Abstract
Purpose
Few studies have compared robotic and laparoscopic intersphincteric resection (ISR) in rectal cancer. Therefore, we performed a meta-analysis of recently published studies to compare perioperative outcomes of ISR for the treatment of low rectal cancer.
Methods
We performed a systematic literature search of the Ovid-Medline, Ovid-EMBASE, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials databases for studies comparing robotic and laparoscopic ISR in patients with low rectal cancer. Demographic and clinical data were extracted from articles that met the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Perioperative outcomes of interest included the rate of diverting stoma, open conversion rate, operation time, estimated blood loss, length of hospital stay, time to first flatus, and time to initiate the postoperative diet. Oncological outcomes included the number of retrieved lymph nodes, distal resection margin, proximal resection margin, circumferential resection margin, 3-year overall survival, 3-year disease-free survival, and local recurrence. Postoperative complications included overall complications, a Dindo-Clavien classification ≥ III, and anastomotic leakage. All outcomes were compared between the two groups.
Results
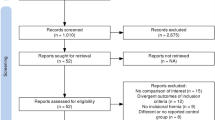
We included 5 retrospective cohort studies with a total of 510 patients undergoing 273 (53.5%) robotic ISR procedures and 237 (46.5%) laparoscopic ISR procedures. The robotic ISR group lower conversion rate, lower blood loss, and longer operation times than the laparoscopic group. We also noted that fewer lymph nodes were harvested in the robotic ISR group; however, this difference was not statistically significant. Other outcomes were similar between the two groups.
Conclusions
Robotic and laparoscopic ISR showed comparable perioperative outcomes, functional outcomes, and 3-year oncologic outcomes; however, robotic ISR was associated with a lower conversion rate and less blood loss despite longer operation times compared to laparoscopic ISR. These findings suggest that robotic ISR maybe a safe and effective technique for treating low rectal cancer in selected patients. The potential oncologic and functional benefits of robotic ISR should be evaluated in larger randomized controlled trials.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jeong SY, Park JW, Nam BH, Kim S, Kang SB, Lim SB, Choi HS, Kim DW, Chang HJ, Kim DY, Jung KH, Kim TY, Kang GH, Chie EK, Kim SY, Sohn DK, Kim DH, Kim JS, Lee HS, Kim JH, Oh JH (2014) Open versus laparoscopic surgery for mid-rectal or low-rectal cancer after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (COREAN trial): survival outcomes of an open-label, non-inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 15(7):767–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70205-0
Stevenson AR, Solomon MJ, Lumley JW, Hewett P, Clouston AD, Gebski VJ, Davies L, Wilson K, Hague W, Simes J (2015) Effect of laparoscopic-assisted resection vs open resection on pathological outcomes in rectal cancer: the ALaCaRT randomized clinical trial. JAMA 314(13):1356–1363. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2015.12009
Martinez-Perez A, Carra MC, Brunetti F, de’ Angelis N (2017) Pathologic outcomes of laparoscopic vs open mesorectal excision for rectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Surg 152(4):e165665. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2016.5665
Kang J, Yoon KJ, Min BS, Hur H, Baik SH, Kim NK, Lee KY (2013) The impact of robotic surgery for mid and low rectal cancer: a case-matched analysis of a 3-arm comparison--open, laparoscopic, and robotic surgery. Ann Surg 257(1):95–101. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e3182686bbd
Kim JY, Kim NK, Lee KY, Hur H, Min BS, Kim JH (2012) A comparative study of voiding and sexual function after total mesorectal excision with autonomic nerve preservation for rectal cancer: laparoscopic versus robotic surgery. Ann Surg Oncol 19(8):2485–2493. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-012-2262-1
Scarpinata R, Aly EH (2013) Does robotic rectal cancer surgery offer improved early postoperative outcomes? Dis Colon Rectum 56(2):253–262. https://doi.org/10.1097/DCR.0b013e3182694595
Rullier E, Sa Cunha A, Couderc P, Rullier A, Gontier R, Saric J (2003) Laparoscopic intersphincteric resection with coloplasty and coloanal anastomosis for mid and low rectal cancer. Br J Surg 90(4):445–451. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.4052
Lim SW, Huh JW, Kim YJ, Kim HR (2011) Laparoscopic intersphincteric resection for low rectal cancer. World J Surg 35(12):2811–2817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-011-1277-2
Kim JC, Lim SB, Yoon YS, Park IJ, Kim CW, Kim CN (2014) Completely abdominal intersphincteric resection for lower rectal cancer: feasibility and comparison of robot-assisted and open surgery. Surg Endosc 28(9):2734–2744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3509-7
Luca F, Valvo M, Guerra-Cogorno M, Simo D, Blesa-Sierra E, Biffi R, Garberoglio C (2016) Functional results of robotic total intersphincteric resection with hand-sewn coloanal anastomosis. Eur J Surg Oncol 42(6):841–847
Leong QM, Son DN, Cho JS, Baek SJ, Kwak JM, Amar AH, Kim SH (2011) Robot-assisted intersphincteric resection for low rectal cancer: technique and short-term outcome for 29 consecutive patients. Surg Endosc 25(9):2987–2992
Park JS, Kim NK, Kim SH, Lee KY, Lee KY, Shin JY, Kim CN, Choi GS, Korean Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery Study G (2015) Multicentre study of robotic intersphincteric resection for low rectal cancer. Br J Surg 102 (12):1567–1573
Kuo LJ, Lin YK, Chang CC, Tai CJ, Chiou JF, Chang YJ (2014) Clinical outcomes of robot-assisted intersphincteric resection for low rectal cancer: comparison with conventional laparoscopy and multifactorial analysis of the learning curve for robotic surgery. Int J Color Dis 29(5):555–562
Park SY, Choi GS, Park JS, Kim HJ, Ryuk JP (2013) Short-term clinical outcome of robot-assisted intersphincteric resection for low rectal cancer: a retrospective comparison with conventional laparoscopy. Surg Endosc 27(1):48–55
Baek SJ, Al-Asari S, Jeong DH, Hur H, Min BS, Baik SH, Kim NK (2013) Robotic versus laparoscopic coloanal anastomosis with or without intersphincteric resection for rectal cancer. Surg Endosc 27(11):4157–4163
Yoo BE, Cho JS, Shin JW, Lee DW, Kwak JM, Kim J, Kim SH (2015) Robotic versus laparoscopic intersphincteric resection for low rectal cancer: comparison of the operative, oncological, and functional outcomes. Ann Surg Oncol 22(4):1219–1225
Zhang X, Wei Z, Bie M, Peng X, Chen C (2016) Robot-assisted versus laparoscopic-assisted surgery for colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Surg Endosc 30(12):5601–5614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-4892-z
Lee SH, Lim S, Kim JH, Lee KY (2015) Robotic versus conventional laparoscopic surgery for rectal cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg Treat Res 89(4):190–201. https://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2015.89.4.190
Lim S, Kim JH, Baek SJ, Kim SH, Lee SH (2016) Comparison of perioperative and short-term outcomes between robotic and conventional laparoscopic surgery for colonic cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg Treat Res 90(6):328–339. https://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2016.90.6.328
Lin S, Jiang HG, Chen ZH, Zhou SY, Liu XS, Yu JR (2011) Meta-analysis of robotic and laparoscopic surgery for treatment of rectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 17(47):5214–5220. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i47.5214
Kim SY, Park JE, Lee YJ, Seo HJ, Sheen SS, Hahn S, Jang BH, Son HJ (2013) Testing a tool for assessing the risk of bias for nonrandomized studies showed moderate reliability and promising validity. J Clin Epidemiol 66(4):408–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.09.016
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA (2004) Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 240(2):205–213
Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I (2005) Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 5:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-5-13
Xiong B, Ma L, Zhang C, Cheng Y (2014) Robotic versus laparoscopic total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer: a meta-analysis. J Surg Res 188(2):404–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2014.01.027
Jayne D, Pigazzi A, Marshall H, Croft J, Corrigan N, Copeland J, Quirke P, West N, Rautio T, Thomassen N, Tilney H, Gudgeon M, Bianchi PP, Edlin R, Hulme C, Brown J (2017) Effect of robotic-assisted vs conventional laparoscopic surgery on risk of conversion to open laparotomy among patients undergoing resection for rectal cancer: the ROLARR randomized clinical trial. JAMA 318(16):1569–1580. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.7219
Liao G, Zhao Z, Lin S, Li R, Yuan Y, Du S, Chen J, Deng H (2014) Robotic-assisted versus laparoscopic colorectal surgery: a meta-analysis of four randomized controlled trials. World J Surg Oncol 12:122. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7819-12-122
Sng KK, Hara M, Shin JW, Yoo BE, Yang KS, Kim SH (2013) The multiphasic learning curve for robot-assisted rectal surgery. Surg Endosc 27(9):3297–3307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-2909-4
Jimenez-Rodriguez RM, Diaz-Pavon JM, de la Portilla de Juan F, Prendes-Sillero E, Dussort HC, Padillo J (2013) Learning curve for robotic-assisted laparoscopic rectal cancer surgery. Int J Color Dis 28(6):815–821. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-012-1620-6
D’Annibale A, Pernazza G, Monsellato I, Pende V, Lucandri G, Mazzocchi P, Alfano G (2013) Total mesorectal excision: a comparison of oncological and functional outcomes between robotic and laparoscopic surgery for rectal cancer. Surg Endosc 27(6):1887–1895. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2731-4
Yamaguchi T, Kinugasa Y, Shiomi A, Sato S, Yamakawa Y, Kagawa H, Tomioka H, Mori K (2015) Learning curve for robotic-assisted surgery for rectal cancer: use of the cumulative sum method. Surg Endosc 29(7):1679–1685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3855-5
Jimenez-Rodriguez RM, Rubio-Dorado-Manzanares M, Diaz-Pavon JM, Reyes-Diaz ML, Vazquez-Monchul JM, Garcia-Cabrera AM, Padillo J, De la Portilla F (2016) Learning curve in robotic rectal cancer surgery: current state of affairs. Int J Colorectal Dis 31(12):1807–1815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-016-2660-0
Compton CC, Greene FL (2004) The staging of colorectal cancer: 2004 and beyond. CA Cancer J Clin 54(6):295–308
Compton CC, Fielding LP, Burgart LJ, Conley B, Cooper HS, Hamilton SR, Hammond ME, Henson DE, Hutter RV, Nagle RB, Nielsen ML, Sargent DJ, Taylor CR, Welton M, Willett C (2000) Prognostic factors in colorectal cancer. College of American Pathologists Consensus Statement 1999. Arch Pathol Lab Med 124(7):979–994. https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-9985(2000)124<0979:PFICC>2.0.CO;2
Sobin LH, Greene FL (2001) TNM classification: clarification of number of regional lymph nodes for pNo. Cancer 92(2):452. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(20010715)92:2<452::AID-CNCR1342>3.0.CO;2-B
Park SY, Choi GS, Park JS, Kim HJ, Ryuk JP, Yun SH (2014) Urinary and erectile function in men after total mesorectal excision by laparoscopic or robot-assisted methods for the treatment of rectal cancer: a case-matched comparison. World J Surg 38(7):1834–1842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-013-2419-5
Kim HJ, Choi GS, Park JS, Park SY, Yang CS, Lee HJ (2018) The impact of robotic surgery on quality of life, urinary and sexual function following total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer: a propensity score-matched analysis with laparoscopic surgery. Color Dis 20(5):O103–O113. https://doi.org/10.1111/codi.14051
Panteleimonitis S, Ahmed J, Ramachandra M, Farooq M, Harper M, Parvaiz A (2017) Urogenital function in robotic vs laparoscopic rectal cancer surgery: a comparative study. Int J Color Dis 32(2):241–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-016-2682-7
Baek JH, McKenzie S, Garcia-Aguilar J, Pigazzi A (2010) Oncologic outcomes of robotic-assisted total mesorectal excision for the treatment of rectal cancer. Ann Surg 251(5):882–886. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181c79114
Kim J, Baek SJ, Kang DW, Roh YE, Lee JW, Kwak HD, Kwak JM, Kim SH (2017) Robotic resection is a good prognostic factor in rectal cancer compared with laparoscopic resection: long-term survival analysis using propensity score matching. Dis Colon rectum 60(3):266–273. https://doi.org/10.1097/DCR.0000000000000770
Baek JH, Pastor C, Pigazzi A (2011) Robotic and laparoscopic total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer: a case-matched study. Surg Endosc 25(2):521–525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-010-1204-x
Baek SJ, Kim SH, Cho JS, Shin JW, Kim J (2012) Robotic versus conventional laparoscopic surgery for rectal cancer: a cost analysis from a single institute in Korea. World J Surg 36(11):2722–2729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-012-1728-4
Funding
This research was supported by the Hallym University Research Fund (HURF-2016-07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
We the authors, Drs. Lee Seon Heui, Kim Dong Hyun, and Lim Sang Woo, have complied with all applicable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.H., Kim, D.H. & Lim, S.W. Robotic versus laparoscopic intersphincteric resection for low rectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Colorectal Dis 33, 1741–1753 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-018-3145-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-018-3145-0