Abstract
Purpose
Several studies have examined the prognostic value of the TP53 Arg72Pro polymorphism (rs1042522) and/or MDM2 SNP309 (rs2279744) in multiple tumors. Our aim was to determine whether these two genetic variants were correlated with clinical outcome of gastric cancer.
Methods
We genotyped the two SNPs, TP53 codon 72 polymorphism and MDM2 SNP309, in 940 gastric cancer patients with complete follow-up information and analyzed the correlation between the SNPs and gastric cancer survival.
Results
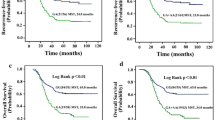
The two SNPs were not significantly associated with gastric cancer survival. However, the TP53 codon 72 polymorphism had a prominent correlation with clinical outcome of patients receiving 5-fluorouracil (5-Fu)-based postoperative chemotherapy [Arg/Arg + Arg/Pro vs. Pro/Pro, adjusted hazard ratio (HR) = 1.63, 95 % confidence interval (CI) = 1.08–2.44]. Moreover, the unfavorable effect of Arg allele on survival outcome was more predominant for subgroups of older (age >60 years), male, intestinal histology type, advanced stage (T3/T4), and none metastasis of lymph node (N0) or distant (M0) (adjusted HR = 2.34, 95 % CI = 1.24–4.44 for age >60 years; 1.72, 1.10–2.69 for male; 2.30, 1.10–4.80 for intestinal; 1.62, 1.01–2.59 for T3/T4; 3.42, 1.26–9.24 for N0; and 1.62, 1.06–2.47 for M0). Among multiple chemotherapy regimens, the association was only significant in the subgroup of 5-Fu/calcium folinate plus oxaliplatin (FOLFOX) chemotherapy regimen (adjusted HR = 4.47, 95 % CI = 1.21–16.55).
Conclusions
Our findings showed that TP53 codon 72 polymorphism was associated with survival of gastric cancer patients treated with 5-Fu-based postoperative chemotherapy. The codon 72 polymorphism may be a potential prognostic factor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang L (2006) Incidence and mortality of gastric cancer in China. World J Gastroenterol 12(1):17–20
Hartgrink HH, Jansen EP, van Grieken NC, van de Velde CJ (2009) Gastric cancer. Lancet 374(9688):477–490. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60617-6
Ludwig JA, Weinstein JN (2005) Biomarkers in cancer staging, prognosis and treatment selection. Nat Rev Cancer 5(11):845–856. doi:10.1038/nrc1739
Shi Y, Hu Z, Wu C, Dai J, Li H, Dong J, Wang M, Miao X, Zhou Y, Lu F, Zhang H, Hu L, Jiang Y, Li Z, Chu M, Ma H, Chen J, Jin G, Tan W, Wu T, Zhang Z, Lin D, Shen H (2011) A genome-wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for non-cardia gastric cancer at 3q13.31 and 5p13.1. Nat Genet. doi:10.1038/ng.978
Park SR, Kong SY, Nam BH, Choi IJ, Kim CG, Lee JY, Cho SJ, Kim YW, Ryu KW, Lee JH, Rhee J, Park YI, Kim NK (2011) CYP2A6 and ERCC1 polymorphisms correlate with efficacy of S-1 plus cisplatin in metastatic gastric cancer patients. Br J Cancer 104(7):1126–1134. doi:10.1038/bjc.2011.24
Yin M, Yan J, Martinez-Balibrea E, Graziano F, Lenz HJ, Kim HJ, Robert J, Im SA, Wang WS, Etienne-Grimaldi MC, Wei Q (2011) ERCC1 and ERCC2 polymorphisms predict clinical outcomes of oxaliplatin-based chemotherapies in gastric and colorectal cancer: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Clin Cancer Res 17(6):1632–1640. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2169
Vogelstein B, Lane D, Levine AJ (2000) Surfing the p53 network. Nature 408(6810):307–310. doi:10.1038/35042675
Olivier M, Hussain SP, de Caron Fromentel C, Hainaut P, Harris CC (2004) TP53 mutation spectra and load: a tool for generating hypotheses on the etiology of cancer. IARC Sci Publ 157:247–270
Fenoglio-Preiser CM, Wang J, Stemmermann GN, Noffsinger A (2003) TP53 and gastric carcinoma: a review. Hum Mutat 21(3):258–270. doi:10.1002/humu.10180
Chua HW, Ng D, Choo S, Lum SS, Li H, Soh LY, Sabapathy K, Seow A (2010) Effect of MDM2 SNP309 and p53 codon 72 polymorphisms on lung cancer risk and survival among non-smoking Chinese women in Singapore. BMC Cancer 10:88. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-10-88
Tang NP, Wu YM, Wang B, Ma J (2010) Systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between P53 codon 72 polymorphism and colorectal cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 36(5):431–438. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2010.03.010
Matakidou A, Eisen T, Houlston RS (2003) TP53 polymorphisms and lung cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mutagenesis 18(4):377–385
Francisco G, Menezes PR, Eluf-Neto J, Chammas R (2011) Arg72Pro TP53 polymorphism and cancer susceptibility: a comprehensive meta-analysis of 302 case-control studies. Int J Cancer 129(4):920–930. doi:10.1002/ijc.25710
Huang ZH, Hua D, Li LH, Zhu JD (2008) Prognostic role of p53 codon 72 polymorphism in gastric cancer patients treated with fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 134(10):1129–1134. doi:10.1007/s00432-008-0380-8
Huang ZH, Hua D, Du X (2009) Polymorphisms in p53, GSTP1 and XRCC1 predict relapse and survival of gastric cancer patients treated with oxaliplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 64(5):1001–1007. doi:10.1007/s00280-009-0956-2
Kim JG, Sohn SK, Chae YS, Song HS, Kwon KY, Do YR, Kim MK, Lee KH, Hyun MS, Lee WS, Sohn CH, Jung JS, Kim GC, Chung HY, Yu W (2009) TP53 codon 72 polymorphism associated with prognosis in patients with advanced gastric cancer treated with paclitaxel and cisplatin. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 64(2):355–360. doi:10.1007/s00280-008-0879-3
Momand J, Zambetti GP, Olson DC, George D, Levine AJ (1992) The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell 69(7):1237–1245
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A, Oren M (1997) Mdm2 promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature 387(6630):296–299. doi:10.1038/387296a0
Bond GL, Hu W, Bond EE, Robins H, Lutzker SG, Arva NC, Bargonetti J, Bartel F, Taubert H, Wuerl P, Onel K, Yip L, Hwang SJ, Strong LC, Lozano G, Levine AJ (2004) A single nucleotide polymorphism in the MDM2 promoter attenuates the p53 tumor suppressor pathway and accelerates tumor formation in humans. Cell 119(5):591–602. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.022
Hirata H, Hinoda Y, Kikuno N, Kawamoto K, Suehiro Y, Tanaka Y, Dahiya R (2007) MDM2 SNP309 polymorphism as risk factor for susceptibility and poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 13(14):4123–4129. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0609
Huang CY, Su CT, Chu JS, Huang SP, Pu YS, Yang HY, Chung CJ, Wu CC, Hsueh YM (2011) The polymorphisms of P53 codon 72 and MDM2 SNP309 and renal cell carcinoma risk in a low arsenic exposure area. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2011.09.018
Toffoli G, Biason P, Russo A, De Mattia E, Cecchin E, Hattinger CM, Pasello M, Alberghini M, Ferrari C, Scotlandi K, Picci P, Serra M (2009) Effect of TP53 Arg72Pro and MDM2 SNP309 polymorphisms on the risk of high-grade osteosarcoma development and survival. Clin Cancer Res 15(10):3550–3556. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2249
Yang M, Guo Y, Zhang X, Miao X, Tan W, Sun T, Zhao D, Yu D, Liu J, Lin D (2007) Interaction of P53 Arg72Pro and MDM2 T309G polymorphisms and their associations with risk of gastric cardia cancer. Carcinogenesis 28(9):1996–2001. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgm168
Ohmiya N, Taguchi A, Mabuchi N, Itoh A, Hirooka Y, Niwa Y, Goto H (2006) MDM2 promoter polymorphism is associated with both an increased susceptibility to gastric carcinoma and poor prognosis. J Clin Oncol 24(27):4434–4440. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.04.1459
Wang M, Bai J, Tan Y, Wang S, Tian Y, Gong W, Zhou Y, Gao Y, Zhou J, Zhang Z (2011) Genetic variant in PSCA predicts survival of diffuse-type gastric cancer in a Chinese population. Int J Cancer 129(5):1207–1213. doi:10.1002/ijc.25740
Greenland S, Rothman KJ (1998) Introduction to stratified analysis. Mod Epidemiol 2:253–279
Jackson JG, Pant V, Li Q, Chang LL, Quintas-Cardama A, Garza D, Tavana O, Yang P, Manshouri T, Li Y, El-Naggar AK, Lozano G (2012) p53-mediated senescence impairs the apoptotic response to chemotherapy and clinical outcome in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 21(6):793–806
Wang S, Li W, Xue Z, Lu Y, Narsinh K, Fan W, Li X, Bu Q, Wang F, Liang J, Wu K, Cao F (2012) Molecular imaging of p53 signal pathway in lung cancer cell cycle arrest induced by cisplatin. Mol Carcinog. doi:10.1002/mc.21930
El-Rifai W, Powell SM (2002) Molecular biology of gastric cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol 12(2):128–140. doi:10.1053/srao.2002.30815
Birch JM, Blair V, Kelsey AM, Evans DG, Harris M, Tricker KJ, Varley JM (1998) Cancer phenotype correlates with constitutional TP53 genotype in families with the Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Oncogene 17(9):1061–1068. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202033
Hrstka R, Coates PJ, Vojtesek B (2009) Polymorphisms in p53 and the p53 pathway: roles in cancer susceptibility and response to treatment. J Cell Mol Med 13(3):440–453. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00634.x
Tommiska J, Eerola H, Heinonen M, Salonen L, Kaare M, Tallila J, Ristimaki A, von Smitten K, Aittomaki K, Heikkila P, Blomqvist C, Nevanlinna H (2005) Breast cancer patients with p53 Pro72 homozygous genotype have a poorer survival. Clin Cancer Res 11(14):5098–5103. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0173
Xu Y, Yao L, Ouyang T, Li J, Wang T, Fan Z, Lin B, Lu Y, Xie Y (2005) p53 Codon 72 polymorphism predicts the pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11(20):7328–7333. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0507
Santos AM, Sousa H, Portela C, Pereira D, Pinto D, Catarino R, Rodrigues C, Araujo AP, Lopes C, Medeiros R (2006) TP53 and P21 polymorphisms: response to cisplatinum/paclitaxel-based chemotherapy in ovarian cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 340(1):256–262. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.11.176
Galic V, Willner J, Wollan M, Garg R, Garcia R, Goff BA, Gray HJ, Swisher EM (2007) Common polymorphisms in TP53 and MDM2 and the relationship to TP53 mutations and clinical outcomes in women with ovarian and peritoneal carcinomas. Genes Chromosom Cancer 46(3):239–247. doi:10.1002/gcc.20407
Han JY, Lee GK, Jang DH, Lee SY, Lee JS (2008) Association of p53 codon 72 polymorphism and MDM2 SNP309 with clinical outcome of advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer 113(4):799–807. doi:10.1002/cncr.23668
Katkoori VR, Jia X, Shanmugam C, Wan W, Meleth S, Bumpers H, Grizzle WE, Manne U (2009) Prognostic significance of p53 codon 72 polymorphism differs with race in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 15(7):2406–2416. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1719
Zhang ZW, Laurence NJ, Hollowood A, Newcomb P, Moorghen M, Gupta J, Feakins R, Farthing MJ, Alderson D, Holly J (2004) Prognostic value of TP53 codon 72 polymorphism in advanced gastric adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 10(1 Pt 1):131–135
Godai TI, Suda T, Sugano N, Tsuchida K, Shiozawa M, Sekiguchi H, Sekiyama A, Yoshihara M, Matsukuma S, Sakuma Y, Tsuchiya E, Kameda Y, Akaike M, Miyagi Y (2009) Identification of colorectal cancer patients with tumors carrying the TP53 mutation on the codon 72 proline allele that benefited most from 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) based postoperative chemotherapy. BMC Cancer 9:420. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-9-420
Dumont P, Leu JI, Della Pietra AC III, George DL, Murphy M (2003) The codon 72 polymorphic variants of p53 have markedly different apoptotic potential. Nat Genet 33(3):357–365. doi:10.1038/ng1093
Kerr JF, Winterford CM, Harmon BV (1994) Apoptosis. Its significance in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer 73(8):2013–2026
Stacey SN, Sulem P, Jonasdottir A, Masson G, Gudmundsson J, Gudbjartsson DF, Magnusson OT, Gudjonsson SA, Sigurgeirsson B, Thorisdottir K, Ragnarsson R, Benediktsdottir KR, Nexo BA, Tjonneland A, Overvad K, Rudnai P, Gurzau E, Koppova K, Hemminki K, Corredera C, Fuentelsaz V, Grasa P, Navarrete S, Fuertes F, Garcia-Prats MD, Sanambrosio E, Panadero A, De Juan A, Garcia A, Rivera F, Planelles D, Soriano V, Requena C, Aben KK, van Rossum MM, Cremers RG, van Oort IM, van Spronsen DJ, Schalken JA, Peters WH, Helfand BT, Donovan JL, Hamdy FC, Badescu D, Codreanu O, Jinga M, Csiki IE, Constantinescu V, Badea P, Mates IN, Dinu DE, Constantin A, Mates D, Kristjansdottir S, Agnarsson BA, Jonsson E, Barkardottir RB, Einarsson GV, Sigurdsson F, Moller PH, Stefansson T, Valdimarsson T, Johannsson OT, Sigurdsson H, Jonsson T, Jonasson JG, Tryggvadottir L, Rice T, Hansen HM, Xiao Y, Lachance DH, BP ON, Kosel ML, Decker PA, Thorleifsson G, Johannsdottir H, Helgadottir HT, Sigurdsson A, Steinthorsdottir V, Lindblom A, Sandler RS, Keku TO, Banasik K, Jorgensen T, Witte DR, Hansen T, Pedersen O, Jinga V, Neal DE, Catalona WJ, Wrensch M, Wiencke J, Jenkins RB, Nagore E, Vogel U, Kiemeney LA, Kumar R, Mayordomo JI, Olafsson JH, Kong A, Thorsteinsdottir U, Rafnar T, Stefansson K (2011) A germline variant in the TP53 polyadenylation signal confers cancer susceptibility. Nat Genet 43(11):1098–1103. doi:10.1038/ng.926
Hof J, Krentz S, van Schewick C, Korner G, Shalapour S, Rhein P, Karawajew L, Ludwig WD, Seeger K, Henze G, von Stackelberg A, Hagemeier C, Eckert C, Kirschner-Schwabe R (2011) Mutations and deletions of the TP53 gene predict nonresponse to treatment and poor outcome in first relapse of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 29(23):3185–3193. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.34.8144
Blumrich A, Zapatka M, Brueckner LM, Zheglo D, Schwab M, Savelyeva L (2011) The FRA2C common fragile site maps to the borders of MYCN amplicons in neuroblastoma and is associated with gross chromosomal rearrangements in different cancers. Hum Mol Genet 20(8):1488–1501. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddr027
Rakyan VK, Down TA, Balding DJ, Beck S (2011) Epigenome-wide association studies for common human diseases. Nat Rev Genet 12(8):529–541. doi:10.1038/nrg3000
Zhang W, Winder T, Ning Y, Pohl A, Yang D, Kahn M, Lurje G, Labonte MJ, Wilson PM, Gordon MA, Hu-Lieskovan S, Mauro DJ, Langer C, Rowinsky EK, Lenz HJ (2011) A let-7 microRNA-binding site polymorphism in 3′-untranslated region of KRAS gene predicts response in wild-type KRAS patients with metastatic colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab monotherapy. Ann oncol: off J Eur Soc Med Oncol/ESMO 22(1):104–109. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdq315
Sun Q, Gu H, Zeng Y, Xia Y, Wang Y, Jing Y, Yang L, Wang B (2010) Hsa-mir-27a genetic variant contributes to gastric cancer susceptibility through affecting miR-27a and target gene expression. Cancer Sci 101(10):2241–2247. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01667.x
Gschwend JE, Dahm P, Fair WR (2002) Disease specific survival as endpoint of outcome for bladder cancer patients following radical cystectomy. Eur Urol 41(4):440–448
Winder T, Zhang W, Yang D, Ning Y, Bohanes P, Gerger A, Wilson PM, Pohl A, Mauro DJ, Langer C, Rowinsky EK, Lenz HJ (2010) Germline polymorphisms in genes involved in the IGF1 pathway predict efficacy of cetuximab in wild-type KRAS mCRC patients. Clin Cancer Res 16(22):5591–5602. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2092
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81230068, 30972444, 81001274, and 81102089), the Undergraduates Practice and Innovation Program of Higher School in Jiangsu Province, the Key Program of Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK2010080), National Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK2011773 and BK2012842), the Key Program for Basic Research of Jiangsu Provincial Department of Education (11KJB330002 and 12KJA330002), the Qing-Lan Project of Jiangsu Provincial Department of Education, and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (Public Health and Preventive Medicine). We thank Yanyan Zhu, Weiwei Zhuang, Hanying Lu, and Mao Liu for participating part of epidemiology investigation and experiments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests exist in relation to the publication of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Shizi Wang, Lulu Chen and Qinghong Zhao contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Chen, L., Zhao, Q. et al. Effect of TP53 codon 72 and MDM2 SNP309 polymorphisms on survival of gastric cancer among patients who receiving 5-fluorouracil-based postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 71, 1073–1082 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2103-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2103-3