Abstract
Introduction
With the implementation of fast-track surgery with optimization of both logistical and clinical features, the postoperative convalescence has been reduced as functional milestones have been achieved earlier and consequently length of stay (LOS) in hospital has been reduced. However, it has been speculated that a decrease in LOS may be associated with an increase in readmissions in general, including risk of dislocation after total hip arthroplasty (THA) or manipulation after total knee arthroplasty (TKA).
Materials and methods
1,731 consecutive, unselected patients were operated with primary THA or TKA in a well-described standardized fast-track setup from 2004 to 2008. All readmissions and deaths within 90 days were analyzed using the national health register.
Results
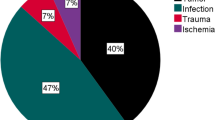
Mean LOS decreased from 6.3 to 3.1 days. Within 90 days, 15.6% of patients following TKA were readmitted as opposed to 10.9% after THA (p = 0.005). Three deaths (0.17%) were associated with clotting episodes. Suspicion of DVT (not found) and suspicion of infection made up half of the readmissions. Readmissions in general and for thromboembolic events, dislocations and manipulations in specific did not increase with decreasing LOS. There was no difference between readmission rates per year for either TKA or THA but there was a significantly reduced risk of dislocation found with decreasing LOS comparing each year from 2005 to 2007 with the index year of 2004 (with the longest LOS and the highest incidence of dislocation).
Conclusion
Fast-track TKA and THA do not increase the readmission rate. Readmissions are more frequent after TKA than THA, but dislocation after THA and manipulation after TKA do not increase as LOS is decreasing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbieri A, Vanhaecht K, Van Herck P, Sermeus W, Faggiano F, Marchisio S, Panella M (2009) Effects of clinical pathways in the joint replacement: a meta-analysis. BMC Med 7:32
Mauerhan DR, Lonergan RP, Mokris JG, Kiebzak GM (2003) Relationship between length of stay and dislocation rate after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 18:963–967
Fisher DA, Trimble S, Clapp B, Dorsett K (1997) Effect of a patient management system on outcomes of total hip and knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 345:155–160
Mauerhan DR, Mokris JG, Ly A, Kiebzak GM (1998) Relationship between length of stay and manipulation rate after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 13:896–900
Husted H, Holm G, Jacobsen S (2008) Predictors of length of stay and patient satisfaction after hip and knee replacement surgery: fast-track experience in 712 patients. Acta Orthop 79:168–173
Kerr DR, Kohan L (2008) Local infiltration analgesia: a technique for the control of acute postoperative pain following knee and hip surgery: a case study of 325 patients. Acta Orthop 79:174–183
Andersen LØ, Husted H, Otte KS, Kristensen BB, Kehlet H (2008) High-volume infiltration in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 52:1331–1335
Andersen LØ, Kristensen BB, Husted H, Otte KS, Kehlet H (2008) Local anaesthetics after total knee arthroplasty: intraarticular or extraarticular administration? A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Acta Orthop 79:800–805
Holte K, Kristensen BB, Valentiner L, Foss NB, Husted H, Kehlet H (2007) Liberal versus restrictive fluid management in knee arthroplasty: a randomized, double-blind study. Anesth Analg 105:465–474
Husted H, Blønd L, Sonne-Holm S, Holm G, Jacobsen TW, Gebuhr P (2003) Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and blood transfusions in primary total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Scand 74:665–669
Andersen LØ, Husted H, Otte KS, Kristensen BB, Kehlet H (2008) A compression bandage improves local infiltration analgesia in total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop 79:806–811
Cusick LA, Beverland DE (2009) The incidence of fatal pulmonary embolism after primary hip and knee replacement in a consecutive series of 4253 patients. J Bone Joint Surg 91:645–648
Aynardi M, Pulido L, Parvizi J, Sharkey PF, Rothman RH (2009) Early mortality after modern total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467:213–218
Blom A, Pattison G, Whitehouse S, Taylor A, Bannistar G (2006) Early death following primary total hip arthroplasty: 1, 727 procedures with mechanical thrombo-prophylaxis. Acta Orthop 77:345–346
Eriksson BI, Borris LC, Friedman RJ, Haas S, Huisman MV, Kakkar AK, Bandel TJ, Beckmann H, Muehlhofer E, Misselwitz F, Geerts W (2008) RECORD1 study group. N Engl Med 358:2765–2775
Lachiewicz PF, Soileau ES (2006) Multimodal prophylaxis for THA with mechanical compression. Clin Orthop Relat Res 453:225–230
Lachiewicz PF, Soileau ES (2007) Mechanical calf compression and aspirin prophylaxis for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 464:61–64
Lassen MR, Raskob GE, Gallus A, Pineo G, Chen D, Portman RJ (2009) Apixaban or enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after knee replacement. N Engl J Med 361:594–604
Mantilla CB, Horlocker TT, Schroeder DR, Berry DJ, Brown DL (2002) Frequency of myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, deep venous thrombosis, and death following primary hip or knee arthroplasty. Anaesthesiology 96:1140–1146
Samama CM, Raynaud P, Parent F, Barré J, Mertl P, Mismetti P (2007) Epidemiology of venous thromboembolism after lower limb arthroplasty: the FOTO study. J Thromb Haemost 5:2360–2367
Tarity TD, Herz AL, Parvizi J, Rothman RH (2006) Ninety-day mortality after hip arthroplasty: a comparison between unilateral and simultaneous bilateral procedures. J Arthroplasty 21:60–64
Rodgers A, Walker N, Schug S, McKee A, Kehlet H, van Zundert A, Sage D, Futter M, Saville G, Clark T, MacMahon S (2000) Reduction of postoperative mortality and morbidity with epidural or spinal anaesthesia: results from overview of randomised trials. BMJ 321:1493
Dowsey MM, Kilgour ML, Santamaria NM, Choong PFM (1999) Clinical pathways in hip and knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomised controlled study. Med J Aust 170:59–62
Gaine WJ, Ramamohan NA, Hussein NA, Hullin MG, McCreath SW (2000) Wound infection in hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br 82(4):561–565
Dale H, Hallan G, Hallan G, Espehaug B, Havelin LI, Engesaeter LB (2009) Increasing risk of revision due to deep infection after hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop 80:639–645
Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Lau E, Bozic KJ, Berry D, Parvizi J (2010) Prosthetic joint infection risk after TKA in the Medicare population. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:52–56
Kwon MS, Kuskowski M, Mulhall KJ, Macaulay W, Brown TE, Saleh KJ (2006) Does surgical approach affect total hip arthroplasty dislocation rates? Clin Orthop Relat Res 447:34–38
Dobbs RE, Hanssen AD, Lewallen DG, Pagnano MW (2005) Quadriceps tendon rupture after total knee arthroplasty. Prevalence, complications, and outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg 87:37–45
Gandhi R, Petruccelli D, Devereaux PJ, Adili A, Hubmann M, de Beer J (2006) Incidence and timing of myocardial infarction after total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 21:874–877
Scranton PE (1999) The cost effectiveness of streamlined care pathways and product standardization in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 14(2):182–186
Pearson S, Moraw I, Maddern GJ (2000) Clinical pathway management of total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective comparative study. Aust N Z J Surg 70:351–354
Zhan C, Kaczmarek R, Loyo-Berrios N, Sangl J, Bright RA (2007) Incidence ans short-term outcomes of primary and revision hip replacement in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg 89:526–533
Berger RA, Kusuma SK, Sanders SA, Thill ES, Sporer SM (2009) The feasibility and perioperative complications of outpatient knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467:1443–1449
Fehringer EV, Mikuls TR, Michaud KD, Henderson WG, O’Dell JR (2009) Shoulder arthroplasties have fewer complications than hip or knee arthroplasties in US veterans. Clin Orthop Relat Res (E-pub)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Husted, H., Otte, K.S., Kristensen, B.B. et al. Readmissions after fast-track hip and knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130, 1185–1191 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-010-1131-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-010-1131-2