Abstract
Purpose
This study was designed to identify parameters on CT angiography (CTA) of type II endoleaks following endovascular aortic aneurysm repair (EVAR) for abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), which can be used to predict the subsequent need for reinterventions.
Methods
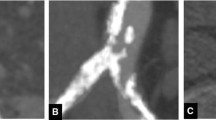
We retrospectively identified 62 patients with type II endoleak who underwent early CTA in mean 3.7 ± 1.9 days after EVAR. On the basis of follow-up examinations (mean follow-up period 911 days; range, 373–1,987 days), patients were stratified into two groups: those who did (n = 18) and those who did not (n = 44) require reintervention. CTA characteristics, such as AAA, endoleak, as well as nidus dimensions, patency of the inferior mesenteric artery, number of aortic branch vessels, and the pattern of endoleak appearance, were recorded and correlated with the clinical outcome.
Results
Univariate and receiver operating characteristic curve regression analyses revealed significant differences between the two groups for the endoleak volume (surveillance group: 1391.6 ± 1427.9 mm3; reintervention group: 3227.7 ± 2693.8 mm3; cutoff value of 2,386 mm3; p = 0.002), the endoleak diameter (13.6 ± 4.3 mm compared with 25.9 ± 9.6 mm; cutoff value of 19 mm; p < 0.0001), the number of aortic branch vessels (2.9 ± 1.2 compared with 4.2 ± 1.4 vessels; p = 0.001), as well as a “complex type” endoleak pattern (13.6 %, n = 6 compared with 44.4 %, n = 8; p = 0.02).
Conclusions
Early CTA can predict the future need for reintervention in patients with type II endoleak. Therefore, treatment decision should be based not only on aneurysm enlargement alone but also on other imaging characteristics.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schlosser FJ, Muhs BE (2012) Endoleaks after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: what one needs to know. Curr Opin Cardiol 27(6):598–603
Buth J, Harris PL, van Marrewijk MC, Fransen G (2003) The significance and management of different types of endoleaks. Semin Vasc Surg 16(2):95–102
Hobo R, Buth J (2006) Secondary interventions following endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair using current endografts. A EUROSTAR report. J Vasc Surg 43(5):896–902
Rhee SJ, Ohki T, Veith FJ, Kurvers H (2003) Current status of management of type II endoleaks after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Ann Vasc Surg 17(3):335–344
Patatas K, Ling L, Dunning J, Shrivastava V (2012) Static sac size with a type II endoleak post-endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: surveillance or embolization? Interact CardioVasc Thorac Surg 15(3):462–466
Silverberg D, Baril DT, Ellozy SH et al (2006) An 8-year experience with type II endoleaks: natural history suggests selective intervention is a safe approach. J Vasc Surg 44(3):453–459
Parent FN, Meier GH, Godziachvili V et al (2002) The incidence and natural history of type I and II endoleak: a 5-year follow-up assessment with color duplex ultrasound scan. J Vasc Surg 35(3):474–481
Jones JE, Atkins MD, Brewster DC et al (2007) Persistent type 2 endoleak after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm is associated with adverse late outcomes. J Vasc Surg 46(1):1–8
Zarins CK, White RA, Hodgson KJ, Schwarten D, Fogarty TJ (2000) Endoleak as a predictor of outcome after endovascular aneurysm repair: AneuRx multicenter clinical trial. J Vasc Surg 32(1):90–107
Timaran CH, Ohki T, Rhee SJ et al (2004) Predicting aneurysm enlargement in patients with persistent type II endoleaks. J Vasc Surg 39(6):1157–1162
van Marrewijk MC, Buth J, Harris PL, Norgren L, Nevelsteen A, Wyatt MG (2002) Significance of endoleaks after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms: The EUROSTAR experience. J Vasc Surg 35(3):461–473
Keedy AW, Yeh BM, Kohr JR, Hiramoto JS, Schneider DB, Breiman RS (2011) Evaluation of potential outcome predictors in type II Endoleak: a retrospective study with CT angiography feature analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 197(1):234–240
van Marrewijk CJ, Fransen G, Laheij RJ, Harris PL, Buth J (2004) Is a type II endoleak after EVAR a harbinger of risk? Causes and outcome of open conversion and aneurysm rupture during follow-up. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 27(2):128–137
Bargellini I, Napoli V, Petruzzi P et al (2005) Type II lumbar endoleaks: hemodynamic differentiation by contrast-enhanced ultrasound scanning and influence on aneurysm enlargement after endovascular aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg 41(1):10–18
Muller-Wille R, Wohlgemuth WA, Heiss P et al (2013) Transarterial embolization of type II endoleaks after EVAR: the role of ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer (Onyx). Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 36(5):1288–1295
Gorlitzer M, Mertikian G, Trnka H et al (2008) Translumbar treatment of type II endoleaks after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Interact CardioVasc Thorac Surg 7(5):781–784
Dudeck O, Jurczyk K, Abdo G et al (2005) Volume determination of intracranial aneurysms using 16-row multislice computed tomography angiography: a systematic in vitro analysis of different reconstruction methods. J Comput Assist Tomogr 29(6):851–857
Veith FJ, Baum RA, Ohki T et al (2002) Nature and significance of endoleaks and endotension: summary of opinions expressed at an international conference. J Vasc Surg 35(5):1029–1035
Mees B, Voute M, Bastos GF, Mota CL, Verhagen H (2013) Intervention for type II endoleaks? “Primum non nocere”: appraisal for the conservative management of low-pressure endoleaks after endovascular aneurysm repair. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 54(4):477–484
Karthikesalingam A, Thrumurthy SG, Jackson D et al (2012) Current evidence is insufficient to define an optimal threshold for intervention in isolated type II endoleak after endovascular aneurysm repair. J Endovasc Ther 19(2):200–208
Chaikof EL, Blankensteijn JD, Harris PL et al (2002) Reporting standards for endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg 35(5):1048–1060
Fan CM, Rafferty EA, Geller SC et al (2001) Endovascular stent-graft in abdominal aortic aneurysms: the relationship between patent vessels that arise from the aneurysmal sac and early endoleak. Radiology 218(1):176–182
Brountzos E, Karagiannis G, Panagiotou I, Tzavara C, Efstathopoulos E, Kelekis N (2012) Risk factors for the development of persistent type II endoleaks after endovascular repair of infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysms. Diagn Interv Radiol 18(3):307–313
Ward TJ, Cohen S, Patel RS et al (2013) Anatomic risk factors for type-2 endoleak following EVAR: a retrospective review of preoperative CT angiography in 326 patients. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 37(2):324–328
Pitton MB, Scheschkowski T, Ring M et al (2009) Ten-year follow-up of endovascular aneurysm treatment with Talent stent-grafts. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 32(5):906–917
Torsello G, Osada N, Florek HJ et al (2006) Long-term outcome after Talent endograft implantation for aneurysms of the abdominal aorta: a multicenter retrospective study. J Vasc Surg 43(2):277–284
Gould DA, McWilliams R, Edwards RD et al (2001) Aortic side branch embolization before endovascular aneurysm repair: incidence of type II endoleak. J Vasc Interv Radiol 12(3):337–341
Petrik PV, Moore WS (2001) Endoleaks following endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm: the predictive value of preoperative anatomic factors: a review of 100 cases. J Vasc Surg 33(4):739–744
Alerci M, Giamboni A, Wyttenbach R et al (2013) Endovascular abdominal aneurysm repair and impact of systematic preoperative embolization of collateral arteries: endoleak analysis and long-term follow-up. J Endovasc Ther 20(5):663–671
Habets J, Zandvoort HJ, Reitsma JB et al (2013) Magnetic resonance imaging is more sensitive than computed tomography angiography for the detection of endoleaks after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: a systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 45(4):340–350
Conflict of interest
Dudeck O, Schnapauff D, Herzog L, Löwenthal D, Bulla K, Rogits B, Halloul Z, Meyer F, Pech M, Gebauer B, Ricke J have no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures to report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
O. Dudeck and D. Schnapauff have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dudeck, O., Schnapauff, D., Herzog, L. et al. Can Early Computed Tomography Angiography after Endovascular Aortic Aneurysm Repair Predict the Need for Reintervention in Patients with Type II Endoleak?. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 38, 45–52 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-014-0901-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-014-0901-6