Abstract
Background
Healthy vascular endothelium is clothed by the endothelial glycocalyx. This structure plays a key role in the regulation of inflammation and vascular permeability and is known to be degraded by ischemic and inflammatory stress. Our aim was to show whether hydrocortisone and antithrombin stabilize the glycocalyx and, therefore, the vascular barrier, against damage induced by the inflammatory stimulus TNF-α, thus improving the cardio-vascular situation.
Methods
Isolated guinea pig hearts were perfused with Krebs–Henseleit buffer for 20 min at constant flow (baseline perfusion pressure 70 cmH2O). Hydrocortisone in a stress dose (10 µg/ml) or antithrombin in a physiological dose (1 U/ml) were then applied for 15 min before infusion of TNF-α (4 ng/ml, 10 min). Coronary net fluid filtration was assessed directly by measuring transudate formation on the epicardial surface. Hearts were perfusion-fixed to visualize the glycocalyx.
Results
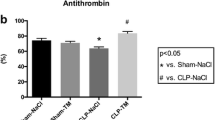
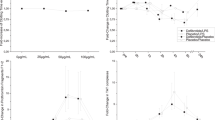
TNF-α induced severe degradation of the glycocalyx, increased coronary resistance, heightened vascular leak and permeability to hydroxyethyl starch and caused mast-cell degranulation. Hydrocortisone and antithrombin both reduced all of these effects. Electron microscopy revealed a mostly intact glycocalyx after treatment with either drug.
Conclusions
Both hydrocortisone and antithrombin clearly preserve the endothelial glycocalyx in the face of inflammatory degradation initiated by TNF-α, however, with different mechanisms. This is an important new facet in the pathophysiology and therapy of sepsis, since preservation of the glycocalyx should help prevent vasoconstriction, tissue edema as well as leukocyte and platelet adhesion, thus mitigating inflammation and tissue hypoxia.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annane D (2005) Glucocorticoids in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. Curr Opin Crit Care 11:449–453
Bar-Ner M, Eldor A, Wasserman L, Matzner Y, Cohen IR, Fuks Z, Vlodavsky I (1987) Inhibition of heparanase-mediated degradation of extracellular matrix heparan sulfate by non-anticoagulant heparin species. Blood 70:551–557
Baudo F, de CF (2000) Antithrombin III concentrates in the treatment of sepsis and septic shock: indictions, limits and future prospects. Minerva Anestesiol 66:3–23
Becker BF (1993) Towards the physiological function of uric acid. Free Radic Biol Med 14:615–631
Bose D, Leineweber K, Konorza T, Zahn A, Brocker-Preuss M, Mann K, Haude M, Erbel R, Heusch G (2007) Release of TNF-alpha during stent implantation into saphenous vein aortocoronary bypass grafts and its relation to plaque extrusion and restenosis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292:H2295–H2299
Boyer A, Chadda K, Salah A, Annane D (2006) Glucocorticoid treatment in patients with septic shock: effects on vasopressor use and mortality. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 44:309–318
Brown KA, Brain SD, Pearson JD, Edgeworth JD, Lewis SM, Treacher DF (2006) Neutrophils in development of multiple organ failure in sepsis. Lancet 368:157–169
Chappell D, Jacob M, Hofmann-Kiefer K, Bruegger D, Rehm M, Conzen P, Welsch U, Becker BF (2007) Hydrocortison prevserves the vascular barrier by protecting the endothelial glycocalyx. Anesthesiology 107:776–784
Chappell D, Jacob M, Rehm M, Stoeckelhuber M, Welsch U, Conzen P, Becker BF (2008) Heparinase selectively sheds heparan sulphate from the endothelial glycocalyx. Biol Chem 389:79–82
Constantinescu AA, Vink H, Spaan JA (2003) Endothelial cell glycocalyx modulates immobilization of leukocytes at the endothelial surface. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:1541–1547
Czarnowska E, Karwatowska-Prokopczuk E (1995) Ultrastructural demonstration of endothelial glycocalyx disruption in the reperfused rat heart. Involvement of oxygen free radicals. Basic Res Cardiol 90:357–364
Fert-Bober J, Leon H, Sawicka J, Basran RS, Devon RM, Schulz R, Sawicki G (2008) Inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2 reduces protein release into coronary effluent from isolated rat hearts during ischemia-reperfusion. Basic Res Cardiol 103:431–443
Forster C, Burek M, Romero IA, Weksler B, Couraud PO, Drenckhahn D (2008) Differential effects of hydrocortisone and TNFalpha on tight junction proteins in an in vitro model of the human blood-brain barrier. J Physiol 586:1937–1949
Forster H, Wicarkzyk C, Dudziak R (1981) Determination of the plasma elimination of hydroxyethyl starch and dextran using improved analytical methods. Infusionsther Klin Ernahr 8:88–94
Gando S, Nanzaki S, Sasaki S, Aoi K, Kemmotsu O (1998) Activation of the extrinsic coagulation pathway in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med 26:2005–2009
Gao X, Belmadani S, Picchi A, Xu X, Potter BJ, Tewari-Singh N, Capobianco S, Chilian WM, Zhang C (2007) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces endothelial dysfunction in Lepr(db) mice. Circulation 115:245–254
Gilles S, Zahler S, Welsch U, Sommerhoff CP, Becker BF (2003) Release of TNF-alpha during myocardial reperfusion depends on oxidative stress and is prevented by mast cell stabilizers. Cardiovasc Res 60:608–616
Gotz AK, Zahler S, Stumpf P, Welsch U, Becker BF (2005) Intracoronary formation and retention of micro aggregates of leukocytes and platelets contribute to postischemic myocardial dysfunction. Basic Res Cardiol 100:413–421
Grunfeld JP, Eloy L (1987) Glucocorticoids modulate vascular reactivity in the rat. Hypertension 10:608–618
Hafezi-Moghadam A, Simoncini T, Yang Z, Limbourg FP, Plumier JC, Rebsamen MC, Hsieh CM, Chui DS, Thomas KL, Prorock AJ, Laubach VE, Moskowitz MA, French BA, Ley K, Liao JK (2002) Acute cardiovascular protective effects of corticosteroids are mediated by non-transcriptional activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Nat Med 8:473–479
Harada N, Okajima K, Kushimoto S, Isobe H, Tanaka K (1999) Antithrombin reduces ischemia/reperfusion injury of rat liver by increasing the hepatic level of prostacyclin. Blood 93:157–164
Henry CB, Duling BR (2000) TNF-alpha increases entry of macromolecules into luminal endothelial cell glycocalyx. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 279:H2815-H2823
Jacob M, Bruegger D, Rehm M, Stoeckelhuber M, Welsch U, Conzen P, Becker BF (2007) The endothelial glycocalyx affords compatibility of Starling’s principle and high cardiac interstitial albumin levels. Cardiovasc Res 73:575–586
Jacob M, Rehm M, Loetsch M, Paul JO, Bruegger D, Welsch U, Conzen P, Becker BF (2007) The endothelial glycocalyx prefers albumin for evoking shear stress-induced, nitric oxide-mediated coronary dilatation. J Vasc Res 44:435–443
Kapilevich LV, Anfinogenova YD, Nosarev AV, Baskakov MB, Kovalev IV, D’yakova EY, Medvedev MA (2001) Histaminergic regulation of smooth muscles in rabbit pulmonary arteries. Bull Exp Biol Med 132:731–733
Kilger E, Weis F, Briegel J, Frey L, Goetz AE, Reuter D, Nagy A, Schuetz A, Lamm P, Knoll A, Peter K (2003) Stress doses of hydrocortisone reduce severe systemic inflammatory response syndrome and improve early outcome in a risk group of patients after cardiac surgery. Crit Care Med 31:1068–1074
Marsden PA, Ballermann BJ (1990) Tumor necrosis factor alpha activates soluble guanylate cyclase in bovine glomerular mesangial cells via an l-arginine-dependent mechanism. J Exp Med 172:1843–1852
Massoudy P, Mempel T, Raschke P, Becker BF (1999) Reduction of oxygen delivery during post-ischemic reperfusion protects the isolated guinea pig heart. Basic Res Cardiol 94:231–237
Matsuki T, Beach JM, Klindt RL, Duling BR (1993) Modification of vascular reactivity by alteration of intimal permeability: effect of TNF-alpha. Am J Physiol 264:H1847–H1853
Matsuki T, Duling BR (2000) TNF-alpha modulates arteriolar reactivity secondary to a change in intimal permeability. Microcirculation 7:411–418
Mulivor AW, Lipowsky HH (2002) Role of glycocalyx in leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 283:H1282–H1291
Mulivor AW, Lipowsky HH (2004) Inflammation- and ischemia-induced shedding of venular glycocalyx. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286:H1672–H1680
Nieuwdorp M, van Haeften TW, Gouverneur MC, Mooij HL, van Lieshout MH, Levi M, Meijers JC, Holleman F, Hoekstra JB, Vink H, Kastelein JJ, Stroes ES (2006) Loss of endothelial glycocalyx during acute hyperglycemia coincides with endothelial dysfunction and coagulation activation in vivo. Diabetes 55:480–486
Okajima K, Uchiba M (1998) The anti-inflammatory properties of antithrombin III: new therapeutic implications. Semin Thromb Hemost 24:27–32
Pejler G, Abrink M, Ringvall M, Wernersson S (2007) Mast cell proteases. Adv Immunol 95:167–255
Picchi A, Gao X, Belmadani S, Potter BJ, Focardi M, Chilian WM, Zhang C (2006) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces endothelial dysfunction in the prediabetic metabolic syndrome. Circ Res 99:69–77
Pries AR, Kuebler WM (2006) Normal endothelium. Handb Exp Pharmacol 1:1–40
Pries AR, Secomb TW, Gaehtgens P (2000) The endothelial surface layer. Pflugers Arch 440:653–666
Rehm M, Bruegger D, Christ F, Thiel M, Conzen P, Jacob M, Chappell D, Stoeckelhuber M, Welsch U, Reichart B, Peter K, Becker BF (2007) Shedding of the endothelial glycocalyx in patients undergoing major vascular surgery with global and regional ischemia. Circulation 116:1896–1906
Rehm M, Zahler S, Lotsch M, Welsch U, Conzen P, Jacob M, Becker BF (2004) Endothelial glycocalyx as an additional barrier determining extravasation of 6% hydroxyethyl starch or 5% albumin solutions in the coronary vascular bed. Anesthesiology 100:1211–1223
Roemisch J, Gray E, Hoffmann JN, Wiedermann CJ (2002) Antithrombin: a new look at the actions of a serine protease inhibitor. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 13:657–670
Sakata Y, Chancey AL, Divakaran VG, Sekiguchi K, Sivasubramanian N, Mann DL (2008) Transforming growth factor-beta receptor antagonism attenuates myocardial fibrosis in mice with cardiac-restricted overexpression of tumor necrosis factor. Basic Res Cardiol 103:60–68
Sanderson RD, Yang Y, Kelly T, MacLeod V, Dai Y, Theus A (2005) Enzymatic remodeling of heparan sulfate proteoglycans within the tumor microenvironment: growth regulation and the prospect of new cancer therapies. J Cell Biochem 96:897–905
Skyschally A, Gres P, Hoffmann S, Haude M, Erbel R, Schulz R, Heusch G (2007) Bidirectional role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in coronary microembolization: progressive contractile dysfunction versus delayed protection against infarction. Circ Res 100:140–146
Sprung CL, Annane D, Keh D, Moreno R, Singer M, Freivogel K, Weiss YG, Benbenishty J, Kalenka A, Forst H, Laterre PF, Reinhart K, Cuthbertson BH, Payen D, Briegel J (2008) Hydrocortisone therapy for patients with septic shock. N Engl J Med 358:111–124
Thielmann M, Dorge H, Martin C, Belosjorow S, Schwanke U, van de Sand A, Konietzka I, Buchert A, Kruger A, Schulz R, Heusch G (2002) Myocardial dysfunction with coronary microembolization: signal transduction through a sequence of nitric oxide, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and sphingosine. Circ Res 90:807–813
Underwood JL, Murphy CG, Chen J, Franse-Carman L, Wood I, Epstein DL, Alvarado JA (1999) Glucocorticoids regulate transendothelial fluid flow resistance and formation of intercellular junctions. Am J Physiol 277:C330–C342
van den Berg BM, Vink H, Spaan JA (2003) The endothelial glycocalyx protects against myocardial edema. Circ Res 92:592–594
Vink H, Constantinescu AA, Spaan JA (2000) Oxidized lipoproteins degrade the endothelial surface layer: implications for platelet-endothelial cell adhesion. Circulation 101:1500–1502
Vogel J, Sperandio M, Pries AR, Linderkamp O, Gaehtgens P, Kuschinsky W (2000) Influence of the endothelial glycocalyx on cerebral blood flow in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:1571–1578
Westermann D, Van LS, Dhayat S, Dhayat N, Schmidt A, Noutsias M, Song XY, Spillmann F, Riad A, Schultheiss HP, Tschope C (2007) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonism protects from myocardial inflammation and fibrosis in experimental diabetic cardiomyopathy. Basic Res Cardiol 102:500–507
Yang S, Zhang L (2004) Glucocorticoids and vascular reactivity. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2:1–12
Zahler S, Heindl B, Becker BF (2002) Selectin-mediated rolling of neutrophils is essential for their activation and retention in the reperfused coronary system. Basic Res Cardiol 97:359–364
Acknowledgments
The study was performed using departmental resources and a competitive grant of the Friedrich Baur Foundation (0027/2007) of the Ludwig-Maximilians University, Munich, Germany.
Conflict of interest None of the authors have any conflicts of interest in connection with this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Returned for 1. Revision: 19 June 2008 1. Revision received: 12 August 2008 Returned for 2. Revision: 20 August 2008 2. Revision received: 21 August 2008
The work was performed at the Walter-Brendel Centre of Experimental Medicine, Ludwig-Maximilians-University, Nussbaumstraße 20, 80336 Munich, Germany.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chappell, D., Hofmann-Kiefer, K., Jacob, M. et al. TNF-α induced shedding of the endothelial glycocalyx is prevented by hydrocortisone and antithrombin. Basic Res Cardiol 104, 78–89 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-008-0749-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-008-0749-5