Abstract
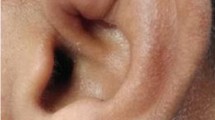
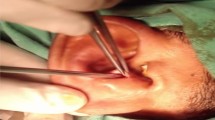
The aims of the article were to study the clinical characteristic of patients with pseudocysts and to compare different common modalities of treatment and introduce the concept of observation in pseudocyst management. Twenty-eight patients were diagnosed with pseudocyst of the auricle between June 2009 and June 2011 in a medical college hospital. The patients were divided into four groups each of seven patients on the basis of primary treatment offered. Four primary treatments offered were simple aspiration, aspiration with intralesional steroid, incision and drainage with removal of anterior cartilage leaflet with buttoning, and lastly, simple observation and reassurance. All 28 patients were male with involvement of right side more than left and no one had bilateral involvement. Adults in the age group of 30–40 were commonly affected. Most of the patients had history of significant trauma by security forces. Most common site of involvement was scaphoid and triangular fossa. The best form of treatment with minimum recurrence was incision and drainage with removal of anterior cartilage leaflet with buttoning. Simple observation as a treatment option was found to be as good as intralesional steroids. Pseudocyst of the pinna is a benign condition of unknown etiology affecting the pinna, commonly encountered in middle-aged men. It is a rare condition and is hardly encountered in routine ENT practice. Bilateral diseases are uncommon. Most common site of occurrence is triangular and scaphoid fossa. Many modalities of treatment have been recommended in literature with varied recurrence and failure rates. The best treatment is surgical deroofing followed by buttoning with minimum recurrences. An option of simple observation for 2–3 months should be discussed with each patient and was found to be as good as intralesional steroids.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramadass T, Ayyaswamy G (2006) Pseudocyst of auricle etiopathogenesis, treatment update and literature review. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 58(2):156–159
Hartmann A (1846) Uber Cystenbildung in der Ohrenmuschel. Arch Ohren Nasen Kehlkopfheilkd 15:156–166
Engel D (1966) Pseudocyst of the auricle in Chinese. Arch Otolaryngol 83:197–202
Hansen JE (1967) Pseudocyst of the auricle in Caucasians. Arch Otolaryngol 85:1–13
Supiyaphun P, Decha W (2001) Auricular pseudocysts: a treatment with the Chulalongkorn University vacuum device. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 124:213–216
Choi S, Lam K, Chan KW, Cohadially FN, Anthony SM (1984) Endochondral pseudocyst of the auricle in Chinese. Arch Otolaryngol 110:792–796
Karabulut H, Acar B, Selçuk K (2009) Treatment of the non-traumatic auricula pseudocyst with aspiration and intralesional steroid injection. New J Med 26:117–119
Lee YK, Ku BS, Kim YH (2007) A case of pseudocyst of the auricle treated by incisional biopsy. Korean J Dermatol 45(5):518–520
Kanotra SP, Lateef M (2009) Pseudocyst of pinna: a recurrence-free approach. Am J Otolaryngol 30(2):73–79
Hegde R, Bhargava S, Bhargava KB (1996) _Pseudocyst of the auricle: a new method of treatment. J Laryngol Otol 110:767–769
Ramalingam R, Ramalingam KK (1998) Pseudocyst of the auricle—a new method of treatment. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 50(2):172–174
Sangeetha RH, Vijayendra H (2004) A safe and reliable technique in the management of pseudocysts. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 56(I):29–30
Oyama N, Satoh M, Iwatsuki K, Kaneko F (2001) Treatment of recurrent auricle pseudocyst with intralesional injection of minocycline: a report of two cases. J Am Acad Dermatol 45(4):554–556
Lim CM, Goh YH, Chao SS, Lim Lynne (2002) Psuedocyst of the auricle. Laryngoscope 12:2033–2036
Salgado CJ, Hardy JE, Mardni S, Dockery JM, Matthews MS (2006) Treatment of auricular pseudocyst with aspiration and local pressure. J Plastic Reconstr Aesthet Surg 59:1450–1452
Tuncer S, Basterzi Y, Yavuzer R (2003) Recurrent auricular pseudocyst: anew treatment recommendation with curettage and fibrin glue. Dermatol Surg 29:1080–1083
Tan BY (2004) Auricular pseudocyst in the tropics: a multi-racial Singapore experience. J Laryngol Otol 118(3):185–188
Cohen PR, Grossman ME (1990) Pseudocyst of the auricle: case report and world literature review. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 116:1202–1204
Shanmugham MS (1985) Pseudocyst of the auricle. J Laryngol Otol 99:701–703
Devlin J, Harrison CJ, Whitby DJ et al (1990) Cartilaginous pseudocyst of the external auricle in children with atopic eczema. Br J Dermatol 112:699–704
Bhandary S, Mannil TV (2000) A comparative study in the management of auricular pseudocysts. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 52(3):246–250
Vishwakarma SC, Gupta D, Verma SK (1987) Pseudocyst of the auricle. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 39(4):170
Okuma M (1985) Treatment for pseudocyst of the auricle. Jpn Dermatol 95:390 (in Japanese)
Miyamoto H, Oida M, Onuma S, Uchiyama M (1994) Steroid injection therapy for pseudocyst of the auricle. Acta Derm Venereol 74:140–142
Harder MK, Zachary CB (1993) Pseudocyst of the ear. Surgical treatment. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 19(6):585–588
Chang CH, Kuo WR, Lin CH, Wang LF, Ho KY, Tsai KB (2004) Deroofing surgical treatment for pseudocyst of the auricle. J Otolaryngol 33(3):177–180
Hoffmann TJ, Richardson TF, Jacobs RJ, Torres (1993) A pseudocyst of the auricle. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 19(3):259–262
Mohammed E, Jakubikova J (2007) Bilateral pseudocyst of pinna: a case report. Bratisl Lek Listy 108(10–11):470–473
Conflict of interest
We have no financial relationship with the organization that sponsored the research and in fact no organization sponsored our research and it was self-funded. We have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patigaroo, S.A., Mehfooz, N., Patigaroo, F.A. et al. Clinical characteristics and comparative study of different modalities of treatment of pseudocyst pinna. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269, 1747–1754 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-011-1805-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-011-1805-6