Abstract
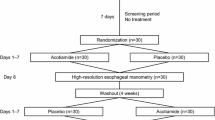
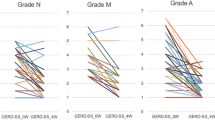
The purpose of the present study was to prospectively determine if healing of esophagitis as assessed by endoscopy results in improved esophageal motility. Thirty-one patients with erosive esophagitis who were randomized to receive either omeprazole 20 mg once daily or placebo completed the double-blind study. All patients underwent endoscopy and esophageal motility before treatment and at four weeks after treatment. Twenty-two healthy volunteers underwent esophageal manometry and served as normal controls. Manometric tracings were coded, randomized, and analyzed blindly. Compared to normal controls, patients with esophagitis had significantly lower LESP, decreased amplitude of peristaltic contractions, and increased occurrence of abnormal contractions. Omeprazole was superior to placebo in healing of esophagitis. However, healing of esophagitis was not associated with any improvement in esophageal motility. The manometric data suggest that the motility disturbance seen in esophagitis is not secondary to the esophagitis but rather a primary phenomenon. The lack of improvement of esophageal motility with healing may explain the high recurrence of esophagitis in clinical trials following discontinuation of omeprazole.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pope CE: A dynamic test of sphincter strength: Its application to the lower esophageal sphincter. Gastroenterology 52:779–786, 1967
Haddad JK: Relation of gastroesophageal reflux to yield sphincter pressures. Gastroenterology 58:175–184, 1970
Cohen S, Harris LD: Does hiatus hernia affect the competence of the lower esophageal sphincter? N Engl J Med 284:1053–1056, 1971
Ahtaridis G, Snape WJ, Cohen S: Clinical and manometric findings in benign peptic strictures of the esophagus. Dig Dis Sci 24:858–861, 1979
Burns TW, Venturatos SG: Esophageal motor function and response to acid perfusion in patients with symptomatic reflux esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci 30:529–535, 1985
Eastwood GL, Castell DO, Higgs RH: Experimental esophagitis in cats impairs lower esophageal sphincter pressure. Gastroenterology 69:146–153, 1975
Sinar DR, Fletcher JR, Cordova CC, Eastwood GL, Castell DO: Acute acid-induced esophagitis impairs esophageal peristalsis in baboons. Gastroenterology 80:1286, 1981 (abstract)
Gill RC, Bowes KL, Murphy PD, Kingman YJ: Esophageal motor abnormalities in gastroesophageal reflux and the effects of fundoplication. Gastroenterology 91:364–369, 1986
Eckardt VF: Does healing of esophagitis improve esophageal motor function? Dig Dis Sci 33:161–165, 1988
Behar J, Sheahan DG, Biancani P, Spiro HM, Storer EH: Medical and surgical management of reflux esophagitis. A 38-month report on a prospective clinical trial. N Engl J Med 293:263–268, 1975
Baldi F, Ferrarini F, Longanesi A, Angeloni M, Ragazzini M, Miglioli M, Barbara L: Oesophageal function before, during, and after healing of erosive esophagitis. Gut 29:157–160, 1988
Cucchiara S, Staiano A, Di Lorenzo C, D'Ambrosio R, Andreaotti MR, Orato M, De Filippo P, Auricchio S: Esophageal motor abnormalities in children with gastroesophageal reflux and peptic esophagitis. J Pediatr 108:907–910, 1986
Marshall JB, Gerhardt DC: Improvement in esophageal motor dysfunction with treatment of reflux esophagitis: A report of two cases. Am J Gastroenterol 77:351–354, 1982
Wesdorp E, Bartelsman J, Pape K, Dekker W, Tytgat GN: Oral cimetidine in reflux esophagitis: A double blind controlled trial. Gastroenterology 74:821–824, 1978
Sonnenberg A, Lepsien G, Mueller-Lissner SA, Koelz HR, Siewert R, Blum AL: When is esophagitis healed? Esophageal endoscopy, histology, and function before and after cimetidine treatment. Dig Dis Sci 27:297–302, 1982
Katz PO, Knuff TF, Benjamin SB, Castell DO: Abnormal esophageal pressures in reflux esophagitis: Cause or effect? Am J Gastroenterol 81:744–746, 1986
Downton J, Dent J, Heddle R, Toouli J, Buckle PJ, MacKinnon AM, Wyman JB: Elevation of gastric pH heals peptic esophagitis—a role for omeprazole. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2:317–324, 1987
Allen ML, McIntosh DL, Robinson MG: Healing or amelioration of esophagitis does not result in increased lower esophageal sphincter or esophageal contractile pressure. Am J Gastroenterol 85:1331–1334, 1990
Singh P, Adamopoulos A, Taylor RH, Colin-Jones DG: Oesophageal motor function before and after healing of esophagitis. Gut 33:1590–1596, 1992
Fiasse R, Hanin C, Lepot A, Descamps C, Lamy F, Dive C: Controlled trial of cimetidine in reflux esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci 25:750–755, 1980
Goy JA, Maynard JH, McNaughton WM, O'Shea A: Ranitidine and placebo in the treatment of reflux esophagitis. A double-blind randomized trial. Med J Aust 2:558–561, 1983
Klinkenberg-Knol EC, Jansen JMBJ, Festen HPM, Meuwissen SGM, Lamers CBHW: Double-blind multicentre comparison of omeprazole and ranitidine in the treatment of reflux esophagitis. Lancet 1:349–351, 1987
Zeitoun P, Desjars De Keranroue N, Isal JP: Omeprazole versus ranitidine in erosive oesophagitis. Lancet 2:621–622, 1987 (letter)
Havelund T, Laursen LS, Skoubo-Kristensen E, Anderson BN, Pedersen SA, Jensen KB, Fenger C, Hanberg-Sorensen F, Lauritsen K: Omeprazole and ranitidine in treatment of reflux esophagitis: Double blind comparative trial. Br Med J 296:89–92, 1988
Vantrappen G, Rutgeerts L, Schurmans P, Coenegrachts J-L: Omeprazole (40 mg) is superior to ranitidine in shortterm treatment of ulcerative reflux esophagitis. Dig Dis Sci 33:523–529, 1988
Sandmark S, Carlsson R, Fausa O, Lundell L: Omeprazole or ranitidine in the treatment of reflux esophagitis. Results of a double-blind, randomized, Scandinavian multicenter study. Scand J Gastroenterol 23:625–632, 1988
Pedersen SA, Kraglund K, Vinter-Jensen L: The effects of omeprazole on gastro-oesophageal sphincter pressure, gastric pH, and the migrating motor complex in fasting healthy subjects. Scand J Gastroenterol 22:735–730, 1987
Richter JE, Wu WC, Johns DN, Blackwell JN, Nelson JL, Castell JA, Castell DO: Esophageal manometry in 95 healthy adult volunteers. Dig Dis Sci 32:583–592, 1987
Rehfeld JF, Stadil F, Rubin B: Production and evaluation of antibody for the radioimmunoassay of gastrin. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 30:231–232, 1972
Hetzel DJ, Dent J, Reed WD, Narielvala FM, MacKinnon M, McCarthy JH, Mitchell B, Beveridge BR, Laurence BH, Gibson GG, Grant AK, Schearman DJC, Whitehead R, Buckle PJ: Healing and relapse of severe peptic esophagitis after treatment with omeprazole. Gastroenterology 95:903–912, 1988
Moses FM: Reversible aperistalsis as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol 82:272–275, 1987
De Haro LM, Paricio PP, Escandell MAO, Cuenca GM, Troncoso DV, Tebar JC, Pelegrin VG: Antireflux mechanism of Nissen fundoplication. A manometric study. Scand J Gastroenterol 27:417–420, 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by a grant from Astra Canada, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Howard, J.M., Reynolds, R.P.E., Frei, J.V. et al. Macroscopic healing of esophagitis does not improve esophageal motility. Digest Dis Sci 39, 648–654 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02088355
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02088355