Abstract
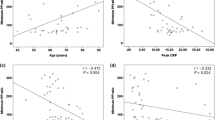
High-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1) is a late mediator of inflammatory responses that can cause acute lung injury. We examined the significance of serum HMGB1 elevation in the development of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and lung oxygenation impairment (LOI) after thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) repair. Serial measurements of the serum HMGB1 level and SIRS score for 7 days after surgery were determined in 20 patients with TAA who underwent surgical repair. Arterial oxygen tension was measured serially for at least 4 days after surgery, and LOI was defined as the lowest PaO2/FiO2 ratio ≤200 mmHg. The serum HMGB1 level was markedly increased after surgery, peaking on day 2, and remained significantly elevated on day 7. Peak HMGB1 level positively correlated with SIRS duration and the cumulative SIRS score during postoperative days 1–7 (P = 0.0013 and P = 0.0004, respectively). Peak HMGB1 level and cumulative SIRS score were higher in patients with LOI than in those without (P = 0.01 and P = 0.044, respectively). Peak HMGB1 level was negatively correlated with the lowest PaO2/FiO2 ratio (P = 0.0077) and positively correlated with postoperative length of hospitalization (P = 0.042). A greater serum HMGB1 elevation after TAA repair was associated with more severe SIRS and a higher incidence of LOI. HMGB1 might play a key role in the pathogenesis of SIRS and LOI after surgical TAA repair.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Welborn MB, Oldenburg HS, Hess PJ, Huber TS, Martin TD, Rauwerda JA, Wesdorp RI, Espat NJ, Copeland EM 3rd, Moldawer LL, Seeger JM (2000) The relationship between visceral ischemia, proinflammatory cytokines, and organ injury in patients undergoing thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Crit Care Med 28:3191–3197
Roumen RM, Hendriks T, van der Ven-Jongekrijg J, Nieuwenhuijzen GA, Sauerwein RW, van der Meer JW, Goris RJ (1993) Cytokine patterns in patients after major vascular surgery, hemorrhagic shock, and severe blunt trauma. Relation with subsequent adult respiratory distress syndrome and multiple organ failure. Ann Surg 218:769–776
Shindo S, Ogata K, Kubota K, Kojima A, Kobayashi M, Tada Y, Okuyama K (2003) Vascular prosthetic implantation is associated with prolonged inflammation following aortic aneurysm surgery. J Artif Organs 6:173–178
Fiane AE, Videm V, Lingaas PS, Heggelund L, Nielsen EW, Geiran OR, Fung M, Mollnes TE (2003) Mechanism of complement activation and its role in the inflammatory response after thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Circulation 108:849–856
Hanssen SJ, Derikx JP, Vermeulen Windsant IC, Heijmans JH, Koeppel TA, Schurink GW, Buurman WA, Jacobs MJ (2008) Visceral injury and systemic inflammation in patients undergoing extracorporeal circulation during aortic surgery. Ann Surg 248:117–125
Norwood MG, Bown MJ, Lloyd G, Bell PR, Sayers RD (2004) The clinical value of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) in abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 27:292–298
Bustin M (1999) Regulation of DNA-dependent activities by the functional motifs of the high-mobility-group chromosomal proteins. Mol Cell Biol 19:5237–5246
Lotze MT, Tracey KJ (2005) High-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1): nuclear weapon in the immune arsenal. Nat Rev Immunol 5:331–342
Wang H, Bloom O, Zhang M, Vishnubhakat JM, Ombrellino M, Che J, Frazier A, Yang H, Ivanova S, Borovikova L, Manogue KR, Faist E, Abraham E, Andersson J, Andersson U, Molina PE, Abumrad NN, Sama A, Tracey KJ (1999) HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science 285:248–251
Scaffidi P, Misteli T, Bianchi ME (2002) Release of chromatin protein HMGB1 by necrotic cells triggers inflammation. Nature 418:191–195
Andersson U, Wang H, Palmblad K, Aveberger AC, Bloom O, Erlandsson-Harris H, Janson A, Kokkola R, Zhang M, Yang H, Tracey KJ (2000) High mobility group 1 protein (HMG-1) stimulates proinflammatory cytokine synthesis in human monocytes. J Exp Med 192:565–570
Kohno T, Anzai T, Naito K, Miyasho T, Okamoto M, Yokota H, Yamada S, Maekawa Y, Takahashi T, Yoshikawa T, Ishizaka A, Ogawa S (2009) Role of high-mobility group box 1 protein in post-infarction healing process and left ventricular remodelling. Cardiovasc Res 81:565–573
Tsung A, Sahai R, Tanaka H, Nakao A, Fink MP, Lotze MT, Yang H, Li J, Tracey KJ, Geller DA, Billiar TR (2005) The nuclear factor HMGB1 mediates hepatic injury after murine liver ischemia-reperfusion. J Exp Med 201:1135–1143
Levy RM, Mollen KP, Prince JM, Kaczorowski DJ, Vallabhaneni R, Liu S, Tracey KJ, Lotze MT, Hackam DJ, Fink MP, Vodovotz Y, Billiar TR (2007) Systemic inflammation and remote organ injury following trauma require HMGB1. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 293:R1538–R1544
Ueno H, Matsuda T, Hashimoto S, Amaya F, Kitamura Y, Tanaka M, Kobayashi A, Maruyama I, Yamada S, Hasegawa N, Soejima J, Koh H, Ishizaka A (2004) Contributions of high mobility group box protein in experimental and clinical acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170:1310–1316
Suda K, Kitagawa Y, Ozawa S, Saikawa Y, Ueda M, Ebina M, Yamada S, Hashimoto S, Fukata S, Abraham E, Maruyama I, Kitajima M, Ishizaka A (2006) Anti-high-mobility group box chromosomal protein 1 antibodies improve survival of rats with sepsis. World J Surg 30:1755–1762
Ogawa EN, Ishizaka A, Tasaka S, Koh H, Ueno H, Amaya F, Ebina M, Yamada S, Funakoshi Y, Soejima J, Moriyama K, Kotani T, Hashimoto S, Morisaki H, Abraham E, Takeda J (2006) Contribution of high-mobility group box-1 to the development of ventilator-induced lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 174:400–407
Kim JY, Park JS, Strassheim D, Douglas I, Diaz del Valle F, Asehnoune K, Mitra S, Kwak SH, Yamada S, Maruyama I, Ishizaka A, Abraham E (2005) HMGB1 contributes to the development of acute lung injury after hemorrhage. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288:L958–L965
Kim JB, Sig Choi J, Yu YM, Nam K, Piao CS, Kim SW, Lee MH, Han PL, Park JS, Lee JK (2006) HMGB1, a novel cytokine-like mediator linking acute neuronal death and delayed neuroinflammation in the postischemic brain. J Neurosci 26:6413–6421
Milot J, Perron J, Lacasse Y, Letourneau L, Cartier PC, Maltais F (2001) Incidence and predictors of ARDS after cardiac surgery. Chest 119:884–888
Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, Schein RM, Sibbald WJ (1992) Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest 101:1644–1655
Yamada S, Inoue K, Yakabe K, Imaizumi H, Maruyama I (2003) High mobility group protein 1 (HMGB1) quantified by ELISA with a monoclonal antibody that does not cross-react with HMGB2. Clin Chem 49:1535–1537
Sugano Y, Anzai T, Yoshikawa T, Satoh T, Iwanaga S, Hayashi T, Maekawa Y, Shimizu H, Yozu R, Ogawa S (2005) Serum C-reactive protein elevation predicts poor clinical outcome in patients with distal type acute aortic dissection: association with the occurrence of oxygenation impairment. Int J Cardiol 102:39–45
Bown MJ, Nicholson ML, Bell PR, Sayers RD (2003) The systemic inflammatory response syndrome, organ failure, and mortality after abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg 37:600–606
Tan J, Hua Q, Li J, Fan Z (2009) Prognostic value of interleukin-6 during a 3-year follow-up in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Heart Vessels 24:329–334
Jug B, Salobir BG, Vene N, Sebestjen M, Sabovic M, Keber I (2009) Interleukin-6 is a stronger prognostic predictor than high-sensitive C-reactive protein in patients with chronic stable heart failure. Heart Vessels 24:271–276
Suda K, Kitagawa Y, Ozawa S, Saikawa Y, Ueda M, Abraham E, Kitajima M, Ishizaka A (2006) Serum concentrations of high-mobility group box chromosomal protein 1 before and after exposure to the surgical stress of thoracic esophagectomy: a predictor of clinical course after surgery? Dis Esophagus 19:5–9
Dybdahl B, Wahba A, Lien E, Flo TH, Waage A, Qureshi N, Sellevold OF, Espevik T, Sundan A (2002) Inflammatory response after open heart surgery: release of heat-shock protein 70 and signaling through toll-like receptor-4. Circulation 105:685–690
Suda K, Kitagawa Y, Ozawa S, Miyasho T, Okamoto M, Saikawa Y, Ueda M, Yamada S, Tasaka S, Funakoshi Y, Hashimoto S, Yokota H, Maruyama I, Ishizaka A, Kitajima M (2007) Neutrophil elastase inhibitor improves postoperative clinical courses after thoracic esophagectomy. Dis Esophagus 20:478–486
Suda K, Takeuchi H, Hagiwara T, Miyasho T, Okamoto M, Kawasako K, Yamada S, Suganuma K, Wada N, Saikawa Y, Fukunaga K, Funakoshi Y, Hashimoto S, Yokota H, Maruyama I, Ishizaka A, Kitagawa Y (2009) Neutrophil elastase inhibitor improves survival of rats with clinically relevant sepsis. Shock 33:526–531
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (20790548 to T.K.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kohno, T., Anzai, T., Shimizu, H. et al. Impact of serum high-mobility group box 1 protein elevation on oxygenation impairment after thoracic aortic aneurysm repair. Heart Vessels 26, 306–312 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-010-0056-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-010-0056-6