were measured according to a standardized protocol among 1.079 children aged 6–9 years. Overweight and obesity were classified according to the definitions of the International Obesity Task Force. Parents completed a questionnaire on potential determinants of overweight. Logistic regression models were calculated for determinants of overweight and obesity. The prevalence of overweight was 16.5% in boys and 17.3% in girls and of obesity 3.5% and 3.6%, respectively. Migration (29.4 %) was correlated with overweight and obesity. In particular, among boys with migration background, overweight (24.0%) and obesity (6.6%) were highly prevalent. Higher obesity prevalence was associated with maternal smoking during pregnancy, parental overweight, and low parental education. Indicators for physical inactivity such as watching television more than 1 h per weekday, participation in club sports less than once a week, consumption of sweetened drinks (≥3 times per week), and skipping breakfast before school were associated with childhood obesity. Our results provide further evidence that parental factors such as migration background and education are strongly associated with body mass of the offspring. Physically inactive children with regular consumption of sweetened drinks and no breakfast were prone to be overweight or obese. Changes of these lifestyle factors as targets of interventions are promising to prevent childhood obesity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen RE, Crespo CJ, Bartlett SJ et al (1998) Relationship of physical activity and television watching with body weight and level of fatness among children: results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. JAMA 279:938–942
Brussaard JH, Erp-Baart MA, Brants HA et al (2001) Nutrition and health among migrants in The Netherlands. Public Health Nutr 4:659–664
Christakis NA, Fowler JH (2007) The spread of obesity in a large social network over 32 years. N Engl J Med 357:370–379
Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH (2000) Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ 320:1240–1243
Danielzik S, Czerwinski-Mast M, Langnase K et al (2004) Parental overweight, socioeconomic status and high birth weight are the major determinants of overweight and obesity in 5–7 y-old children: baseline data of the Kiel Obesity Prevention Study (KOPS). Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 28:1494–1502
Danielzik S, Pust S, Muller MJ (2007) School-based interventions to prevent overweight and obesity in prepubertal children: process and 4-years outcome evaluation of the Kiel Obesity Prevention Study (KOPS). Acta Paediatr Suppl 96:19–25
Davies PS, Eisenmann JC (2006) Waist circumference percentiles for 7–15-year-old Australian children. Acta Paediatr 95:1017
Ebbeling CB, Pawlak DB, Ludwig DS (2002) Childhood obesity: public-health crisis, common sense cure. Lancet 360:473–482
Engeland A, Bjorge T, Tverdal A, Sogaard AJ (2004) Obesity in adolescence and adulthood and the risk of adult mortality. Epidemiology 15:79–85
Fredriks AM, Van Buuren S, Fekkes M et al (2005) Are age references for waist circumference, hip circumference and waist–hip ratio in Dutch children useful in clinical practice? Eur J Pediatr 164:216–222
Hatipoglu N, Ozturk A, Mazicioglu MM et al (2007) Waist circumference percentiles for 7- to 17-year-old Turkish children and adolescents. Eur J Pediatr 167:383–389
Herpertz-Dahlmann B, Geller F, Bohle C et al (2003) Secular trends in body mass index measurements in preschool children from the City of Aachen, Germany. Eur J Pediatr 162:104–109
Hosper K, Klazinga NS, Stronks K (2007) Acculturation does not necessarily lead to increased physical activity during leisure time: a cross-sectional study among Turkish young people in the Netherlands. BMC Public Health 7:230
James J, Thomas P, Cavan D, Kerr D (2004) Preventing childhood obesity by reducing consumption of carbonated drinks: cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ 328:1237
Kalies H, Lenz J, von Kries R (2002) Prevalence of overweight and obesity and trends in body mass index in German pre-school children, 1982–1997. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 26:1211–1217
Kleiser C, Schaffrath RA, Mensink GB et al (2009) Potential determinants of obesity among children and adolescents in Germany: results from the cross-sectional KiGGS Study. BMC Public Health 9:46
Kromeyer-Hauschild K, Wabitsch M, Kunze D et al (2001) Percentilen für den Body-mass-Index für das Kindes und Jugendalter unter Heranziehung verschiedener deutscher Stichproben. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd 149:807–818
Kuepper-Nybelen J, Lamerz A, Bruning N et al (2005) Major differences in prevalence of overweight according to nationality in preschool children living in Germany: determinants and public health implications. Arch Dis Child 90:359–363
Kurth BM, Schaffrath RA (2007) [The prevalence of overweight and obese children and adolescents living in Germany. Results of the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Children and Adolescents (KiGGS)]. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 50:736–743
Lamerz A, Kuepper-Nybelen J, Wehle C et al (2005) Social class, parental education, and obesity prevalence in a study of six-year-old children in Germany. Int J Obes (Lond) 29:373–380
Lampert T, Sygusch R, Schlack R (2007) [Use of electronic media in adolescence. Results of the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Children and Adolescents (KiGGS)]. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 50:643–652
Langnase K, Mast M, Muller MJ (2002) Social class differences in overweight of prepubertal children in northwest Germany. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 26:566–572
Leary SD, Smith GD, Rogers IS et al (2006) Smoking during pregnancy and offspring fat and lean mass in childhood. Obesity (Silver Spring) 14:2284–2293
Liese AD, Hirsch T, von Mutius E, Weiland SK (2006) Burden of overweight in Germany: prevalence differences between former East and West German children. Eur J Public Health 16:526–531
Lobstein T, Frelut ML (2003) Prevalence of overweight among children in Europe. Obes Rev 4:195–200
Maffeis C (2000) Aetiology of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents. Eur J Pediatr 159(Suppl 1):S35–S44
Malik VS, Schulze MB, Hu FB (2006) Intake of sugar-sweetened beverages and weight gain: a systematic review. Am J Clin Nutr 84:274–288
McCarthy HD, Jarrett KV, Crawley HF (2001) The development of waist circumference percentiles in British children aged 5.0–16.9 y. Eur J Clin Nutr 55:902–907
Muller MJ, Asbeck I, Mast M et al (2001) Prevention of obesity—more than an intention. Concept and first results of the Kiel Obesity Prevention Study (KOPS). Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 25(Suppl 1):S66–S74
Muller MJ, Danielzik S (2007) Childhood overweight: is there need for a new societal approach to the obesity epidemic? Obes Rev 8:87–90
Must A, Anderson SE (2006) Body mass index in children and adolescents: considerations for population-based applications. Int J Obes (Lond) 30:590–594
Nagel G, Rapp K, Wabitsch M et al (2008) Prevalence and cluster of cardiometabolic biomarkers in overweight and obese schoolchildren: results from a large survey in southwest Germany. Clin Chem 54:317–325
Nicklas TA, Yang SJ, Baranowski T et al (2003) Eating patterns and obesity in children. The Bogalusa Heart Study. Am J Prev Med 25:9–16
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR et al (2006) Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA 295:1549–1555
Ohrig E, Geiss HC, Haas GM, Schwandt P (2001) The Prevention Education Program (PEP) Nuremberg: design and baseline data of a family oriented intervention study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 25(Suppl 1):S89–S92
Ong KK, Ahmed ML, Emmett PM et al (2000) Association between postnatal catch-up growth and obesity in childhood: prospective cohort study. BMJ 320:967–971
Owen CG, Martin RM, Whincup PH et al (2005) The effect of breastfeeding on mean body mass index throughout life: a quantitative review of published and unpublished observational evidence. Am J Clin Nutr 82:1298–1307
Padez C, Fernandes T, Mourao I et al (2004) Prevalence of overweight and obesity in 7–9-year-old Portuguese children: trends in body mass index from 1970–2002. Am J Hum Biol 16:670–678
Power C, Jefferis BJ (2002) Fetal environment and subsequent obesity: a study of maternal smoking. Int J Epidemiol 31:413–419
Prentice AM, Jebb SA (2003) Fast foods, energy density and obesity: a possible mechanistic link. Obes Rev 4:187–194
Rampersaud GC, Pereira MA, Girard BL et al (2005) Breakfast habits, nutritional status, body weight, and academic performance in children and adolescents. J Am Diet Assoc 105:743–760
Rapp K, Schick KH, Bode H, Weiland SK (2005) Type of kindergarten and other potential determinants of overweight in pre-school children. Public Health Nutr 8:642–649
Reilly JJ, Armstrong J, Dorosty AR et al (2005) Early life risk factors for obesity in childhood: cohort study. BMJ 330:1357
Robinson TN (1999) Reducing children's television viewing to prevent obesity: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 282:1561–1567
Stolzenberg H, Kahl H, Bergmann KE (2007) [Body measurements of children and adolescents in Germany. Results of the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Children and Adolescents (KiGGS)]. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 50:659–669
Summerbell CD, Waters E, Edmunds LD et al (2005) Interventions for preventing obesity in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (3):CD001871
Toschke AM, Martin RM, von Kries R et al (2007) Infant feeding method and obesity: body mass index and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry measurements at 9–10 y of age from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC). Am J Clin Nutr 85:1578–1585
Voigt M, Schneider KT, Jahrig K (1996) Analysis of a 1992 birth sample in Germany. 1: new percentile values of the body weight of newborn infants. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd 56:550–558
von Kries R, Toschke AM, Koletzko B, Slikker W Jr (2002) Maternal smoking during pregnancy and childhood obesity. Am J Epidemiol 156:954–961
Wabitsch M (2000) Overweight and obesity in European children: definition and diagnostic procedures, risk factors and consequences for later health outcome. Eur J Pediatr 159(Suppl 1):S8–S13
Wang Y (2001) Cross-national comparison of childhood obesity: the epidemic and the relationship between obesity and socioeconomic status. Int J Epidemiol 30:1129–1136
Will B, Zeeb H, Baune BT (2005) Overweight and obesity at school entry among migrant and German children: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 5:45
Yach D, Stuckler D, Brownell KD (2006) Epidemiologic and economic consequences of the global epidemics of obesity and diabetes. Nat Med 12:62–66
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the participating children as well as their parents and the teachers. The authors thank all members of the study team for their excellent work.
The study has been funded by the Landesstiftung Baden-Württemberg, Stuttgart.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Stephan K. Weiland (deceased).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagel, G., Wabitsch, M., Galm, C. et al. Determinants of obesity in the Ulm Research on Metabolism, Exercise and Lifestyle in Children (URMEL-ICE). Eur J Pediatr 168, 1259–1267 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-009-1016-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-009-1016-y