Abstract
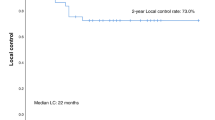
The treatment of unresectable “non-early” (according to the BCLC classification) hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in cirrhotic patients with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) followed by radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is retrospectively evaluated and possible prognostic factors of this combined therapy are investigated. Forty-six consecutive cirrhotic patients (Child-Pugh class A or B) with solitary or oligonodular HCC underwent RFA after TACE. The treated lesions were 51 overall (size 30–80 mm, mean 48.9). RFA was performed by a multitined expandable electrodes device after one TACE administration. Local efficacy was evaluated with multiphasic computed tomography (CT) performed an average of 2 months after treatment and then during follow-up. Patient survival rate was also evaluated (follow-up time 1–51 months, mean 15 months). Technical success (defined as complete devascularization during the arterial phase) was achieved in 34/51 lesions (66.7%) at the first CT check and in 29/51 (56.9%) during the succeeding follow-up. Among the considered prognostic factors, only lesion diameter (< or >=50 mm) was statistically significant in the Fisher's exact test in terms of local control (85.2 vs. 45.8% at first CT, p=.0065; 70.4 vs. 41.7% during follow-up, p=.051). There were two major complications (6.5%): one hepatic failure and one death. A Kaplan-Meier analysis showed survival rates of 89.7% at 12 months and 67.1% at 24 months. Combined therapy for non-early HCC shows a relatively high complete local response (especially in lesions less than 5 cm in diameter) and promising mid-term clinical success. Its overall usefulness has yet to be established by a larger series and risk-benefit analysis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
El-Serag HB (2002) Hepatocellular carcinoma: an epidemiologic view. J Clin Gastroenterol 35(5):s72–s78
Bruix J, Sherman M, Llovet JM et al (2001) Clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma: conclusions of the Barcelona-2000 EASL conference. J Hepatol 35:421–430
Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL et al (1973) Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg 60(8):646–649
Sobin LH, Wittekind Ch (eds) (1997) TNM classification of malignant tumours, 5h edn. Wiley, New York, pp 74–77
Okuda K, Ohtsuki T, Obata H et al (1985) Natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma and prognosis in relation to treatment: study of 850 patients. Cancer 56(4):918–928
Chevret S, Trinchet JC, Mathieu D, et al (1999) A new prognostic classification for predicting survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 31(1):133–141
The Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) investigators. (1998) A new prognostic system for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study of 435 patients. Hepatology 28(3):751–755
Llovet JM, Bruix J, Bru C (1999) Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: the BCLC staging classification. Semin Liver Dis 19(3):329–338
Lau W, Leung T, Yu S et al (2003) Percutaneous local ablative therapy for hepatocellualr carcinoma: a review and look into the future. Ann Surg 237(2):171–179
Rossi S, Buscarini E, Garbagnati F (1998) Percutaneous treatment of small hepatic tumors by an expandable RF needle electrode. Am J Roentgenol 170(4):1015–1022
Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Lazzaroni S et al (1999) Small hepatocellular carcinoma: treatment with radio-frequency ablation versus ethanol injection. Radiology 210(3):655–661
Dodd GD III, Soulen MC, Kane RA et al (2000) Minimally invasive treatment of malignant hepatic tumors: at the threshold of a major breakthrough. Radiographics 20(1):9–27
Livraghi T, Meloni F, Goldberg SN et al (2000) Hepatocellular carcinoma: radiofrequency ablation of medium and large lesions. Radiology 214:761–768
Gazelle GS, Goldberg SN, Solbiati L et al (2000) Tumor ablation with radio-frequency energy. Radiology 217:633–646
McGahan JF, Dodd GD III (2001) Radiofrequency ablation of the liver: current status. Am J Roentgenol 176(1):3–16
Dupuy DE, Goldberg SN (2001) Image-guided radiofrequency tumor ablation: challenges and opportunities, part II. J Vasc Interv Radiol 12(10):1135–1148
Lencioni R, Allgaier HP, Cioni D et al (2003) Small hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: randomized comparison of radio-frequency thermal ablation versus percutaneous ethanol injection. Radiology 228(1):235–240
Buscarini L, Buscarini E, Di Stasi M et al (2001) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of small hepatocellular carcinoma: long term results. Eur Radiol 11(6):914–921
Rossi S, Di Stasi M, Buscarini E et al (1996) Percutaneous US-guided RF tissue ablation in the treatment of hepatic cancer. Am J Roentgenol 167(3):759–768
Curley SA (2003) Radiofrequency ablation of malignant liver tumors. Ann Surg Oncol 10(4):338–347
Yamakado K, Nakatsuka A, Ohmori S et al (2002) Radiofrequency ablation combined with chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma: treatment response based on tumor size and morphology. J Vasc Interv Radiol 13(12):1225–1232
Maataoui A, Qian J, Vossoughi D et al (2005) Transarterial chemoembolization alone and in combination with other therapies: a comparative study in an animal HCC model. Eur Radiol 15:127–133
Buscarini E, Savoia A, Brambilla G et al (2005) Radiofrequency thermal ablation of liver tumors. Eur Radiol 15:884–894
Buscarini L, Buscarini E, Di Stasi M et al (1999) Percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation combined with transcatheter arterial embolization in the treatment of large hepatocellular carcinoma. Ultraschall Med 20(2):47–53
Lencioni R, Cioni D, Donati F et al (2001) Combination of interventional therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 48(37):8–14
Vogl TJ, Mack MG, Balzer JO et al (2003) Liver metastases: neoadjuvant downsizing with trans-arterial chemoembolization before laser-induced thermotheraphy. Radiology 229(2):457–464
Goldberg SN, Dupuy DE (2001) Image-guided radiofrequency tumor ablation: challenges and opportunities, part I. J Vasc Interv Radiol 12(9):1021–1032
Ahrar K, Newmann RA, Pang J et al (2004) 2004 Dr. Gary J. Becker Young Investigator Award: relative thermosensitivity of cytotoxic drugs used in transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. J Vascular Interv Radiol 15:901–905
Solbiati L, Tonolini M, Cova L (2004) Monitoring RF ablation. Eur Radiol 14(Suppl 8):34–42
Adam A, Hatzidakis A, Hamady M et al (2004) Percutaneous coil placement prior to radiofrequency ablation of poorly visible hepatic tumors. Eur Radiol 14:1688–1691
Hansler J, Frieser M, Schaber S et al (2003) Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma with a saline solution perfusion device: a pilot study. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14(5):575–580
Rossi S, Garbagnati F, Lencioni R et al (2000) Percutaneous radio-frequency thermal ablation of nonresectable hepatocellular carcinoma after occlusion of tumor blood supply. Radiology 217:119–126
Gaiani S, Piscaglia F, Celli N et al (2001) Percutaneous radio-frequency thermal ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: results and follow-up in primary and recurrent nodules. Hepatology 34(s):323
Veltri A, Barisone F, Falco M et al (2001) Local efficacy of radiofrequency thermal ablation (RITA) for newly diagnosed vs. recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Radiology 221(s):250
Vetter D, Wenger JJ, Bergier JM et al (1991) Transcatheter oily chemoembolization in the management of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: results of a western comparative study in 60 patients. Hepatology 13(3):427–433
Geschwind JFH (2001) Interventional Radiology. In: DeVita VT, Rosenberg SA, Hellmann S (eds). Cancer, principles and practice of oncology, 6th edn. Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 32–49
Cammà et al (2002) Transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Radiology 224:47–54
Geschwind JF, Ramsey DE, Choti MA et al (2003) Chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma: results of a metaanalysis. Am J Clin Oncol 26(4):344–349
Barbara L, Benzi G, Gaiani S et al (1992) Natural history of small untreated hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: a multivariate analysis of prognostic factors of tumor growth rate and patient survival. Hepatology 16(1):132–137
Llovet JM, Bustamante J, Castells A et al (1999) Natural history of untreated nonsurgical hepatocellular carcinoma: rationale for the design and evaluation of therapeutic trials. Hepatology 29(1):62–67
Bruix J, Llovet JM, Castells A et al (1998) Transarterial embolization versus symptomatic treatment in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: results of a randomised controlled trial in a single institution. Hepatology 27(6):1578–1583
Castells A, Bruix J, Bru C et al (1995) Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with tamoxifen: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial in 120 patients. Gastroenterology 109(3):917–922
Acknowledgement
The work of Eva Pagano was supported by the Compagnia di San Paolo, Special Project Oncology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veltri, A., Moretto, P., Doriguzzi, A. et al. Radiofrequency thermal ablation (RFA) after transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) as a combined therapy for unresectable non-early hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Eur Radiol 16, 661–669 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-0029-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-0029-9