Abstract
Purpose
We evaluated the impact of age on PCA3 score and the utility of age-specific reference values in predicting initial prostate biopsy (pBx) outcomes.
Patients and methods
This single-center, retrospective study included 205 men who underwent an initial 14-core TRUS-guided pBx due to PSA > 3.0 ng/ml or suspicious digital-rectal examination (DRE). PCA3 scores were measured with the Progensa assay. Linear regression models were fit to identify factors that impact PCA3 score and to determine age-specific reference values. Predictive accuracies of logistic regression models predicting presence of prostate cancer (PCa) were analyzed.
Results
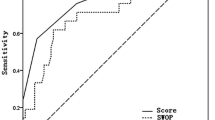
The positive biopsy rate was 37%. In multivariable linear regression, age (P < 0.001), presence of PCa (P < 0.001), and multifocal HG-PIN (P = 0.012) were independent predictors of PCA3 score. Age showed the strongest impact on PCA3 score (T = 4.77). The upper 95% confidence interval of PCA3 score in each age category was defined as the age-specific limit. A PCA3-score over the age-specific limit (PCA3-age) was associated with an 4.17-fold increased odds of being diagnosed with PCa (P < 0.001). In multivariable logistic regression models predicting the presence of PCa, predictive accuracy of a base model (age, DRE, PSA, volume) increased from 69.6 to 75.4% (P = 0.037) by adding the continuous PCA3 score, to 73.9% (P = 0.098) with the 35 cutoff (PCA3-35) and to 77.1% (P = 0.008) with PCA3-age.
Conclusions
PCA3 score increases with age, independent of PCa presence. Age-specific PCA3 score reference values are superior to PSA, continuous PCA3 score, and PCA3-35 in predicting initial pBx outcome. Therefore, an age-adjusted PCA3 score should be used for interpretation of the results.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heidenreich A, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Joniau S, Mason M, Matveev V, Mottet N, Schmid HP, van der Kwast T, Wiegel T, Zattoni F (2011) EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: screening, diagnosis, and treatment of clinically localised disease. Eur Urol 59:61–71
Stephan C, Kramer J, Meyer HA, Kristiansen G, Ziemer S, Deger S, Lein M, Loening SA, Jung K (2007) Different prostate-specific antigen assays give different results on the same blood sample: an obstacle to recommending uniform limits for prostate biopsies. BJU Int 99:1427–1431
Ponholzer A, Temml C, Madersbacher S (2010) Has blood volume an impact on serum PSA levels? World J Urol 28:693–697
Gosselaar C, Kranse R, Roobol MJ, Roemeling S, Schröder FH (2008) The interobserver variability of digital rectal examination in a large randomized trial for the screening of prostate cancer. Prostate 68:985–993
Evans CP (2009) Identification of molecular targets in urologic oncology. World J Urol 27:3–8
Prior C, Guillen-Grima F, Robles JE, Rosell D, Fernandez-Montero JM, Agirre X, Catena R, Calvo A (2010) Use of a combination of biomarkers in serum and urine to improve detection of prostate cancer. World J Urol 28:681–686
Herrmann TR, Merseburger AS, Burchardt M (2010) Prostate cancer: novel aspects of diagnostics and surgical technology. World J Urol 28:665
Durand X, Moutereau S, Xylinas E, de la Taille A (2011) Progensa PCA3 test for prostate cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 11:137–144
de la Taille A, Irani J, Graefen M, Chun F, de Reijke T, Kil P, Gontero P, Mottaz A, Haese A (2011) Clinical evaluation of the PCA3 assay in guiding initial biopsy decisions. J Urol 185:2119–2125
Haese A, de la Taille A, van Poppel H, Marberger M, Stenzl A, Mulders PF, Huland H, Abbou CC, Remzi M, Tinzl M, Feyerabend S, Stillebroer AB, van Gils MP, Schalken JA (2008) Clinical utility of the PCA3 urine assay in European men scheduled for repeat biopsy. Eur Urol 54:1081–1088
Remzi M, Haese A, Van Poppel H, de la Taille A, Stenzl A, Hennenlotter J, Marberger M (2010) Follow-up of men with an elevated PCA3 score and a negative biopsy: does an elevated PCA3 score indeed predict the presence of prostate cancer? BJU Int 106:1138–1142
Aubin SM, Reid J, Sarno MJ, Blase A, Aussie J, Rittenhouse H, Rittmaster R, Andriole GL, Groskopf J (2010) PCA3 molecular urine test for predicting repeat prostate biopsy outcome in populations at risk: validation in the placebo arm of the dutasteride REDUCE trial. J Urol 184:1947–1952
Marks LS, Fradet Y, Deras IL, Blase A, Mathis J, Aubin SM, Cancio AT, Desaulniers M, Ellis WJ, Rittenhouse H, Groskopf J (2007) PCA3 molecular urine assay for prostate cancer in men undergoing repeat biopsy. Urology 69:532–535
Deras IL, Aubin SM, Blase A, Day JR, Koo S, Partin AW, Ellis WJ, Marks LS, Fradet Y, Rittenhouse H, Groskopf J (2008) PCA3: a molecular urine assay for predicting prostate biopsy outcome. J Urol 179:1587–1592
Tombal B, Ameye F, de la Taille A, de Reijke T, Gontero P, Haese A, Kil P, Perrin P, Remzi M, Schroder J, Speakman M, Volpe A, Meesen B, Stoevelaar H (2011) Biopsy and treatment decisions in the initial management of prostate cancer and the role of PCA3; a systematic analysis of expert opinion. World J Urol. doi: 10.1007/s00345-00011-00721-00340 (in press)
Ploussard G, Durand X, Xylinas E, Moutereau S, Radulescu C, Forgue A, Nicolaiew N, Terry S, Allory Y, Loric S, Salomon L, Vacherot F, de la Taille A (2011) Prostate cancer antigen 3 score accurately predicts tumour volume and might help in selecting prostate cancer patients for active surveillance. Eur Urol 59:422–429
Nakanishi H, Groskopf J, Fritsche HA, Bhadkamkar V, Blase A, Kumar SV, Davis JW, Troncoso P, Rittenhouse H, Babaian RJ (2008) PCA3 molecular urine assay correlates with prostate cancer tumor volume: implication in selecting candidates for active surveillance. J Urol 179:1804–1810
Whitman EJ, Groskopf J, Ali A, Chen Y, Blase A, Furusato B, Petrovics G, Ibrahim M, Elsamanoudi S, Cullen J, Sesterhenn IA, Brassell S, Rittenhouse H, Srivastava S, McLeod DG (2008) PCA3 score before radical prostatectomy predicts extracapsular extension and tumor volume. J Urol 180:1975–1978, discussion 1978–1979
Liss MA, Santos R, Osann K, Lau A, Ahlering TE, Ornstein DK (2010) PCA3 molecular urine assay for prostate cancer: association with pathologic features and impact of collection protocols. World J Urol. doi:10.1007/s00345-00010-00623-00346 (in press)
Oesterling JE, Jacobsen SJ, Chute CG, Guess HA, Girman CJ, Panser LA, Lieber MM (1993) Serum prostate-specific antigen in a community-based population of healthy men. Establishment of age-specific reference ranges. JAMA 270:860–864
Epstein JI, Allsbrook WC Jr, Amin MB, Egevad LL (2005) The 2005 international society of urological pathology (ISUP) consensus conference on gleason grading of prostatic carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 29:1228–1242
Vickers AJ, Elkin EB (2006) Decision curve analysis: a novel method for evaluating prediction models. Med Decis Making 26:565–574
Auprich M, Chun FK, Ward JF, Pummer K, Babaian R, Augustin H, Luger F, Gutschi S, Budaus L, Fisch M, Huland H, Graefen M, Haese A (2011) Critical assessment of preoperative urinary prostate cancer antigen 3 on the accuracy of prostate cancer staging. Eur Urol 59:96–105
Chun FK, de la Taille A, van Poppel H, Marberger M, Stenzl A, Mulders PF, Huland H, Abbou CC, Stillebroer AB, van Gils MP, Schalken JA, Fradet Y, Marks LS, Ellis W, Partin AW, Haese A (2009) Prostate cancer gene 3 (PCA3): development and internal validation of a novel biopsy nomogram. Eur Urol 56:659–667
Bianchi-Frias D, Vakar-Lopez F, Coleman IM, Plymate SR, Reed MJ, Nelson PS (2010) The effects of aging on the molecular and cellular composition of the prostate microenvironment. PLoS One 5:e12501
Morote J, Rigau M, Garcia M, Mir C, Ballesteros C, Planas J, Raventos CX, Placer J, de Torres IM, Reventos J, Doll A (2010) Behavior of the PCA3 gene in the urine of men with high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. World J Urol 28:677–680
Wang R, Chinnaiyan AM, Dunn RL, Wojno KJ, Wei JT (2009) Rational approach to implementation of prostate cancer antigen 3 into clinical care. Cancer 115:3879–3886
Lee MC, Moussa AS, Yu C, Kattan MW, Magi-Galluzzi C, Jones JS (2010) Multifocal high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia is a risk factor for subsequent prostate cancer. J Urol 184:1958–1962
Auprich M, Haese A, Walz J, Pummer K, de la Taille A, Graefen M, de Reijke T, Fisch M, Kil P, Gontero P, Irani J, Chun FK (2010) External validation of urinary PCA3-based nomograms to individually predict prostate biopsy outcome. Eur Urol 58:727–732
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klatte, T., Waldert, M., de Martino, M. et al. Age-specific PCA3 score reference values for diagnosis of prostate cancer. World J Urol 30, 405–410 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-011-0749-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-011-0749-1