Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of shear wave elastography (SWE) and transient elastography (TE) in the evaluation of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B (CHB) and C (CHC) patients taking liver biopsy as gold standard.
Methods
Ethics committee approved this prospective cross-sectional study. Between October 2012 and December 2014, consecutive CHB/CHC patients fulfilling the inclusion criteria were included—age more than 18 years, informed written consent, willing and suitable for liver biopsy. SWE, TE, and biopsy were performed the same day. Liver stiffness measurement (LSM) cut-offs for various stages of fibrosis were generated for SWE and TE. AUC, sensitivity, specificity, and positive/negative predictive values were estimated individually or in combination.
Results
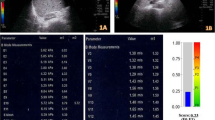
CH patients (n = 240, CHB 172, CHC 68), 176 males, 64 females, mean age 32.6 ± 11.6 years were enrolled. Mean LSM of patients with no histological fibrosis (F0) was 5.0 ± 0.7 and 5.1+1.4 kPa on SWE and TE, respectively. For differentiating F2 and F3–4 fibrosis on SWE, at 7.0 kPa cut-off, the sensitivity was 81.3% and specificity 77.6%. For TE, at 8.3 kPa cut-off, sensitivity was 81.8% and specificity 83.1%. For F3 vs. F4, SWE sensitivity was 83.3% and specificity 90.7%. At 14.8 kPa cut-off, TE showed similar sensitivity (83.3%) but specificity increased to 96.5%. Significant correlation between SWE and TE was observed (r = 0.33, p < 0.001). On combining SWE and TE, a drop in sensitivity with increased specificity for all stages of liver fibrosis occured.
Conclusion
SWE is an accurate technique for evaluating liver fibrosis. SWE compares favorably with TE especially for predicting advanced fibrosis/cirrhosis. Combining SWE and TE further improves specificity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rockey DC (2005) Anti fibrotic therapy in chronic liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:95–107
Rockey DC, Bissell DM (2006) Noninvasive measures of liver fibrosis. Hepatology 43:S113–S120
Bataller R, Brenner DA (2005) Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest 115:209–218
Friedman SL (2003) Liver fibrosis: from bench to bedside. J Hepatol 38:S38–S53
Zeuzem S (2004) Standard treatment in acute and chronic hepatitis C. Z Gastroenterol 42:714–719
Fleig WE, Krummener P, Lesske J, et al. (2004) Diagnosis, progression and therapy of hepatitis C virus infection as well as viral infection in children and adolescents: results of an evidence based consensus conference of the German society for Alimentary Metabolic Disorders and in cooperation with the Hepatitis Competence Network. Z Gastroenterol 42:703–704
Cadranel JF, Rufat P, Degos F (2000) Practices of liver biopsy in France: results of a prospective nationwide survey. For the Group of Epidemiology of the French Association for the Study of the Liver (AFEF). Hepatology 32:477–481
Castéra L, Nègre I, Samii K, Buffet C (1999) Pain experienced during percutaneous liver biopsy. Hepatology 30:1529–1530
Maharaj B, Maharaj RJ, Leary WP, et al. (1986) Sampling variability and its influence on the diagnostic yield of percutaneous needle biopsy of the liver. Lancet 1:523–525
Regev A, Berho M, Jeffers LJ, et al. (2002) Sampling error and intraobserver variation in liver biopsy in patients with chronic HCV infection. Am J Gastroenterol 97:2614–2618
Ferraioli G, Filice C, Castera L, et al. (2015) WFUMB guidelines and recommendations for clinical use of ultrasound elastography. Part 3: liver. Ultrasound Med Biol 41:1161–1179
Tatsumi C, Kudo M, Ueshima K, et al. (2008) Noninvasive evaluation of hepatic fibrosis using serum fibrotic markers, transient elastography (FibroScan) and real-time tissue elastography. Intervirology 51:27–33
Friedrich-Rust M, Ong MF, Herrmann E, et al. (2007) Real-time elastography for noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis in chronic viral hepatitis. Am J Roentgenol 188:758–764
Samir AE, Dhyani M, Vij A, et al. (2015) Shear-wave elastography for the estimation of liver fibrosis in chronic liver disease: determining accuracy and ideal site for measurement. Radiology 274:888–896
Chung JH, Ahn HS, Kim SG, et al. (2013) The usefulness of transient elastography, acoustic-radiation-force impulse elastography, and real-time elastography for the evaluation of liver fibrosis. Clin Mol Hepatol 19:156–164
Li C, Zhang C, Li J, Huo H, Song D (2016) Diagnostic accuracy of real-time shear wave elastography for staging of liver fibrosis: a meta-analysis. Med Sci Monit 22:1349–1359
Acharya SK, Madan K, Dattagupta S, Panda SK (2006) Viral hepatitis in India. Natl Med J India 19:203–217
Batham A, Narula D, Toteja T, Sreenivas V, Puliyel JM (2007) Sytematic review and meta-analysis of prevalence of hepatitis B in India. Indian Pediatr 44:663–674
Boozari B, Potthoff A, Mederacke I, et al. (2010) Evaluation of sound speed for detection of liver fibrosis: prospective comparison with transient dynamic elastography and histology. J Ultrasound Med 29:1581–1588
Jeong JY, Kim TY, Sohn JH, et al. (2014) Real time shear wave elastography in chronic liver diseases: accuracy for predicting liver fibrosis, in comparison with serum markers. World J Gastroenterol 20:13920–13929
Yoon JH, Lee JM, Joo I, et al. (2014) Hepatic fibrosis: prospective comparison of MR elastography and US shear-wave elastography for evaluation. Radiology 273:772–782
Zheng J, Guo H, Zeng J, et al. (2015) Two-dimensional shear-wave elastography and conventional US: the optimal evaluation of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Radiology 275:290–300
Ferraioli G, Tinelli C, Dal Bello B, et al. (2012) Liver Fibrosis Study Group. Accuracy of real-time shear wave elastography for assessing liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C: a pilot study. Hepatology 56:2125–2133
Bavu E, Gennisson JL, Couade M, et al. (2011) Noninvasive in vivo liver fibrosis evaluation using supersonic shear imaging: a clinical study on 113 hepatitis C virus patients. Ultrasound Med Biol 37:1361–1373
Leung VY, Shen J, Wong VW, et al. (2013) Quantitative elastography of liver fibrosis and spleen stiffness in chronic hepatitis B carriers: comparison of shear-wave elastography and transient elastography with liver biopsy correlation. Radiology 269:910–918
Zeng J, Liu GJ, Huang ZP, et al. (2014) Diagnostic accuracy of two-dimensional shear wave elastography for the non-invasive staging of hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B: a cohort study with internal validation. Eur Radiol 24:2572–2581
Cassinotto C, Lapuyade B, Mouries A, et al. (2014) Non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis with impulse elastography: comparison of supersonic shear imaging with ARFI and Fibroscan. J Hepatol 61:550–557
Barr RG, Ferraioli G, Palmeri ML, et al. (2015) Elastography assessment of liver fibrosis: society of radiologists in ultrasound consensus conference statement. Radiology 276:845–861
Cosgrove D, Piscaglia F, Bamber J, et al. (2013) EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography. Part 2: clinical applications. Ultraschall Med 34:238–253
Goyal R, Mallick SR, Mahanta M, et al. (2013) Fibroscan can avoid liver biopsy in Indian patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 28:1738–1745
Suh CH, Kim SY, Kim KW, et al. (2014) Determination of normal hepatic elasticity by using real-time shear-wave elastography. Radiology 271:895–900
Ferraioli G, Tinelli C, Zicchetti M, et al. (2012) Reproducibility of real-time shear wave elastography in the evaluation of liver elasticity. Eur J Radiol 81:3102–3106
Muller M, Gennisson JL, Deffieux T, Tanter M, Fink M (2009) Quantitative viscoelasticity mapping of human liver using supersonic shear imaging: preliminary in vivo feasibility study. Ultrasound Med Biol 35:219–229
Strader DB, Wright T, Thomas DL, Seeff LB (2004) American Association for the study of liver diseases. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C. Hepatology 39:1147–1171
Feng JC, Li J, Wu XW, Peng XY (2016) Diagnostic accuracy of supersonic shear imaging for staging of liver fibrosis: a meta-analysis. J Ultrasound Med 35:329–339
Tsochatzis EA, Gurusamy KS, Ntaoula S, et al. (2011) Elastography for the diagnosis of severity of fibrosis in chronic liver disease: a meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy. J Hepatol 54:650–659
Poynard T, Pham T, Perazzo H, et al. (2016) Real-time shear wave versus transient elastography for predicting fibrosis: applicability, and impact of inflammation and steatosis. A non-invasive comparison. PLoS ONE. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0163276
Kim HJ, Lee HK, Cho JH, Yang HJ (2015) Quantitative comparison of transient elastography (TE), shear wave elastography (SWE) and liver biopsy results of patients with chronic liver disease. J Phys Ther Sci 26:2465–2468
Poynard T, Munteanu M, Luckina E, et al. (2013) Liver fibrosis evaluation using real-time shear wave elastography: applicability and diagnostic performance using methods without a gold standard. J Hepatol 58:928–935
Acknowledgments
Authors want to acknowledge Mr. Sanjeev Negi and Mr. Dilshad Ali, the research staff, for handling the data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was performed after approval from the Ethics committee of our institute and all procedures performed on human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards.
Informed consent
A written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, S.B., Das, P., Mahanta, M. et al. Assessment of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis: comparison of shear wave elastography and transient elastography. Abdom Radiol 42, 2864–2873 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-017-1213-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-017-1213-5