Abstract
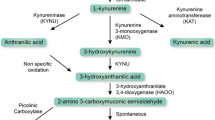
Kynurenic acid (KynA), a broad spectrum antagonist of excitatory amino acid receptors, may serve as a protective agent in neurological disorders. The potential anti-inflammatory effect of KynA in human leukocytes has not been characterized. The aim of this study was to compare the effects of KynA with those of a new analogue, 2-(2-N,N-dimethylaminoethylamine-1-carbonyl)-1H-quinolin-4-one hydrochloride on tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) production and high mobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1) secretion. The effects of KynA on granulocyte activation were investigated via the secretion of human neutrophil peptide 1–3 (HNP1–3). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells and granulocytes or CD14 positive monocytes were applied as effector cells, or whole blood cultures were used. TNF-α, HMGB1 and HNP1–3 concentrations were determined by ELISA, TNF-α and HNP1–3 mRNA expressions were quantified by reverse transcription PCR. KynA attenuated the TNF-α production of human mononuclear cells activated by heat-inactivated Staphylococcus aureus, inhibiting TNF-α production at the transcription level. Furthermore, KynA diminished HMGB1 secretion by U 937 monocytic cells and by peripheral blood monocytes. KynA inhibited the HNP1–3 secretion in whole blood and in granulocyte cultures. The suppressive effect of the KynA analogue was more potent than that of an equimolar concentration KynA in TNF-α, HMGB1 and HNP1–3 inhibition. These results suggest that the new KynA analogue has a more potent immunoregulatory effect than KynA on human mononuclear cells, monocytes and granulocytes and indicate the potential benefits of further exploration of its uses in human inflammatory disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson U, Wang HC, Palmblad K, Aveberger AC, Bloom O, Erlandsson-Harris H, Janson A, Kokkola R, Zhang MH, Yang H, Tracey KJ (2002) High mobility group 1 protein (HMG-1) stimulates proinflammatory cytokine synthesis in human monocytes. J Exp Med 192:565–570
Bonaldi T, Talamo P, Scaffidi P, Ferrera D, Porto A, Bachi A, Rubartelli A, Agresti A, Bianchi ME (2003) Monocytic cells hyperacetylate chromatin protein HMGB1 to redirect it towards secretion. EMBO J 22:5551–5560
Bradley JR (2008) TNF-mediated inflammatory disease. J Pathol 214:149–160
Ganz T (1987) Extracellular release of antimicrobial defensins by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun 55:568–571
Gigler G, Szenasi G, Simo A, Levay G, Harsing LG, Sas K, Vecsei L, Toldi J (2007) Neuroprotective effect of L-kynurenine sulfate administered before focal cerebral ischemia in mice and global cerebral ischemia in gerbils. Eur J Pharmacol 564:116–122
Fiers W (1991) Tumor necrosis factor. Characterization at the molecular, cellular and in vivo level. FEBS Lett 285:199–212
Harris HE, Andersson U (2004) The nuclear protein HMGB1 as a proinflammatory mediator. Eur J Immunol 34:1503–1512
Hilmas C, Pereira EF, Alkondon M, Rassoulpour A, Schwarcz R, Albuuqerque EX (2001) The brain metabolite kynurenic acid inhibits α7 nicotinic receptor activity and increases non-α7 nicotic expression: physiopathological implications. J Neurosci 21:7463–7473
Kaszaki J, Palasthy Z, Erczes D, Racz A, Torday C, Varga G, Vecsei L, Boros M (2008) Kynurenic acid inhibits intestinal hypermotility and xanthine oxidase activity during experimental colon obstruction in dogs. Neurogastroenterol Motil 20:53–62
Kiss C, Vecsei L (2005) Neuroprotection and kynurenine system. In: Vecsei L (ed) Kynurenines in the brain: from experiment to clinics. Nova Science, New York, pp 173–191
Klivenyi P, Toldi J, Vecsei L (2004) Kynurenines in neurodegenerative disorders: therapeutic consideration. In: Vecsei L (ed) Frontiers in clinical neuroscience: neurodegeneration and neuroprotection. Adv Exp Med Biol, vol 541. Kluwer, New York, pp 169–183
Kocsis AK, Ocsovszky I, Tiszlavicz L, Tiszlavicz Z, Mandi Y (2009a) Helicobacter pylori induces the release of alpha-defensin by human granulocytes. Inflamm Res 58:241–247
Kocsis AK, SzabolcsA HP, Hofner P, Takács T, Farkas G, BodaK G, Mandi Y (2009b) Plasma concentrations of high-mobility group box protein1, soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products and circulating DNA in patients with acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 9:383–391
Lagerström MC, Schiöth HB (2008) Structural diversity of G protein-coupled receptors and significance for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:339–357
Levy RM, Mollen KP, Prince JM, Kaczorowski DJ, Vallabhaneni R, Liu S, Tracey KJ, Lotze MT, Hackam DJ, Fink MP, Vodovotz Y, Billiar TR (2007) Systemic inflammation and remote organ injury following trauma require HMGB1. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 293:R1538–R1544
Lotze MT, Tracey KJ (2005) High-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB): nuclear weapon in the immune arsenal. Nat Rev Immunol 5:331–342
Lögters TT, Laryea MD, Altrichter J, Sokolowski J, Cinatl J, Reipen J, Linhart W, Windolf J, Scholz M, Wild M (2009) Increased plasma kynurenine values and kynurenine-tryptophan ratios after major trauma are early indicators for the developments of sepsis. Shock 32:29–34
Marosi M, Nagy D, Farkas T, Zs K, Rózsa É, Robotka H, Fülöp F, Vécsei L, Toldi J (2010) A novel kynurenic acid analogues: a comparison with kynurenic acid. An in vitro electrophysiological study. J Neural Transm 117:183–188
Mazza J, Rossi A, Weinberg JM (2010) Innovatives uses of tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors. Dermatol Clin 28:559–575
McNearney TA, Ma Y, Chen Y, Taglialatela G, Yin H, Zhang WR, Westlund KN (2010) A peripheral neuroimmune link: glutamate agonists upregulate NMDA NR1 receptor mRNA and protein, vimentin, TNF-alpha, and RANTES in cultured human synoviocytes. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 298:R584–R598
Nemeth H, Toldi J, Vecsei L (2005) Role of kynurenines in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Curr Neurovasc Res 2:249–260
Parrish WR, Rosas-Ballina M, Gallowitsch-Puerta M, Ochani M, Ochani K, Yang LH, Hudson L, Lin X, Patel N, Johnson SM, Chavan S, Goldstein RS, Czura CJ, Miller EJ, Al-Abed Y, Traccy KJ, Pavlov VA (2008) Modulation of TNF release by choline requires alpha7 subunit nicotinic acethylcholine receptor-mediated signaling. Mol Med 14:567–574
Pisetsky DS, Erlandsson-Harris H, Andersson U (2008) High-mobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1): an alarmin mediating the pathogenesis of rheumatic disease. Arthritis Res Ther 10:209–223
Quinn K, Henriques M, Parker T, Slutsky AS, Zhang H (2008) Human neutrophil peptides: a novel potential mediator of inflammatory. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:1817–1824
Robotka H, Toldi J, Vécsei L (2008) L-Kynurenine: metabolism and mechanism of neuroprotection. Future Neurol 3:169–188
Rosas-Ballina M, Tracey KJ (2009) Cholinergic control of inflammation. J Intern Med 265:663–679
Rózsa É, Robotka H, Vécsei L, Toldi J (2008) The Janus-face kynurenic acid. J Neural Transm 115:1087–1091
Sas K, Robotka H, Toldi J, Vecsei L (2007) Mitochondria, metabolic disturbances, oxidative stress and the kynurenine system, with focus on neurodegenerative disorders. J Neurol Sci 257:221–239
Schwarcz R, Ceresoli-Borroni G, Wu HQ, Rassoulpour A, Poeggeler B, Hodgkins PS, Guidetti P (1999) Modulation and function of kynurenic acid in the immature rat brain. Adv Exp Med Biol 467:113–123
Sthoeger ZM, Bezalel S, Chapnik N, Asher I, Froy O (2008) High α-defensin levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology 127:116–122
Stone TW (1993) Neuropharmacology of quinolinic and kynurenic acids. Pharmacol Rev 45:309–379
Stone TW (2000) Development and therapeutic potential of kynurenic acid and kynurenine derivatives for neuroprotection. Trends Pharmacol Sci 21:149–154
Sundén-Cullberg J, Norrby-Teglund A, Treutiger CJ (2006) The role of high mobility group box-1 protein in severe sepsis. Curr Opin Infect Dis 19:231–236
Swartz KJ, During MJ, Freese A, Beal MF (1990) Cerebral synthesis and release of kynurenic acid: an endogenous antagonist of excitatory amino acid receptors. J Neurosci 10:2965–2973
Ulloa L, Messmer D (2006) High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) protein: friend and foe. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 17:189–201
Vamos E, Pardutz A, Klivenyi P, Toldi J, Vecsei L (2009) The role of kynurenines in disorders of the central nervous system: possibilities for neuroprotection. J Neurol Sci 283:21–27
Varga G, Erces D, Fazekas B, Fulop M, Kovacs T, Kaszaki J, Fulop F, Vecsei L, Boros M (2010) N-Methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonism decreases motility and inflammatory activation in the early phase of acute experimental colitis in the rat. Neurogastroenterol Motil 22:217–221
Vecsei L, Miller J, MacGarvey U, Beal MF (1992) Kynurenine and probenecid inhibit pentylenetetrazol-induced and NMDLA-induced seizures and increase kynurenic acid concentrations in the brain. Brain Res Bull 28:233–238
Wang H, Yu M, Ochani M, Amella CA, Tanovic M, Susarla S, Li JH, Wang HC, Yang H, Ulloa L, Al-Abed Y, Czura CJ, Tracey KJ (2003) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha 7 subunit is an essential regulator of inflammation. Nature 421:384–388
Wang H, Liao H, Ochani M, Justiniani M, Lin XC, Yang LH, Al-Abed Y, Wang HC, Metz C, Miller EJ, Tracey KJ, Ulloa L (2004) Cholinergic agonists inhibit HMGB1 release and improve survival in experimental sepsis. Nat Med 10:1216–1221
Wang J, Simonavicius N, Wu X, Swaminath G, Reagan J, Tian H, Ling L (2006) Kynurenic acid as a ligand for orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR35. J Biol Chem 281:22021–22028
Wang JE, Jorgensen PF, Almlof M, Thiemermann C, Foster SJ, Aasen AO, Solberg R (2000) Peptidoglycan and lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus induce tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 6 (IL-6) and IL-10 production in both T cells and monocytes in a human whole blood model. Infect Immun 68:3965–3970
Yang D, Biragyn A, Kwak LW, Oppenheim JJ (2002) Mammalian defensins in immunity: more than just microbicidal. Trends Immunol 23:291–296
Yoshikawa H, Kurokawa M, Ozaki N, Nara K, Atou K, Takada E, Kamochi H, Suzuki N (2006) Nicotine inhibits the production of proinflammatory mediators in human monocytes by suppression of I-kappa B phosphorylation and nuclear factor-kappa B transcriptional activity through nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7. Clin Exp Immunol 146:116–123
Zádori D, Klivényi P, Vámos E, Fülöp F, Toldi J, Vécsei L (2006) Kynurenines in chronic neurodegenerative disorders: future therapeutic strategies. J Neural Transm 116:1403–1409
Acknowledgements
We thank Mrs. Györgyi Müller for expert technical assistance and Mrs. Zsuzsanna Rosztoczy for skillful administration. This work was supported by Hungarian Research Grant OTKA K67889/5K540.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tiszlavicz, Z., Németh, B., Fülöp, F. et al. Different inhibitory effects of kynurenic acid and a novel kynurenic acid analogue on tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) production by mononuclear cells, HMGB1 production by monocytes and HNP1-3 secretion by neutrophils. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 383, 447–455 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-011-0605-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-011-0605-2