Abstract
Purpose
To compare the outcomes and complications between percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG), laparoscopic gastrostomy (LAPG) and open gastrostomy (OG) in children.
Methods
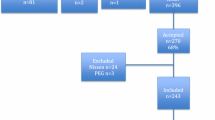
Retrospective review of 369 patients from July 1998 to December 2010 who had their gastrostomies inserted at a single tertiary paediatric institution. Patients who were lost in follow-up (59) and had insufficient data (23) were excluded from this study. Results were analysed using descriptive statistics.
Results
Of the 369 included in our study, 260 patients underwent LAPG, 86 PEG and 23 open gastrostomy (OG) procedures. The early complication rate for PEGs was 10.5 %, and for LAPGS 2.7 % (p = 0.006). The late complication rate was 41.9 % for PEGs and 43.1 % for LAPGs (p = NS). The overall complication rate for PEG was 54.7 % and it was 44.6 % for LAPG (p = NS). Major complications occurred only in the PEG group: gastro-colonic fistula (1), peritonitis (1), and “buried bumper syndrome” (1). The overall complication rate for OG was 78.3 % (p = 0.01, when this was compared to LAPGs and PEGs together), although there were no early complications in the OG group.
Conclusion
PEGs had a significantly higher early complication rate than LAPGs and the only major complications occurred in the PEG group. PEGs also had a higher overall complication rate than LAPGs, although the difference was not statistically significant. Both PEGs and LAPGs were significantly superior to OG in terms of overall complication rates.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braegger C et al (2010) Practical approach to paediatric enteral nutrition: a comment by the ESPGHAN committee on nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 51(1):110–122
Gauderer MW, Ponsky JL, Izant RJ Jr (1980) Gastrostomy without laparotomy: a percutaneous endoscopic technique. J Pediatr Surg 15(6):872–875
Fortunato J, Cuffari C (2011) Outcomes of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in children. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 13(3):293–299
Frohlich T et al (2010) Review article: percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in infants and children. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 31(8):788–801
Consensus Statement (2005) ESPEN guidelines on Artificial enteral nutrition—percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG). Clin Nutr 24(5):848–861
Bankhead RR, Fisher CA, Rolandelli RH (2005) Gastrostomy tube placement outcomes: comparison of surgical, endoscopic, and laparoscopic methods. Nutr Clin Pract 20(6):607–612
Peters RT, Balduyck B, Nour S (2010) Gastrostomy complications in infants and children: a comparative study. Pediatr Surg Int 26(7):707–709
Zamakhshary M et al (2005) Laparoscopic vs percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube insertion: a new pediatric gold standard? J Pediatr Surg 40(5):859–862
Jones VS, La Hei ER, Shun A (2007) Laparoscopic gastrostomy: the preferred method of gastrostomy in children. Pediatr Surg Int 23(11):1085–1089
Smitherman S, Pimpalwar A (2009) Laparoendoscopic gastrostomy tube placement: our all-in-one technique. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech Part A 19(1):119–123
Ackroyd R et al (2011) Gastrostomy tube insertion in children: the Edmonton experience. Can J Gastroenterol 25(5):265–268
Gauderer MW (1991) Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: a 10-year experience with 220 children. J Pediatr Surg 26(3):288–292 discussion 292-4
Vervloessem D et al (2009) Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) in children is not a minor procedure: risk factors for major complications. Semin Pediatr Surg 18(2):93–97
Fox VL et al (1997) Complications following percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy and subsequent catheter replacement in children and young adults. Gastrointest Endosc 45(1):64–71
Wragg RC et al (2012) Gastrostomy insertion in the 21st century: PEG or laparoscopic? Report from a large single-centre series. Pediatr Surg Int 28(5):443–448
Edelman DS, Arroyo PJ, Unger SW (1994) Laparoscopic gastrostomy versus percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. A comparison. Surg Endosc 8(1):47–49
Akay B et al (2010) Gastrostomy tube placement in infants and children: is there a preferred technique? J Pediatr Surg 45(6):1147–1152
Vernon-Roberts A, Sullivan PB (2007) Fundoplication versus post-operative medication for gastro-oesophageal reflux in children with neurological impairment undergoing gastrostomy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1:CD006151
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, R., Jiwane, A., Varjavandi, A. et al. Comparison of percutaneous endoscopic, laparoscopic and open gastrostomy insertion in children. Pediatr Surg Int 29, 613–621 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-013-3313-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-013-3313-9