Abstract
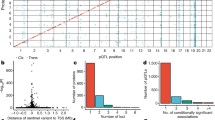
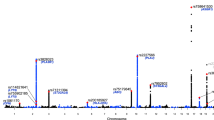
Factor H is a plasma protein that plays a critical role in the regulation of complement activation in fluid phase and on cellular surfaces. Over the years numerous reports have illustrated the association of factor H deficiencies with chronic renal and infectious diseases. Plasma levels of factor H show a five-fold range of variation in humans (116–562 μg/ml), which may also be relevant to disease susceptibility. To quantify the effects of the genetic and environmental factors responsible for the variation in the factor H plasma levels, we have applied variance-component methods to a family-based sample. Factor H plasma levels show an age-dependent increase (P<0.0001) and are decreased in smokers (P<0.0001). Interestingly, the heritability of the factor H trait is very high (h 2=0.62±0.07; P<0.0001), indicating that 62% of the factor H phenotypic variance is due to the additive effects of genes. On this premise, we conducted a genome-wide linkage screen in order to identify genes regulating the factor H trait. Three genomic regions (1q32, 2p21–24 and 15q22–24) provided suggestive evidence of linkage (LOD scores 2.03, 2.15 and 2.00, respectively) with the plasma levels of factor H.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison DB, Neale MC, Zannolli R, Schork NJ, Amos CI, Blangero J (1999) Testing the robustness oh the likelihood-ratio test in a variance-component quantitative-trait loci-mapping procedure. Am J Hum Genet 65:531–544
Almasy L, Blangero J (1998) Multipoint quantitative trait analysis in general pedigrees. Am J Hum Genet 62:1198–1211
Almasy L, Soria JM, Souto JC, Coll I, Bacq D, Faure A, Mateo J, Borrel M, Muñoz X, Sala N, Stone WH, Lathrop M, Fontcuberta J, Blangero J (2003) A quantitative trait locus influencing free PS plasma levels on human chromosome 1q. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:508–511
Ault BH (2000) Factor H and the pathogenesis of renal diseases. Pediatr Nephrol 14:1045–1053
Blangero J, Williams JT, Almasy L (2000) Robust LOD scores for variance component-based linkage analysis. Genet Epidemiol 19 (Suppl 1):S8–S14
Boehnke M, Lange K (1984) Ascertainment and goodness of fit of variance component models for pedigree data. Prog Clin Biol Res 147:173–192
Caprioli J, Bettinaglio P, Zipfel PF, Amadei B, Daina E, Gamba S, Skerka C, Marziliano N, Remuzzi G, Noris M (2001) The molecular basis of familial hemolytic uremic syndrome: mutation analysis of factor H gene reveals a hot spot in short consensus repeat 20. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:297–307
Davis CA, Vallota EH, Forristal EJ (1979) Serum complement levels in infancy: age related changes. Pediatr Res 13:1043–1046
Dyke B (1995) PEDSYS: a pedigree data management system. User’s manual. PGL Tech rep 2. Population laboratory, Department of Genetics, Southwest Foundation for Biomedical Research, San Antonio
Esparza-Gordillo J, Soria JM, Buil A, Souto JC, Almasy L, Blangero J, Fontcuberta J, Rodríguez de Córdoba S (2003) Genetic determinants of variation in the plasma levels of the C4b-Binding protein (C4BP) in Spanish families. Immunogenetics 54:862–866
Fearon DT (1978) Regulation by membrane sialic acid of beta1H-dependent decay-dissociation of amplification C3 convertase of the alternative complement pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:1971–1975
Fijen CA, Kuijper EJ, Te Bulte M, van de Heuvel MM, Holdrinet AC, Sim RB, Daha MR, Dankert J (1996) Heterozygous and homozygous factor H deficiency states in a Dutch family. Clin Exp Immunol 105:511–516
Hopper JL, Mathews JD (1982) Extensions to multivariate normal model for pedigree analysis. Ann Hum Genet 46:373–383
Meri S, Pangburn MK (1990) Discrimination between activators and nonactivators of the alternative pathway of complement: regulation via a sialic acid/polyanion binding site on factor H. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:3982–3986
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acid Res 6:1215–1219
Nilsson UR, Mueller-Eberhard HJ (1965) Isolation of Beta IF-Globulin from human serum and its characterization as the fifth component of complement. J Exp Med 122:277–298
Pangburn MK, Schreiber RD, Muller-Eberhard HJ (1977) Human complement C3b inactivator: isolation, characterization, and demonstration of an absolute requirement for the serum protein β1H for cleavage C3b and C4b in solution. J Exp Med 146:257–270
Pangburn MK, Atkinson MA, Meri S (1991) Localization of the heparin-binding site on complement factor H. J Biol Chem 266:16847–16853
Pérez-Caballero D, González-Rubio C, Gallardo ME, Vera M, López-Trascasa M, Rodríguez de Córdoba S, Sánchez-Corral P (2001) Clustering of missense mutations in the C-terminal region of factor H in atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 68:478–484
Reid KBM, Day AJ (1989) Structure-function relationships of the complement components. Immunol Today 10:177–180
Richards A, Buddles MR, Donne RL, Kaplan BS, Kirk E, Venning MC, Tielemans CL, Goodship JA, Goodship TH (2001) Factor H mutations in hemolytic uremic syndrome cluster in exons 18–20, a domain important for host cell recognition. Am J Hum Genet 68:485–490
Richards A, Kemp EJ, Liszewski MK, Goodship JA, Wen LS, Atkinson JP, Goodship THJ ( 2003) Familial haemolytic uraemic syndrome and mutations in membrane cofactor protein (MCP; CD46) of the complement system. Mol Immunol 40:192
Ripoche J, Day AJ, Harris TJR, Sim RB (1988) The complete amino acid sequence of human complement factor H. Biochem J 249:593–602
Rodríguez de Córdoba S, Rubinstein P (1986) Quantitative variation of the C3b/C4b receptor (CR1) in human erythrocytes are controlled by genes within the Regulator of Complement Activation (RCA) gene cluster. J Exp Med 164:1274–1283
Rodríguez de Córdoba S, Lublin DM, Rubinstein P, Atkinson JP (1985) Human genes for three complement components that regulate the activation of C3 are tightly linked. J Exp Med 161:1189–1195
Rodríguez de Córdoba S, Díaz-Guillen MA, Heine-Suñer D (1999) An integrated map of the human regulator of complement activation (RCA) gene cluster on 1q32. Mol Immunol 36:803–808
Rougier N, Kazatchkine MD, Rougier JP, Fremeaux-Bacchi V, Blouin J, Deschenes G, Soto B, Baudouin V, Pautard B, Proesmans W, Weiss E, Weiss L (1998) Human complement factor H deficiency associated with hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:2318–2326
Sánchez-Corral P, Criado Garcia O, Rodríguez de Córdoba S (1995) Isoforms of human C4b-Binding Protein. I. Molecular basis for the C4BP isoform pattern and its variation in human plasma. J Immunol 155:4030–4036
Sánchez-Corral P, Pérez-Caballero D, Huarte O, Simckes AM, Goicoechea E, López-Trascasa M, Rodríguez de Córdoba S (2002) Structural and functional characterization of factor H mutations associated with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 71:1285–1295
Schreiber RD, Pangburn MK, Lesavre PH, Müller-Eberhard HJ (1978) Initiation if the alternative pathway of complement: Recognition of activators by bound C3b and assembly of the entire pathway from six isolated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:3948–3952
Self SG, Liang KY (1987) Asymptotic properties of maximum likelihood estimators and likelihood ratio tests under non-standard conditions. J Am Stat Assoc 82:605–610
Sonntag J, Brandenburg U, Polzehl D, Struass E, Vogel M, Dudenhausen JW, Oblade M. (1998) Complement system in healthy term newborns: reference values in umbilical cord blood. Pediatr Dev Pathol 1:131–135
Soria JM, Almasy L, Souto JC, Tirado I, Borell M, Mateo J, Slifer S, Stone W, Blangero J, Fontcuberta J (2000) Linkage analysis demonstrates that the prothrombin G20210A mutation jointly influences plasma prothrombin levels and risk of thrombosis. Blood 95:2780–2785
Soria JM, Almasy L, Souto JC, Buil A, Martínez-Sánchez E, Mateo J, Borell M, Stone WH, Lathrop M, Fontcuberta J, Blangero J (2003) A new locus on chromosome 18 that influences normal variation in Activated Protein C Resistance phenotype and factor VIII activity and it’s relation to thrombosis susceptibility. Blood 101:163–167
Souto JC, Almasy L, Borrell M, Garí M, Martínez E, Mateo J, Stone WH, Blangero J, Fontcuberta J (2000) Genetic determinants of hemostasis phenotypes in Spanish families. Circulation 101:1546–1551
Schreiber RD, Pangburn MK, Lesavre PH, Muller-Eberhard HJ (1978) Initiation of the alternative pathway of complement: recognition of activators by bound C3b and assembly of the entire pathway from six isolated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:3948–3952
Warwicker P, Goodship TH, Donne RL, Pirson Y, Nicholls A, Ward RM, Turnpenny P, Goodship JA (1998) Genetic studies into inherited and sporadic hemolytic uremic syndrome. Kidney Int 53:836–844
Weiler JM, Daha MR, Austen KF, Fearon DT (1976) Control of the amplification convertase of complement by the plasma protein beta1H. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:3268–3272
Weis JH, Morton CC, Bruns GA, Weis JJ, Klickstein LB, Wong WW, Fearon DT (1987) A complement receptor locus: genes encoding C3b/C4b receptor and C3d/Epstein-Barr virus receptor map to 1q32. J Immunol 138:312–315
Whaley K, Ruddy S (1976) Modulation of the alternative complement pathways by beta 1 H globulin. J Exp Med 144:1147–1163
Whaley K, Thompson RA (1978) Requirements for β1H globulin and C3b inactivator in the control of the alternative complement pathway in human serum. Immunology 35:1045–1049
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants NIH USA HL70751, FIS 02/0375 from the Fondo Investigación Sanitaria, SAF2002/03449 and SAF2002/01083 from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Technology, 08.6/0028.1/2000 from the Comunidad de Madrid, Fundació “La Caixa” and Fundació de Investgació Sant Pau. Dr. J.M. Soria was supported by the FIS 99/3048 grant from the Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria. J. Esparza-Gordillo was supported by a grant from the Comunidad Autónoma de Madrid. A. Buil was supported by the FIS 01/A046 grant from the Fondo Investigación Sanitaria. We are deeply grateful to the families that participated in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esparza-Gordillo, J., Soria, J.M., Buil, A. et al. Genetic and environmental factors influencing the human factor H plasma levels. Immunogenetics 56, 77–82 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-004-0660-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-004-0660-7