Abstract
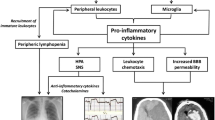
We investigated postmortem human brain tissues to determine whether systemic inflammation causes activation of vascular endothelial cells and perivascular cells. In some cases, we used serum concentrations of an acute-phase reactant, C-reactive protein (CRP), as an index of systemic inflammation. Since the serum concentration of CRP at the agonal stage was available only in a limited number of patients, we estimated the degree of systemic inflammation by the intensity of immunohistochemical staining of the residual blood in brain tissue for CRP. Expressions of intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1, CD40 and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 were used as markers for activation of vascular endothelial cells. Activation of perivascular cells was estimated by the occurrence of HLA-DR- and CD68-positive perivascular cells. In cases without brain lesions, activation of vascular endothelial cells and perivascular cells was related to the degree of systemic inflammation. In cases with brain lesions, these cells are often activated even in the absence of systemic inflammation. We suggest that inflammatory stimuli derived from the peripheral blood and the brain parenchyma adjunctly activate vascular cells. Under such circumstances, low-grade inflammation in the pre-existing brain lesions might enhance inflammatory signaling to the brain parenchyma from the periphery. The results of this study could explain the vulnerability of neurological patients to delirium caused by systemic inflammatory conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others

References
Akiyama H (2001) Neurons. In: Rogers J (ed) Neuroinflammatory mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease. Birkhauser, Basel, pp 225–236
Akiyama H, McGeer PL (1990) Brain microglia constitutively express β-2 integrins. J Neuroimmunol 30:81–93
Akiyama H, Kawamata T, Yamada T, Tooyama I, Ishii T, McGeer, PL (1993) Expression of intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 by a subset of astrocytes in Alzheimer and some other degenerative neurological disorders. Acta Neuropathol 85:628–634
Akiyama H, Tooyama I, Kondo H, Ikeda K, Kimura H, McGeer EG, McGeer PL (1994) Early response of brain resident microglia to kainic acid-induced hippocampal lesions. Brain Res 635:257–268
Alderson MR, Armitage RJ, Tough TW, Strockbine L, Fanslow WC, SpriggsMK (1993) CD40 expression by human monocytes: regulation by cytokines and activation of monocytes by the ligand for CD40. J Exp Med 178:669–674
Blalock JE (1994) The syntax of immune-neuroendocrine communication. Immunol Today 15:505–511
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathological staging of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82:239–259
Carlos TM, Harlan JM (1990) Membrane proteins involved in phagocyte adherence to endothelium. Immunol Rev 114:5–28
Combrinck MI, Perry VH, Cunningham C (2002) Peripheral infection evokes exaggerated sickness behaviour in pre-clinical murine prion disease. Neuroscience 112:7–11
Eikelenboom P, Hoogendijk WJG (1999) Do delirium and Alzheimer’s dementia share specific pathogenetic mechanisms? Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 10:319–324
Eikelenboom P, Zhan S-S, Gool WA van, Allsop D (1994) Inflammatory mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 15:447–450
Eikelenboom P, Hoogendijk WJG, Jonker C, Tilburg W van (2002) Immunological mechanisms and the spectrum of psychiatric syndrome in Alzheimer’s disease. J Psychiatr Res 36:269–280
Ek M, Engblom D, Saha S, Blomqvist A, Jakobsson P-J, Ericsson-Dahlstrand A (2001) Pathway across the blood-brain barrier. Nature 410:430–431
Elie M, Cole MG, Primeau FJ, Bellavance F (1998) Delirium risk factors in elderly hospitalized patients. J Gen Intern Med 13:204–212
Elmquist JK, Breder CD, Sherin JE, Scammell TE, Hickey WF, Dewitt D, Saper CB (1997) Intravenous lipopolysaccharide induces cyclooxygenase 2-like immunoreactivity in rat brain perivascular microglia and meningeal macrophages. J Comp Neurol 381:119–129
Gehrmann J, Matsumoto Y, Kreutzberg GW (1995) Microglia: intrinsic immueffector cell of the brain. Brain Res Rev 20:269–287
Guo J, Yu J, Grass D, Beer FC de, Kindy MS (2002) Inflammation-dependent cerebral deposition of serum amyloid A protein in a mouse model of amyloidosis. J Neurosci 22:5900–5909
Habib A, Creminon C, Frobert Y, Grassi J, Pradelles P, Maclouf J (1993) Demonstration of an inducible cyclooxygenase in human endothelial cells using antibodies raised against the carboxyl-terminal region of the cyclooxygenase-2. J Biol Chem 268:23448–23454
Honda M, Akiyama H, Yamada Y, Kondo H, Kawabe Y, Takeya M, Takahashi K, Suzuki H, Doi T, Sakamoto A, Ookawara S, Mato M, Gough PJ, Greaves DR, Gordon S, Kodama T, Matsushita M (1998) Immunohistochemical evidence for a macrophage scavenger receptor in Mato cells and reactive microglia of ischemia and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem Biophysiol Res Commun 245:734–740
Karmann K, Hughes CCW, Schechner J, Fanslow WC, Pober JS (1995) CD40 on human endothelial cells: inducibility by cytokines and functional regulation of adhesion molecule expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:4342–4346
Kaufmann WE, Worley PF, Pegg J, Bremer M, Isakson P (1996) COX-2, a synaptically induced enzyme, is expressed by excitatory neurons at postsynaptic sites in rat cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:2317–2321
Lerner AJ, Hedera P, Koss E, Stuckey J, Friedland RP (1997) Delirium in Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 11:16–20
Lindsberg PJ, Launes J, Tian M, Valimaa H, Subramanian V, Siren J, Hokkanen L, Hyypia T, Carpen O, Gahmberg CG (2002) Release of soluble ICAM-5, a neuronal adhesion molecule, in acute encephalitis. Neurology 58:446–451
Maier JA, Hia T, Maciag T (1990) Cyclooxygenase is an immediate-early gene induced by interleukin-1 in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 265:10805–10808
Mattiace LA, Davies P, Dickson DW (1990) Detection of HLA-DR on microglia in the humanbrain is a function of both clinical and technical factors. Am J Pathol 136:1101–1114
McGeer PL, McGeer EG (1995) The inflammatory response system of brain: implications for therapy of Alzheimer and other neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Rev 21:195–218
McGeer PL, McGeer EG (2000) Autotoxicity and Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 57:789–790
McGeer PL, McGeer EG (2002) The possible role of complement activation in Alzheimer disease. Trends Mol Med 8:519–523
Milner R, Campbell IL (2003) The extracellular matrix and cytokines regulate microglial integrin expression and activation. J Immunol 170:3850–3858
Murray AM, Levkoff SE, Wetle TT, Beckett L, Clearly PD, Schor JD, Lipsitz LA, Rowe JW, Evans DA (1993) Acute delirium and functional decline in the hospitalized dlderly patient. J Gerontol 48:M181–M186
Neuroinflammation Working Group, Akiyama H, et al (2000) Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 21:383–421
Rosene KA, Copass MK, Kastner LS, Nolan CM, Eschenbach DA (1982) Persistent neuropsychological sequele of toxic shock syndrome. Ann Intern Med 96:865–870
Togo T, Akiyama H, Kondo H, Ikeda K, Kato M, Iseki E, Kosaka K (2000) Expression of CD40 in the brain of Alzheimer’s disease and other neurological diseases. Brain Res 885:117–121
Togo T, Akiyama H, Iseki E, Kondo H, Ikeda K, Kato M, Oda T, Tsuchiya K, Kosaka K (2002) Occurrence of T cells in the brain of Alzheimer’s disease and other neurological diseases. J Neuroimmunol 124:83–92
Van der Maesen K, Hinojoza JR, Sobel RA (1999) Endothelial cell class II major histocompatibility complex molecule expression in stereotactic brain biopsies of patients with acute inflammatory/demyelinating conditions. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58:346–358
Washington R, Burton J, Todd RF 3rd, Newman W, Dragovic L, Dore-Duffy P (1994) Expression of immunologically relevant endothelial cell activation antigens on isolated central nervous system microvessels from patients with multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 35:89–97
Wong Ma-Li, Rettori V, AlShekhlee A, Bongiorno PB, Canteros G, McCann SM, Gold PW, Licinio J (1996) Inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression in the brain during systemic inflammation. Nat Med 2:581–584
Wright GJ, Jones M, Puklavec MJ, Brown MH, Barclay AN (2001) The unusual distribution of the neuronal/lymphoid cell surface CD200 (OX2) glycoprotein is conserved in humans. Immunology 102:173–179
Young GB, Bolton CF, Austin TW, Archibald YM, Conder J, Wells GA (1990) The encephalopathy associated with septic illness. Clin Invest Med 13:297–304
Acknowledgement
We thank Dr. Makoto Honda (Tokyo Institute of Psychiatry) for providing the monoclonal antibody to macrophage scavenger receptor (clone MH1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uchikado, H., Akiyama, H., Kondo, H. et al. Activation of vascular endothelial cells and perivascular cells by systemic inflammation—an immunohistochemical study of postmortem human brain tissues. Acta Neuropathol 107, 341–351 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-003-0815-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-003-0815-x